
Primordial fluctuations
Encyclopedia
Primordial fluctuations are density variations in the early universe which are considered the seeds of all structure in the universe. Currently, the most widely accepted explanation for their origin is in the context of cosmic inflation
. According to the inflationary paradigm, the exponential growth of the scale factor
during inflation caused quantum fluctuation
s of the inflaton field to be stretched to macroscopic scales, and, upon leaving the horizon, to "freeze in".
At the later stages of radiation- and matter-domination, these fluctuations re-entered the horizon, and thus set the initial conditions for structure formation
.
The statistical properties of the primordial fluctuations can be inferred from observations of anisotropies in the cosmic microwave background
and from measurements of the distribution of matter, e.g., galaxy redshift survey
s. Since the fluctuations are believed to arise from inflation, such measurements can also set constraints on parameters within inflationary theory.
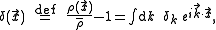
where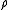 is the energy density,
is the energy density, 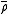 its average and
its average and 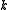 the wavenumber
the wavenumber
of the fluctuations. The power spectrum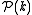 can then be defined via the ensemble average of the Fourier components
can then be defined via the ensemble average of the Fourier components
: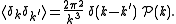
Many inflationary models predict that the scalar component of the fluctuations obeys a power law
in which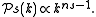
For scalar fluctuations,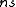 is referred to as the scalar spectral index, with
is referred to as the scalar spectral index, with 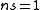 corresponding to scale invariant
corresponding to scale invariant
fluctuations.
and energy
which have equal fractional over/under densities. So for example, an adiabatic photon
overdensity of a factor of two would also correspond to an electron
overdensity of two. For isocurvature fluctuations, the density variations for one component do not necessarily correspond to density variations in other components. While it is usually assumed that the initial fluctuations are adiabatic, the possibility of isocurvature fluctuations can be considered given current cosmological data. While the overall constraints are inconclusive, uncorrelated isocurvature cold dark matter
modes are found to be unlikely.
s) is predicted by many inflationary models. As with scalar fluctuations, tensor fluctuations are expected to follow a power law and are parameterized by the tensor index (the tensor version of the scalar index), and the ratio of the tensor to scalar power.
Cosmic inflation
In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation or just inflation is the theorized extremely rapid exponential expansion of the early universe by a factor of at least 1078 in volume, driven by a negative-pressure vacuum energy density. The inflationary epoch comprises the first part...
. According to the inflationary paradigm, the exponential growth of the scale factor
Scale factor
A scale factor is a number which scales, or multiplies, some quantity. In the equation y=Cx, C is the scale factor for x. C is also the coefficient of x, and may be called the constant of proportionality of y to x...
during inflation caused quantum fluctuation
Quantum fluctuation
In quantum physics, a quantum fluctuation is the temporary change in the amount of energy in a point in space, arising from Werner Heisenberg's uncertainty principle.According to one formulation of the principle,energy and time can be related by the relation...
s of the inflaton field to be stretched to macroscopic scales, and, upon leaving the horizon, to "freeze in".
At the later stages of radiation- and matter-domination, these fluctuations re-entered the horizon, and thus set the initial conditions for structure formation
Structure formation
Structure formation refers to a fundamental problem in physical cosmology. The universe, as is now known from observations of the cosmic microwave background radiation, began in a hot, dense, nearly uniform state approximately 13.7 Gyr ago...
.
The statistical properties of the primordial fluctuations can be inferred from observations of anisotropies in the cosmic microwave background
Cosmic microwave background radiation
In cosmology, cosmic microwave background radiation is thermal radiation filling the observable universe almost uniformly....
and from measurements of the distribution of matter, e.g., galaxy redshift survey
Redshift survey
In astronomy, a redshift survey, or galaxy survey, is a survey of a section of the sky to measure the redshift of astronomical objects. Using Hubble's law, the redshift can be used to calculate the distance of an object from Earth. By combining redshift with angular position data, a redshift...
s. Since the fluctuations are believed to arise from inflation, such measurements can also set constraints on parameters within inflationary theory.
Formalism
Primordial fluctuations are typically quantified by a power spectrum which gives the power of the variations as a function of spatial scale. Within this formalism, one usually considers the fractional energy density of the fluctuations, given by: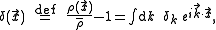
where
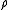 is the energy density,
is the energy density, 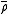 its average and
its average and 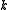 the wavenumber
the wavenumberWavenumber
In the physical sciences, the wavenumber is a property of a wave, its spatial frequency, that is proportional to the reciprocal of the wavelength. It is also the magnitude of the wave vector...
of the fluctuations. The power spectrum
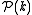 can then be defined via the ensemble average of the Fourier components
can then be defined via the ensemble average of the Fourier componentsFourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
:
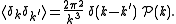
Many inflationary models predict that the scalar component of the fluctuations obeys a power law
Power law
A power law is a special kind of mathematical relationship between two quantities. When the frequency of an event varies as a power of some attribute of that event , the frequency is said to follow a power law. For instance, the number of cities having a certain population size is found to vary...
in which
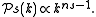
For scalar fluctuations,
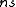 is referred to as the scalar spectral index, with
is referred to as the scalar spectral index, with 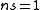 corresponding to scale invariant
corresponding to scale invariantScale invariance
In physics and mathematics, scale invariance is a feature of objects or laws that do not change if scales of length, energy, or other variables, are multiplied by a common factor...
fluctuations.
Adiabatic/isocurvature fluctuations
Adiabatic fluctuations are density variations in all forms of matterMatter
Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects consist. Typically, matter includes atoms and other particles which have mass. A common way of defining matter is as anything that has mass and occupies volume...
and energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
which have equal fractional over/under densities. So for example, an adiabatic photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
overdensity of a factor of two would also correspond to an electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
overdensity of two. For isocurvature fluctuations, the density variations for one component do not necessarily correspond to density variations in other components. While it is usually assumed that the initial fluctuations are adiabatic, the possibility of isocurvature fluctuations can be considered given current cosmological data. While the overall constraints are inconclusive, uncorrelated isocurvature cold dark matter
Cold dark matter
Cold dark matter is the improvement of the big bang theory that contains the additional assumption that most of the matter in the Universe consists of material that cannot be observed by its electromagnetic radiation and whose constituent particles move slowly...
modes are found to be unlikely.
Tensor modes
The presence of primordial tensor fluctuations (manifested as gravity waveGravity wave
In fluid dynamics, gravity waves are waves generated in a fluid medium or at the interface between two media which has the restoring force of gravity or buoyancy....
s) is predicted by many inflationary models. As with scalar fluctuations, tensor fluctuations are expected to follow a power law and are parameterized by the tensor index (the tensor version of the scalar index), and the ratio of the tensor to scalar power.
See also
- Big BangBig BangThe Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
- Cosmic microwave background radiationCosmic microwave background radiationIn cosmology, cosmic microwave background radiation is thermal radiation filling the observable universe almost uniformly....
- Cosmic inflationCosmic inflationIn physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation or just inflation is the theorized extremely rapid exponential expansion of the early universe by a factor of at least 1078 in volume, driven by a negative-pressure vacuum energy density. The inflationary epoch comprises the first part...
- Large-scale structure of the cosmos
- Gravitational radiation

