
Process gain
Encyclopedia
In a spread spectrum
system, the process gain (or 'processing gain') is the ratio of the spread (or RF) bandwidth to the unspread (or baseband) bandwidth. It is usually expressed in decibels (dB).
For example, if a 1 kHz signal is spread to 100 kHz, the process gain expressed as a numerical ratio would be 100,000/1,000 = 100. Or in decibels, 10log10(100) = 20 dB.
Note that process gain does not reduce the effects of wideband thermal noise. It can be shown that a direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) system has exactly the same bit error behavior as a non-spread spectrum system with the same modulation format. Thus, on an additive white Gaussian noise
(AWGN) channel without interference, a spread system requires the same transmitter power as an unspread system, all other things being equal.
Unlike a conventional communication system, however, a DSSS system does have a certain resistance against narrowband interference, as the interference is not subject to the process gain of the DSSS signal and hence the signal-to-interference ratio is improved.
In Frequency Modulation
(FM), the processing gain can be expressed as:
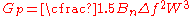
Gp is the processing gain
Bn is the Noise Bandwidth
Δf is the peak frequency deviation and
W is the sinusoidal modulating frequency.
Spread spectrum
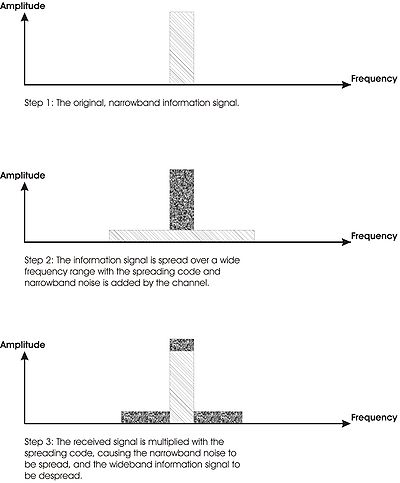
Spread-spectrum techniques are methods by which a signal generated in a particular bandwidth is deliberately spread in the frequency domain, resulting in a signal with a wider bandwidth...
system, the process gain (or 'processing gain') is the ratio of the spread (or RF) bandwidth to the unspread (or baseband) bandwidth. It is usually expressed in decibels (dB).
For example, if a 1 kHz signal is spread to 100 kHz, the process gain expressed as a numerical ratio would be 100,000/1,000 = 100. Or in decibels, 10log10(100) = 20 dB.
Note that process gain does not reduce the effects of wideband thermal noise. It can be shown that a direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) system has exactly the same bit error behavior as a non-spread spectrum system with the same modulation format. Thus, on an additive white Gaussian noise
Additive white Gaussian noise
Additive white Gaussian noise is a channel model in which the only impairment to communication is a linear addition of wideband or white noise with a constant spectral density and a Gaussian distribution of amplitude. The model does not account for fading, frequency selectivity, interference,...
(AWGN) channel without interference, a spread system requires the same transmitter power as an unspread system, all other things being equal.
Unlike a conventional communication system, however, a DSSS system does have a certain resistance against narrowband interference, as the interference is not subject to the process gain of the DSSS signal and hence the signal-to-interference ratio is improved.
In Frequency Modulation
Frequency modulation
In telecommunications and signal processing, frequency modulation conveys information over a carrier wave by varying its instantaneous frequency. This contrasts with amplitude modulation, in which the amplitude of the carrier is varied while its frequency remains constant...
(FM), the processing gain can be expressed as:
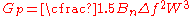
Gp is the processing gain
Bn is the Noise Bandwidth
Δf is the peak frequency deviation and
W is the sinusoidal modulating frequency.


