Product engineering
Encyclopedia
Product engineering refers to the process of designing and developing a device, assembly, or system such that it be produced as an item for sale through some production manufacturing
process. Product engineering
usually entails activity dealing with issues of cost, producibility, quality, performance, reliability, serviceability and user features. These product characteristics are generally all sought in the attempt to make the resulting product attractive to its intended market
and a successful contributor to the business of the organization that intends to offer the product to that market. It includes design, development and transitioning to manufacturing of the product. The term encompasses developing the concept of the product and the design and development of its mechanical, electronics and software components. For example a product like a digital camera
would include defining the feature set, design of the optics, the mechanical and ergonomic design of the packaging, developing the electronics that control the various component and developing the software that allows the user to see the pictures, store it in memory, download to a computer
, etc. After the initial design and development is done, transitioning the product to manufacture it in volumes is considered part of product engineering.
Product engineering is an engineering
discipline that deals with both design and manufacturing
aspects of a product.
(i.e. integrated circuits), semiconductor companies have product engineers to support the production of complex high volume products like microprocessors, DRAM
, digital signal processors or ASIC
. Their role is emphasized since the new generations of technology (90 nm, 65 nm), together with the arrival of new circuit designs, that have increased side effects difficult to simulate and endanger the fast ramp-up of the volume manufacturing in the fab.
Product engineers are the technical interface between the component development team and the production side (Front End and Back End), especially after the development phase and qualifications when the high volume production is running.
Product engineers improve the product quality and secure the product reliability by balancing cost of test and test coverage that could impact the production fall-off. They support failure analysis request from customers.
Wafer map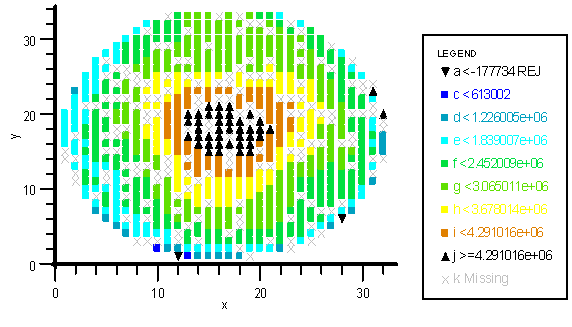 Each chip of a wafer, identified on a diagram by its x and y coordinates, is represented by a specific color or symbol depending on the results of a test. It can be helpful to detect a process problem if a region differentiates itself from the rest of the wafer with a visual signature (e.g. spot at the center, donut ring, strip, cluster...).
Each chip of a wafer, identified on a diagram by its x and y coordinates, is represented by a specific color or symbol depending on the results of a test. It can be helpful to detect a process problem if a region differentiates itself from the rest of the wafer with a visual signature (e.g. spot at the center, donut ring, strip, cluster...).
Failure analysis
To investigate the root cause of FE (Front-End) / BE (Back-End) yield detractors, or analyse return from customers, it could be necessary to send the samples to a failure analysis laboratory. The process in the lab is to verify the failure with a tester, to localize the fault by Emission microscopy, liquid crystal thermography or E-Beam probing for examples. Then the physical failure analysis can be conducted by different methods like: FIB (Focused Ion Beam), SEM (Scanning electron microscope
), AFM Atomic force microscope
. Sometimes a circuit correction is even feasible by FIB.
ATE Automatic test equipment
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
process. Product engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
usually entails activity dealing with issues of cost, producibility, quality, performance, reliability, serviceability and user features. These product characteristics are generally all sought in the attempt to make the resulting product attractive to its intended market
Market
A market is one of many varieties of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations and infrastructures whereby parties engage in exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services in exchange for money from buyers...
and a successful contributor to the business of the organization that intends to offer the product to that market. It includes design, development and transitioning to manufacturing of the product. The term encompasses developing the concept of the product and the design and development of its mechanical, electronics and software components. For example a product like a digital camera
Digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that takes video or still photographs, or both, digitally by recording images via an electronic image sensor. It is the main device used in the field of digital photography...
would include defining the feature set, design of the optics, the mechanical and ergonomic design of the packaging, developing the electronics that control the various component and developing the software that allows the user to see the pictures, store it in memory, download to a computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
, etc. After the initial design and development is done, transitioning the product to manufacture it in volumes is considered part of product engineering.
Product engineering is an engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
discipline that deals with both design and manufacturing
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
aspects of a product.
In the field of integrated circuits
Specifically in the field of electronicsElectronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
(i.e. integrated circuits), semiconductor companies have product engineers to support the production of complex high volume products like microprocessors, DRAM
Dram
Dram or DRAM may refer to:As a unit of measure:* Dram , an imperial unit of mass and volume* Armenian dram, a monetary unit* Dirham, a unit of currency in several Arab nationsOther uses:...
, digital signal processors or ASIC
ASIC
ASIC may refer to:* Application-specific integrated circuit, an integrated circuit developed for a particular use, as opposed to a customised general-purpose device.* ASIC programming language, a dialect of BASIC...
. Their role is emphasized since the new generations of technology (90 nm, 65 nm), together with the arrival of new circuit designs, that have increased side effects difficult to simulate and endanger the fast ramp-up of the volume manufacturing in the fab.
Area of responsibility
- Product engineers define the yield roadmap and drive the fulfillment during ramp-up and volume production,
- Identify and realize measures for yield improvement, test optimization and product cost reduction,
- Provide DFM Design for manufacturabilityDesign for manufacturabilityDesign for manufacturability - is the general engineering art of designing products in such a way that they are easy to manufacture. The basic idea exists in almost all engineering disciplines, but of course the details differ widely depending on the manufacturing technology...
methods, - Define qualification plan and perform electrical characterization analysis.
Product engineers are the technical interface between the component development team and the production side (Front End and Back End), especially after the development phase and qualifications when the high volume production is running.
Product engineers improve the product quality and secure the product reliability by balancing cost of test and test coverage that could impact the production fall-off. They support failure analysis request from customers.
Knowledge and skills
The job requires the product engineer to have a very good working knowledge of:- Statistical methods and tools,
- Manufacturing process,
- Product reliability and qualification,
- Physical analysis methods
- Computer-aided designComputer-aided designComputer-aided design , also known as computer-aided design and drafting , is the use of computer technology for the process of design and design-documentation. Computer Aided Drafting describes the process of drafting with a computer...
and simulation programs - Specific technology
- Automatic test equipment and tools
- Strong analytic work methodology and problem solving skills
- Project managementProject managementProject management is the discipline of planning, organizing, securing, and managing resources to achieve specific goals. A project is a temporary endeavor with a defined beginning and end , undertaken to meet unique goals and objectives, typically to bring about beneficial change or added value...
skills
Tools
Shmoo plotShmoo plot
In electrical engineering, a shmoo plot is a graphical display of the response of a component or system varying over a range of conditions and inputs. Often used to represent the results of the testing of complex electronic systems such as computers, ASICs or microprocessors...
Wafer map

Failure analysis
To investigate the root cause of FE (Front-End) / BE (Back-End) yield detractors, or analyse return from customers, it could be necessary to send the samples to a failure analysis laboratory. The process in the lab is to verify the failure with a tester, to localize the fault by Emission microscopy, liquid crystal thermography or E-Beam probing for examples. Then the physical failure analysis can be conducted by different methods like: FIB (Focused Ion Beam), SEM (Scanning electron microscope
Scanning electron microscope
A scanning electron microscope is a type of electron microscope that images a sample by scanning it with a high-energy beam of electrons in a raster scan pattern...
), AFM Atomic force microscope
Atomic force microscope
Atomic force microscopy or scanning force microscopy is a very high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy, with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit...
. Sometimes a circuit correction is even feasible by FIB.
ATE Automatic test equipment
Automatic test equipment
Automatic or Automated Test Equipment is any apparatus that performs tests on a device, known as the Device Under Test , using automation to quickly perform measurements and evaluate the test results...
External links
- http://www.semiconductor.net/article/CA6602542.html Application note "Yield Learning Flow Provides Faster Production Ramp"
- http://www.infras.com/Tutorial/sld016.htm Tutorial about yield impact

