
Prokaryotic elongation factors
Encyclopedia
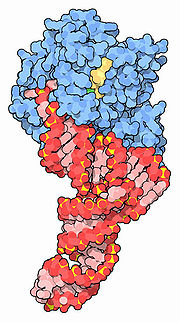
Elongation factor
Elongation factors are a set of proteins that facilitate the events of translational elongation, the steps in protein synthesis from the formation of the first peptide bond to the formation of the last one.Elongation is the most rapid step in translation:...
s are required for translation
Prokaryotic translation
Prokaryotic translation is the process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in prokaryotes.-Initiation:Initiation of translation in prokaryotes involves the assembly of the components of the translation system which are: the two ribosomal subunits , the mRNA to be translated, the...
: EF-Tu
EF-Tu
EF-Tu is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors.The prokaryotic factor EF-Tu mediates the entry of the aminoacyl-tRNA into a free site of the ribosome. EF-Tu functions by binding an aminoacylated, or charged, tRNA molecule in the cytoplasm...
, EF-Ts
EF-Ts
EF-Ts is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors.EF-Ts serves as the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for EF-Tu , catalyzing the release of guanosine diphosphate from EF-Tu...
, and EF-G
EF-G
EF-G or elongation factor G is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors.-Function:The factor EF-G catalyzes the translocation of the tRNA and mRNA down the ribosome at the end of each round of polypeptide elongation. Homologous to EF-Tu + tRNA, EF-G also binds to the ribosome in its GTP-bound...
.
- EF-TuEF-TuEF-Tu is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors.The prokaryotic factor EF-Tu mediates the entry of the aminoacyl-tRNA into a free site of the ribosome. EF-Tu functions by binding an aminoacylated, or charged, tRNA molecule in the cytoplasm...
(elongation factor thermo unstable) mediates the entry of the aminoacyl tRNA into a free site of the ribosomeRibosomeA ribosome is a component of cells that assembles the twenty specific amino acid molecules to form the particular protein molecule determined by the nucleotide sequence of an RNA molecule....
.- EF-TsEF-TsEF-Ts is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors.EF-Ts serves as the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for EF-Tu , catalyzing the release of guanosine diphosphate from EF-Tu...
serves as the guanine nucleotide exchange factorNucleotide exchange factorNucleotide exchange factors are proteins that stimulate the exchange of nucleoside diphosphates for nucleoside triphosphates bound to other proteins.-Function:...
for EF-Tu, catalyzing the release of GDP from EF-Tu.
- EF-Ts
- EF-GEF-GEF-G or elongation factor G is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors.-Function:The factor EF-G catalyzes the translocation of the tRNA and mRNA down the ribosome at the end of each round of polypeptide elongation. Homologous to EF-Tu + tRNA, EF-G also binds to the ribosome in its GTP-bound...
catalyzes the translocationTranslocationTranslocation may refer to:* Chromosomal translocation, in genetics* Translocation in plants, transport of food or pesticides through phloem or xylem* Protein translocation or protein targeting, a process in protein biosynthesis...
of the tRNA and mRNA down the ribosome at the end of each round of polypeptide elongation.

