Prostacyclin synthase
Encyclopedia
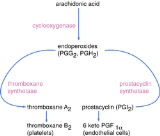
Prostaglandin-I synthase also known as prostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) synthase (PTGIS) or CYP8A1 is an enzyme
involved in prostanoid
biosynthesis that in humans is encoded by the PTGIS gene
. This enzyme belongs to the family of cytochrome P450 isomerase
s.
s. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenase
s which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. However, this protein is considered a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily on the basis of sequence similarity rather than functional similarity. This endoplasmic reticulum
membrane protein catalyzes the conversion of prostaglandin H2
to prostacyclin
(prostaglandin I2), a potent vasodilator and inhibitor of platelet aggregation. An imbalance of prostacyclin and its physiological antagonist thromboxane A2
contribute to the development of myocardial infarction
, stroke
, and atherosclerosis
.
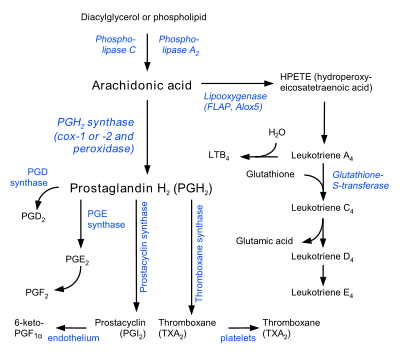
Unlike most P450 enzymes, PGIS does not require molecular oxygen (O2). Instead it uses its heme
cofactor to catalyze the isomerization of prostaglandin H2 to prostacyclin. Prostaglandin H2 is produced by cyclooxygenase
in the first committed step of prostaglandin
biosynthesis.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
involved in prostanoid
Prostanoid
Prostanoid is the term used to describe a subclass of eicosanoids consisting of: the prostaglandins , the thromboxanes and the prostacyclins - Biosynthesis : Cyclooxygenase catalyzes the conversion of the free essential fatty acids to...
biosynthesis that in humans is encoded by the PTGIS gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
. This enzyme belongs to the family of cytochrome P450 isomerase
Isomerase
In biochemistry, an isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the structural rearrangement of isomers. Isomerases thus catalyze reactions of the formwhere B is an isomer of A.-Nomenclature:...
s.
Function
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymeEnzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenase
Monooxygenase
Monooxygenases are enzymes that incorporate one hydroxyl group into substrates in many metabolic pathways. In this reaction, two atoms of dioxygen are reduced to one hydroxyl group and one H2O molecule by the concomitant oxidation of NADH.-Classification:...
s which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. However, this protein is considered a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily on the basis of sequence similarity rather than functional similarity. This endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle of cells in eukaryotic organisms that forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae...
membrane protein catalyzes the conversion of prostaglandin H2
Prostaglandin H2
Prostaglandin H2 is a type of Prostaglandin which is derived from arachidonic acid and is a precursor for many other biologically significant molecules.It is acted upon by:* prostacyclin synthase to create prostacyclin...
to prostacyclin
Prostacyclin
Prostacyclin is a member of the family of lipid molecules known as eicosanoids.As a drug, it is also known as "epoprostenol". The terms are sometimes used interchangeably.-History:...
(prostaglandin I2), a potent vasodilator and inhibitor of platelet aggregation. An imbalance of prostacyclin and its physiological antagonist thromboxane A2
Thromboxane A2
Thromboxane A2 is a thromboxane. It is produced by activated platelets and has prothrombotic properties: it stimulates activation of new platelets as well as increases platelet aggregation. This is achieved by mediating expression of the glycoprotein complex GP IIb/IIIa in the cell membrane of...
contribute to the development of myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction or acute myocardial infarction , commonly known as a heart attack, results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, causing heart cells to die...
, stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
, and atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a condition in which an artery wall thickens as a result of the accumulation of fatty materials such as cholesterol...
.
Unlike most P450 enzymes, PGIS does not require molecular oxygen (O2). Instead it uses its heme
Heme
A heme or haem is a prosthetic group that consists of an iron atom contained in the center of a large heterocyclic organic ring called a porphyrin. Not all porphyrins contain iron, but a substantial fraction of porphyrin-containing metalloproteins have heme as their prosthetic group; these are...
cofactor to catalyze the isomerization of prostaglandin H2 to prostacyclin. Prostaglandin H2 is produced by cyclooxygenase
Cyclooxygenase
Cyclooxygenase is an enzyme that is responsible for formation of important biological mediators called prostanoids, including prostaglandins, prostacyclin and thromboxane. Pharmacological inhibition of COX can provide relief from the symptoms of inflammation and pain...
in the first committed step of prostaglandin
Prostaglandin
A prostaglandin is any member of a group of lipid compounds that are derived enzymatically from fatty acids and have important functions in the animal body. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring....
biosynthesis.
Nomenclature
The systematic name of this enzyme class is (5Z,13E)-(15S)-9alpha,11alpha-epidioxy-15-hydroxyprosta-5,13-dienoate 6-isomerase. Other names in common use include prostacyclin synthase, prostacyclin synthetase, prostagladin I2 synthetase, PGI2 synthase, PGIS, PTGIS, and PGI2 synthetase.Pathways
 |
 |

