
Proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptors
Encyclopedia
Membrane receptor
Cell surface receptors are specialized integral membrane proteins that take part in communication between the cell and the outside world...
which sense acidic pH and include G2A
GPR132
Probable G-protein coupled receptor 132 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR132 gene.-Further reading:...
, GPR4
GPR4
G-protein coupled receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR4 gene.-Further reading:...
, OGR1
GPR68
Ovarian cancer G-protein coupled receptor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR68 gene.-Further reading:...
and TDAG8
GPR65
Psychosine receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR65 gene.-Further reading:...
. These G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors , also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein-linked receptors , comprise a large protein family of transmembrane receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal...
s are activated when extracellular
Extracellular fluid
Extracellular fluid usually denotes all body fluid outside of cells. The remainder is called intracellular fluid.In some animals, including mammals, the extracellular fluid can be divided into two major subcompartments, interstitial fluid and blood plasma...
pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
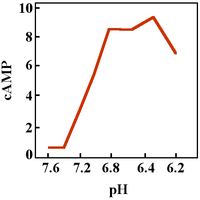
falls into the range of 6.4-6.8 (typical values are above 7.0). The functional role of the low pH sensitivity of the proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptors is being studied in several tissues where cells respond to conditions of low pH including bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
and inflamed
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
tissues. The four known proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptors are Class A
Rhodopsin-like receptors
Rhodopsin-like receptors are a family of proteins that comprise the largest group of G protein-coupled receptors.- Scope :G-protein-coupled receptors, GPCRs, constitute a vast protein family that encompasses a wide range of functions...
receptors in subfamily A15.
Nociception
PainPain
Pain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
sensation can be initiated by nociceptor
Nociceptor
A nociceptor is a sensory receptor that responds to potentially damaging stimuli by sending nerve signals to the spinal cord and brain. This process, called nociception, usually causes the perception of pain.-History:...
cells that are sensory neuron
Sensory neuron
Sensory neurons are typically classified as the neurons responsible for converting external stimuli from the environment into internal stimuli. They are activated by sensory input , and send projections into the central nervous system that convey sensory information to the brain or spinal cord...
s with cell bodies located in the dorsal root ganglia
Dorsal root ganglion
In anatomy and neuroscience, a dorsal root ganglion is a nodule on a dorsal root that contains cell bodies of neurons in afferent spinal nerves.-Unique unipolar structure:...
. Some nociceptors respond to low pH and the pH-sensitive amiloride-sensitive cation channel 3
ACCN3
Amiloride-sensitive cation channel 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACCN3 gene.- Function :This gene encodes a member of the degenerin/epithelial sodium channel superfamily...
has been described as a modulator of acid-induced pain sensation. However, results with amiloride-sensitive cation channel 3 gene knockout
Gene knockout
A gene knockout is a genetic technique in which one of an organism's genes is made inoperative . Also known as knockout organisms or simply knockouts, they are used in learning about a gene that has been sequenced, but which has an unknown or incompletely known function...
mice
MICE
-Fiction:*Mice , alien species in The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy*The Mice -Acronyms:* "Meetings, Incentives, Conferencing, Exhibitions", facilities terminology for events...
suggest that those channels do not fully account for acid-induced pain sensation. Proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptors have been shown to be expressed in small-diameter neurons responsible for nociception where they may play a role in acid-induced pain sensation. Acid-sensing neuron-mediated immediate pungent pain has been associated with acid-sensing ion channel
Acid-sensing ion channel
Acid-sensing ion channels are neuronal voltage-insensitive cationic channels activated by extracellular protons. ASIC proteins are a subfamily of the ENaC/Deg superfamily of proteins. To date six proteins of the ASIC family have been identified that arise from four genes, ASIC1, ASIC2, ASIC3, and...
s.
Other functions
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell in the vertebrate immune system.Under the microscope, lymphocytes can be divided into large lymphocytes and small lymphocytes. Large granular lymphocytes include natural killer cells...
s and macrophage
Macrophage
Macrophages are cells produced by the differentiation of monocytes in tissues. Human macrophages are about in diameter. Monocytes and macrophages are phagocytes. Macrophages function in both non-specific defense as well as help initiate specific defense mechanisms of vertebrate animals...
s), but due to redundancy and expression of multiple proton-sensing GPCRs family members in the same cell, multiple gene knockouts are needed. Results for mice lacking OGR1 suggested a possible role for proton-sensing GPCRs in osteoclast
Osteoclast
An osteoclast is a type of bone cell that removes bone tissue by removing its mineralized matrix and breaking up the organic bone . This process is known as bone resorption. Osteoclasts were discovered by Kolliker in 1873...
s.

