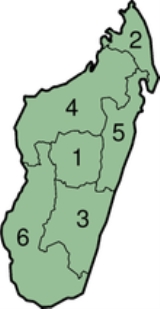
Provinces of Madagascar
Encyclopedia
|
|
Madagascar
is divided into six "autonomous province
s" (faritany mizakatena):
The provinces were dissolved as a result of the new regional subdivision
and the constitutional referendum of 2007
. There was a time frame of thirty months (until October 2009) for the transition. But in the new constitution, adopted in 2010, six autonomous provinces are listed again.
The new constitution of 1992 stated that the country should be divided into decentralised territorial entities, without going into detail. By law of 1994, three entity levels were defined: regions, departments and communes. The provinces were not mentioned in the law.
After former president Didier Ratsiraka was re-elected in 1997, he 1998 introduced a revised constitution in which the still existing provinces were transformed to "autonomous provinces". Before that, no constitution had stated any details about the subdivisions of the country, leaving it to be ruled by law. The autonomous provinces were created in 2000. The official motivation was to make Madagascar a decentralised federal state. Critics say that the hidden motivation was to make sure that Ratsiraka had a solid support from most of the provinces; his party AREMA won the provincial elections 2000 in all provinces except Antananarivo
.
With the presidential elections of 2001, in which opposition candidate Ravalomanana claimed that the official figures were fraudulent, the five AREMA provincial governors came out in support of Ratsiraka and even declared themselves independent from the republic.
When Ravalomanana had secured the position as president of the republic, the provincial governors were replaced with PDS'es (Presidents by special delegation), who are still in place. This effectively put an end to the "autonomous provinces", although they nominally remain in place because they are included in the constitution.
Rumours about the dissolution of the autonomous provinces had been around for some time, when on 4 April 2007 a constitutional referendum was held, in which the majority of the voters backed a revised constitution without any provinces. The new regions
will become the highest level of subdivision.
The years after independence 1960, Madagascar had a French-inspired division system.
During the second republic (1975–1991), Madagascar was divided into four levels of government:
Today there are five different levels of division:
The constitution of 1992 ruled that the country should be decentralized into territorial entities. The name, number, and limits of territorial entities should be determined by law. The law passed by the national assembly in 1994 defined three such entity levels: region
(faritra), department (departemanta) and commune (kaominina). The communes were created in 1996. The existing provinces were not mentioned in the law.
With former president Didier Ratsiraka
back in power, the constitution was amended in 1998, to include and specifically mention six autonomous provinces, divided into undefined regions and communes. The autonomous provinces, having the same names and territories as the already existing provinces, were created in 2000. Elections for the six provincial councils were held on 3 December 2000, resulting in an AREMA majority in all provinces except Antananarivo.
During the power struggle after the presidential elections in 2001, five of those provinces, whose governors supported Ratsiraka, declared themselves independent from the republic. The new president, Ravalomanana, replaced the provincial governments by special delegations, appointed by the president. This effectively means that the autonomous provinces have ceased to exist as such, and their dissolution is planned (see below).
In 2004, the regions were finally created by the national assembly in law number 2004-001. Meanwhile the 28 regions originally proposed had become 22. Although they are subdivisions of the provinces, they are representatives (and representing the people) of the republic, not the province. The regions will also take over the assets of the "ex-Fivondronampokontany". It is also mentioned that the communes are the only entities that are operational, and there will be an unspecified period of transition to the new system. The departments are not mentioned in the law, instead the designation "components" of the regions is used.
Also in 2004, the already existing Fokontany were redefined in the presidential decree 2004-299. They are subdivisions of the communes and headed by a chief designated by the mayor.
In 2005, a new entity called "districts" (distrika) was created by presidential decree 2005-012, replacing the department level of 1994. There are 116 districts. They have the same boundaries as the old "Sous-préfectures" or "ex-Fivondronampokontany". They are defined as subdivisions of the regions, and contains one or more "Arrondissements Administratifs". The chief of a district is designated by the chief of the region.
In the 2007 Constitution the autonomous provinces have been removed. Instead, the regions, the communes and the fokontany (but not the districts) are included.
|
Madagascar
Madagascar
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean off the southeastern coast of Africa...
is divided into six "autonomous province
Province
A province is a territorial unit, almost always an administrative division, within a country or state.-Etymology:The English word "province" is attested since about 1330 and derives from the 13th-century Old French "province," which itself comes from the Latin word "provincia," which referred to...
s" (faritany mizakatena):
- Antananarivo ProvinceAntananarivo ProvinceAntananarivo is a former province of Madagascar with an area of 58,283 km². It had a population of 5,370,900 . Its capital was Antananarivo.Except for Antsiranana, Antananarivo Province bordered all of the country's other provinces:*Mahajanga - north...
- Antsiranana ProvinceAntsiranana ProvinceAntsiranana is a former province of Madagascar with an area of 43,406 km2. It had a population of 1,188,425 . Its capital was Antsiranana. Notable is Ankarana Reserve.Antsiranana Province bordered the following provinces:...
- Fianarantsoa ProvinceFianarantsoa ProvinceFianarantsoa is a former province of Madagascar.*Area: 103,272 km2.*Population of 3,366,291 .*Capital: Fianarantsoa.*President: Fidy Mpanjato Rakotonarivo .One of its towns was Andohapatsakana...
- Mahajanga ProvinceMahajanga ProvinceMahajanga is a former province of Madagascar with an area of 150,023 km². It had a population of 1,896,000 . Its capital was Mahajanga.Except for Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga Province bordered all of the country's other provinces:...
- Toamasina ProvinceToamasina ProvinceToamasina is a former province of Madagascar with an area of 71,911 km². It had a population of 2,855,600 . Its capital was Toamasina, the most important seaport of the country....
- Toliara ProvinceToliara ProvinceToliara is a former province of Madagascar with an area of 161,405 km². It had a population of 2,229,550 . Its capital was Toliara...
The provinces were dissolved as a result of the new regional subdivision
Regions of Madagascar
||Madagascar is divided into 22 regions . These formerly second-tier administrative divisions became the first-level administrative divisions when the former six provinces were dissolved on 4 October 2009:- See also :* Subdivisions of Madagascar...
and the constitutional referendum of 2007
Malagasy constitutional referendum, 2007
A constitutional referendum was held in Madagascar on 4 April 2007. The proposed changes, which voters were asked to approve or reject as a whole, included:*expansion of presidential powers in cases of emergency...
. There was a time frame of thirty months (until October 2009) for the transition. But in the new constitution, adopted in 2010, six autonomous provinces are listed again.
History
The provinces were created in 1946, when Madagascar was a French colony. They were originally five, while the sixth (Diego Suarez/Antsiranana) was created later, but before the provincial elections in 1957. The same provinces continued to exist after the independence in 1960.The new constitution of 1992 stated that the country should be divided into decentralised territorial entities, without going into detail. By law of 1994, three entity levels were defined: regions, departments and communes. The provinces were not mentioned in the law.
After former president Didier Ratsiraka was re-elected in 1997, he 1998 introduced a revised constitution in which the still existing provinces were transformed to "autonomous provinces". Before that, no constitution had stated any details about the subdivisions of the country, leaving it to be ruled by law. The autonomous provinces were created in 2000. The official motivation was to make Madagascar a decentralised federal state. Critics say that the hidden motivation was to make sure that Ratsiraka had a solid support from most of the provinces; his party AREMA won the provincial elections 2000 in all provinces except Antananarivo
Antananarivo
Antananarivo , formerly Tananarive , is the capital and largest city in Madagascar. It is also known by its French colonial shorthand form Tana....
.
With the presidential elections of 2001, in which opposition candidate Ravalomanana claimed that the official figures were fraudulent, the five AREMA provincial governors came out in support of Ratsiraka and even declared themselves independent from the republic.
When Ravalomanana had secured the position as president of the republic, the provincial governors were replaced with PDS'es (Presidents by special delegation), who are still in place. This effectively put an end to the "autonomous provinces", although they nominally remain in place because they are included in the constitution.
Rumours about the dissolution of the autonomous provinces had been around for some time, when on 4 April 2007 a constitutional referendum was held, in which the majority of the voters backed a revised constitution without any provinces. The new regions
Regions of Madagascar
||Madagascar is divided into 22 regions . These formerly second-tier administrative divisions became the first-level administrative divisions when the former six provinces were dissolved on 4 October 2009:- See also :* Subdivisions of Madagascar...
will become the highest level of subdivision.
The years after independence 1960, Madagascar had a French-inspired division system.
During the second republic (1975–1991), Madagascar was divided into four levels of government:
- Faritany (province)
- Fivondronana (or fivondronampokontany)
- Firaisana (or firaisampokontany)
- Fokonolona (or fokontany)
Today there are five different levels of division:
- Faritany mizakatena (autonomous provinceProvinceA province is a territorial unit, almost always an administrative division, within a country or state.-Etymology:The English word "province" is attested since about 1330 and derives from the 13th-century Old French "province," which itself comes from the Latin word "provincia," which referred to...
) (6) - Faritra (regionRegionRegion is most commonly found as a term used in terrestrial and astrophysics sciences also an area, notably among the different sub-disciplines of geography, studied by regional geographers. Regions consist of subregions that contain clusters of like areas that are distinctive by their uniformity...
) (22) - Fivondronana (districtDistrictDistricts are a type of administrative division, in some countries managed by a local government. They vary greatly in size, spanning entire regions or counties, several municipalities, or subdivisions of municipalities.-Austria:...
) (116) - Kaominina (commune) (1,548)
- Fokontany (16,969)
The constitution of 1992 ruled that the country should be decentralized into territorial entities. The name, number, and limits of territorial entities should be determined by law. The law passed by the national assembly in 1994 defined three such entity levels: region
Region
Region is most commonly found as a term used in terrestrial and astrophysics sciences also an area, notably among the different sub-disciplines of geography, studied by regional geographers. Regions consist of subregions that contain clusters of like areas that are distinctive by their uniformity...
(faritra), department (departemanta) and commune (kaominina). The communes were created in 1996. The existing provinces were not mentioned in the law.
With former president Didier Ratsiraka
Didier Ratsiraka
Vice Admiral Didier Ratsiraka is a Malagasy politician who was President of Madagascar from 1975 to 1993 and from 1997 to 2002.-Second Republic:...
back in power, the constitution was amended in 1998, to include and specifically mention six autonomous provinces, divided into undefined regions and communes. The autonomous provinces, having the same names and territories as the already existing provinces, were created in 2000. Elections for the six provincial councils were held on 3 December 2000, resulting in an AREMA majority in all provinces except Antananarivo.
During the power struggle after the presidential elections in 2001, five of those provinces, whose governors supported Ratsiraka, declared themselves independent from the republic. The new president, Ravalomanana, replaced the provincial governments by special delegations, appointed by the president. This effectively means that the autonomous provinces have ceased to exist as such, and their dissolution is planned (see below).
In 2004, the regions were finally created by the national assembly in law number 2004-001. Meanwhile the 28 regions originally proposed had become 22. Although they are subdivisions of the provinces, they are representatives (and representing the people) of the republic, not the province. The regions will also take over the assets of the "ex-Fivondronampokontany". It is also mentioned that the communes are the only entities that are operational, and there will be an unspecified period of transition to the new system. The departments are not mentioned in the law, instead the designation "components" of the regions is used.
Also in 2004, the already existing Fokontany were redefined in the presidential decree 2004-299. They are subdivisions of the communes and headed by a chief designated by the mayor.
In 2005, a new entity called "districts" (distrika) was created by presidential decree 2005-012, replacing the department level of 1994. There are 116 districts. They have the same boundaries as the old "Sous-préfectures" or "ex-Fivondronampokontany". They are defined as subdivisions of the regions, and contains one or more "Arrondissements Administratifs". The chief of a district is designated by the chief of the region.
In the 2007 Constitution the autonomous provinces have been removed. Instead, the regions, the communes and the fokontany (but not the districts) are included.
See also
- Ranked list of Malagasy provincesRanked list of Malagasy provincesThese are ranked lists of the provinces of Madagascar. Population figures are from 2001.-By population:-By area:-By density:...
- ISO 3166-2:MGISO 3166-2:MGISO 3166-2:MG is the entry for Madagascar in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Madagascar, ISO 3166-2 codes...
- Subdivisions of Madagascar
- Regions of MadagascarRegions of Madagascar||Madagascar is divided into 22 regions . These formerly second-tier administrative divisions became the first-level administrative divisions when the former six provinces were dissolved on 4 October 2009:- See also :* Subdivisions of Madagascar...
- Districts of MadagascarDistricts of MadagascarDistricts are second-level administrative divisions of Madagascar below the regions. Districts are in their turn divided into communes; while some of the districts on urban areas such as the district of Toliara consists of only one commune, most of the districts are divided typically into...
- List of cities in Madagascar

