
Przeworsk culture
Encyclopedia
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
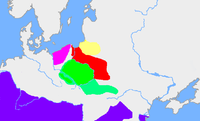
archaeological complex that dates from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD. It was located in what is now central and southern Poland, later spreading to parts of eastern Slovakia and Carpathian Ruthenia
Carpathian Ruthenia
Carpathian Ruthenia is a region in Eastern Europe, mostly located in western Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast , with smaller parts in easternmost Slovakia , Poland's Lemkovyna and Romanian Maramureş.It is...
ranging between the Oder
Oder
The Oder is a river in Central Europe. It rises in the Czech Republic and flows through western Poland, later forming of the border between Poland and Germany, part of the Oder-Neisse line...
and the middle and upper Vistula
Vistula
The Vistula is the longest and the most important river in Poland, at 1,047 km in length. The watershed area of the Vistula is , of which lies within Poland ....
Rivers into the headwaters of the Dniester
Dniester
The Dniester is a river in Eastern Europe. It runs through Ukraine and Moldova and separates most of Moldova's territory from the breakaway de facto state of Transnistria.-Names:...
and Tisza
Tisza
The Tisza or Tisa is one of the main rivers of Central Europe. It rises in Ukraine, and is formed near Rakhiv by the junction of headwaters White Tisa, whose source is in the Chornohora mountains and Black Tisa, which springs in the Gorgany range...
Rivers. It takes its name from the village near the town Przeworsk
Przeworsk
Przeworsk Ukrainian: Переворськ, is a town in south-eastern Poland with 15,675 inhabitants, as of 2 June 2009. Since 1999 it has been in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship, and is the capital of Przeworsk County....
where the first artefacts
Artifact (archaeology)
An artifact or artefact is "something made or given shape by man, such as a tool or a work of art, esp an object of archaeological interest"...
were found.
Influences
Scholars view the Przeworsk culture as an amalgam of a series of localized cultures. Continuity with the preceding Pomeranian culturePomeranian culture
The Pomeranian culture, also Pomeranian or Pomerelian Face Urn culture was an Iron Age culture in Pomerania, northern Poland. About 650 BC, it evolved from the Lusatian culture, often associated with the Nordic Bronze Age, and subsequently expanded southward...
is observed, albeit modified by significant influences from the La Tene
La Tène culture
The La Tène culture was a European Iron Age culture named after the archaeological site of La Tène on the north side of Lake Neuchâtel in Switzerland, where a rich cache of artifacts was discovered by Hansli Kopp in 1857....
and Jastorf
Jastorf culture
The Jastorf culture is an Iron Age material culture in what is now north Germany, spanning the 6th to 1st centuries BC, forming the southern part of the Pre-Roman Iron Age. The culture evolved out of the Nordic Bronze Age, through influence from the Halstatt culture farther south...
cultures.
The Przeworsk culture is sometimes associated with the Vandals
Vandals
The Vandals were an East Germanic tribe that entered the late Roman Empire during the 5th century. The Vandals under king Genseric entered Africa in 429 and by 439 established a kingdom which included the Roman Africa province, besides the islands of Sicily, Corsica, Sardinia and the Balearics....
named by ancient geographers, as well as other "eastern" peoples.
To the east, in what is now northern Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
and southern Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
, was the Zarubintsy culture
Zarubintsy culture
The Zarubintsy culture was a culture that from the 3rd century BC until 1st century AD flourished in the area north of the Black Sea along the upper and middle Dnieper and Pripyat Rivers, stretching west towards the Southern Bug river. Zarubintsy sites were particularly dense between the Rivers...
, to which it is linked as a larger archaeological complex. Much of this area was subsequently absorbed by the Wielbark culture.
Ethnicity
Roman-era writers report this area as being occupied by Veneti, as well as LugiansLugii
The Lugii, Lugi, Lygii, Ligii, Lugiones, Lygians, Ligians, Lugians, or Lougoi were an ancient Germanic tribe attested in the book Germania by the Roman historian Tacitus. They lived in ca...
, to the south. The Burgundians
Burgundians
The Burgundians were an East Germanic tribe which may have emigrated from mainland Scandinavia to the island of Bornholm, whose old form in Old Norse still was Burgundarholmr , and from there to mainland Europe...
and Vandals
Vandals
The Vandals were an East Germanic tribe that entered the late Roman Empire during the 5th century. The Vandals under king Genseric entered Africa in 429 and by 439 established a kingdom which included the Roman Africa province, besides the islands of Sicily, Corsica, Sardinia and the Balearics....
are known to have been settled in portions of the area, prior to their outmigration, toward the end of this cultural period.
Early twentieth century scholars often engaged in heated debates as to the bearers of the Przeworsk culture. A substantial effort has been expended in the past to characterize the latter as an early Slavic
Early Slavs
The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies in Migration period and early medieval Europe whose tribal organizations indirectly created the foundations for today’s Slavic nations .The first mention of the name Slavs dates to the 6th century, by which time the Slavic tribes inhabited a...
-speaking community, whilst German scholars attributed it to Vandals and Burgundians. However, it is impossible to believe that a single people could lay behind such a territorially wide and culturally varied zone. Therefore, modern thinking leans towards assigning the culture to an association of tribes of proto-Slavic, Germanic and Celtic origins.
Features
The main feature of the Przeworsk culture are burials. These are mostly cremations, with occasional inhumation. Warrior burials are notable, which often include horsegear and spurs. Some burials are exceptionally rich, overshadowing the graves of Germanic groups further west, especially after 400 AD. Pottery and metalwork are often rich and show a great varietyDecline
The culture's decline in the late 4th century coincides with invasion of HunsHuns
The Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
and subsequent westward movement of Germanic groups
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
. Others, on the other hand, argue that there was considerable population continuity. They instead emphasize the role of the social crisis which occurred as a result of the collapse of the Roman world and the trade contacts it maintained with peoples beyond its borders. In the late 5th century, the Prague-Korchak
Early Slavs
The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies in Migration period and early medieval Europe whose tribal organizations indirectly created the foundations for today’s Slavic nations .The first mention of the name Slavs dates to the 6th century, by which time the Slavic tribes inhabited a...
culture appears in the Vistula basin.
See also
- VandalsVandalsThe Vandals were an East Germanic tribe that entered the late Roman Empire during the 5th century. The Vandals under king Genseric entered Africa in 429 and by 439 established a kingdom which included the Roman Africa province, besides the islands of Sicily, Corsica, Sardinia and the Balearics....
- BurgundiansBurgundiansThe Burgundians were an East Germanic tribe which may have emigrated from mainland Scandinavia to the island of Bornholm, whose old form in Old Norse still was Burgundarholmr , and from there to mainland Europe...
- Chernyakhov cultureChernyakhov cultureThe Sântana de Mureș–Chernyakhiv culture is the name given to an archaeological culture which flourished between the 2nd and 5th centuries in a wide area of Eastern Europe, specifically in what today constitutes Ukraine, Romania, Moldova, and parts of Belarus...
- East Germanic tribesEast Germanic tribesThe Germanic tribes referred to as East Germanic constitute a wave of migrants who may have moved from Scandinavia into the area between the Oder and Vistula rivers between the years 600 and 300 BC. Later they went to the south...

