
Pulse-position modulation
Encyclopedia
Pulse-position modulation (PPM) is a form of signal modulation
in which M message bits are encoded by transmitting a single pulse in one of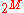 possible time-shifts. This is repeated every T seconds, such that the transmitted bit rate is M/T bits per second. It is primarily useful for optical communication
possible time-shifts. This is repeated every T seconds, such that the transmitted bit rate is M/T bits per second. It is primarily useful for optical communication
s systems, where there tends to be little or no multipath interference.
of one or more echoes can make it extremely difficult, if not impossible, to accurately determine the correct pulse position corresponding to the transmitted pulse.
Multipath in Pulse Position Modulation systems can be easily mitigated by using the same techniques that are used in Radar systems that rely totally on synchronization and time of arrival of the received pulse to obtain their range position in the presence of echoes.
(PLL) to track the phase of the carrier. This makes it a suitable candidate for optical communications systems, where coherent phase modulation and detection are difficult and extremely expensive. The only other common M-ary non-coherent modulation technique is M-ary Frequency Shift Keying
(M-FSK), which is the frequency-domain dual to PPM.
Optical communications systems (even wireless ones) tend to have weak multipath distortions, and PPM is a viable modulation scheme in many such applications.
of model aircraft
, boats and cars. PPM is employed in these systems, with the position of each pulse representing the angular position of an analogue control on the transmitter, or possible states of a binary switch. The number of pulses per frame gives the number of controllable channels available. The advantage of using PPM for this type of application is that the electronics required to decode the signal are extremely simple, which leads to small, light-weight receiver/decoder units.
(Model aircraft require parts that are as lightweight as possible).
Servos
made for model radio control include some of the electronics required to convert the pulse to the motor position – the receiver is merely required to demultiplex
the separate channels and feed the pulses to each servo.
More sophisticated R/C systems are now often based on pulse-code modulation
, which is more complex but offers greater flexibility and reliability.
Pulse position modulation is also used for communication to the ISO/IEC 15693 contactless smart card
as well as the HF
implementation of the EPC Class 1 protocol for RFID tags.
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
in which M message bits are encoded by transmitting a single pulse in one of
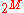 possible time-shifts. This is repeated every T seconds, such that the transmitted bit rate is M/T bits per second. It is primarily useful for optical communication
possible time-shifts. This is repeated every T seconds, such that the transmitted bit rate is M/T bits per second. It is primarily useful for optical communicationOptical communication
Optical communication is any form of telecommunication that uses light as the transmission medium.An optical communication system consists of a transmitter, which encodes a message into an optical signal, a channel, which carries the signal to its destination, and a receiver, which reproduces the...
s systems, where there tends to be little or no multipath interference.
Synchronization
One of the key difficulties of implementing this technique is that the receiver must be properly synchronized to align the local clock with the beginning of each symbol. Therefore, it is often implemented differentially as differential pulse-position modulation, where by each pulse position is encoded relative to the previous , such that the receiver must only measure the difference in the arrival time of successive pulses. It is possible to limit the propagation of errors to adjacent symbols, so that an error in measuring the differential delay of one pulse will affect only two symbols, instead of affecting all successive measurements.Sensitivity to multipath interference
Aside from the issues regarding receiver synchronization, the key disadvantage of PPM is that it is inherently sensitive to multipath interference that arises in channels with frequency-selective fading, whereby the receiver's signal contains one or more echoes of each transmitted pulse. Since the information is encoded in the time of arrival (either differentially, or relative to a common clock), the presenceof one or more echoes can make it extremely difficult, if not impossible, to accurately determine the correct pulse position corresponding to the transmitted pulse.
Multipath in Pulse Position Modulation systems can be easily mitigated by using the same techniques that are used in Radar systems that rely totally on synchronization and time of arrival of the received pulse to obtain their range position in the presence of echoes.
Non-coherent detection
One of the principal advantages of PPM is that it is an M-ary modulation technique that can be implemented non-coherently, such that the receiver does not need to use a phase-locked loopPhase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input "reference" signal. It is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector...
(PLL) to track the phase of the carrier. This makes it a suitable candidate for optical communications systems, where coherent phase modulation and detection are difficult and extremely expensive. The only other common M-ary non-coherent modulation technique is M-ary Frequency Shift Keying
Multiple frequency-shift keying
Multiple frequency-shift keying is a variation of frequency-shift keying that uses more than two frequencies. MFSK is a form of M-ary orthogonal modulation, where each symbol consists of one element from an alphabet of orthogonal waveforms...
(M-FSK), which is the frequency-domain dual to PPM.
PPM vs. M-FSK
PPM and M-FSK systems with the same bandwidth, average power, and transmission rate of M/T bits per second have identical performance in an AWGN (Additive White Gaussian Noise) channel. However, their performance differs greatly when comparing frequency-selective and frequency-flat fading channels. Whereas frequency-selective fading produces echoes that are highly disruptive for any of the M time-shifts used to encode PPM data, it selectively disrupts only some of the M possible frequency-shifts used to encode data for M-FSK. On the other hand, frequency-flat fading is more disruptive for M-FSK than PPM, as all M of the possible frequency-shifts are impaired by fading, while the short duration of the PPM pulse means that only a few of the M time-shifts are heavily impaired by fading.Optical communications systems (even wireless ones) tend to have weak multipath distortions, and PPM is a viable modulation scheme in many such applications.
Applications for RF communications
Narrowband RF (radio frequency) channels with low power and long wavelengths (i.e., low frequency) are affected primarily by flat fading, and PPM is better suited than M-FSK to be used in these scenarios. One common application with these channel characteristics, first used in the early 1960s, is the radio controlRadio control
Radio control is the use of radio signals to remotely control a device. The term is used frequently to refer to the control of model vehicles from a hand-held radio transmitter...
of model aircraft
Model aircraft
Model aircraft are flying or non-flying models of existing or imaginary aircraft using a variety of materials including plastic, diecast metal, polystyrene, balsa wood, foam and fibreglass...
, boats and cars. PPM is employed in these systems, with the position of each pulse representing the angular position of an analogue control on the transmitter, or possible states of a binary switch. The number of pulses per frame gives the number of controllable channels available. The advantage of using PPM for this type of application is that the electronics required to decode the signal are extremely simple, which leads to small, light-weight receiver/decoder units.
(Model aircraft require parts that are as lightweight as possible).
Servos
Servomechanism
thumb|right|200px|Industrial servomotorThe grey/green cylinder is the [[Brush |brush-type]] [[DC motor]]. The black section at the bottom contains the [[Epicyclic gearing|planetary]] [[Reduction drive|reduction gear]], and the black object on top of the motor is the optical [[rotary encoder]] for...
made for model radio control include some of the electronics required to convert the pulse to the motor position – the receiver is merely required to demultiplex
Multiplexing
The multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel, which may be a physical transmission medium. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the low-level communication channel into several higher-level logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred...
the separate channels and feed the pulses to each servo.
More sophisticated R/C systems are now often based on pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form for digital audio in computers and various Blu-ray, Compact Disc and DVD formats, as well as other uses such as digital telephone systems...
, which is more complex but offers greater flexibility and reliability.
Pulse position modulation is also used for communication to the ISO/IEC 15693 contactless smart card
Smart card
A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card , is any pocket-sized card with embedded integrated circuits. A smart card or microprocessor cards contain volatile memory and microprocessor components. The card is made of plastic, generally polyvinyl chloride, but sometimes acrylonitrile...
as well as the HF
High frequency
High frequency radio frequencies are between 3 and 30 MHz. Also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decameters . Frequencies immediately below HF are denoted Medium-frequency , and the next higher frequencies are known as Very high frequency...
implementation of the EPC Class 1 protocol for RFID tags.
See also
- Pulse-amplitude modulationPulse-amplitude modulationPulse-amplitude modulation, acronym PAM, is a form of signal modulation where the message information is encoded in the amplitude of a series of signal pulses....
- Pulse-code modulationPulse-code modulationPulse-code modulation is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form for digital audio in computers and various Blu-ray, Compact Disc and DVD formats, as well as other uses such as digital telephone systems...
- Pulse-density modulationPulse-density modulationPulse-density modulation, or PDM, is a form of modulation used to represent an analog signal with digital data. In a PDM signal, specific amplitude values are not encoded into pulses of different size as they would be in PCM. Instead, it is the relative density of the pulses that corresponds to...
- Pulse-width modulationPulse-width modulationPulse-width modulation , or pulse-duration modulation , is a commonly used technique for controlling power to inertial electrical devices, made practical by modern electronic power switches....
- Ultra wideband

