
Pyranoscope
Encyclopedia
Scientific instrument
A scientific instrument can be any type of equipment, machine, apparatus or device as is specifically designed, constructed and often, through trial and error, ingeniously refined to apply utmost efficiency in the utilization of well proven physical principle, relationship or technology to...
for displaying controlled large flames. The name pyranoscope stems from Greek, "pyr" meaning "fire", "ano" meaning "sky" and , "skopeîn", "to look" or "see". The science
Science
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
of investigating the progression and propagation of flames using such an instrument is called pyranoscopy.

Design of pyranoscopes
In order to attain the proper and controlled combustion of the fuel, a pyranoscope's most important mission is to atomize the fuel rapidly and to ignite it reliably.

Flamethrower
A flamethrower is a mechanical device designed to project a long controllable stream of fire.Some flamethrowers project a stream of ignited flammable liquid; some project a long gas flame. Most military flamethrowers use liquids, but commercial flamethrowers tend to use high-pressure propane and...
or flame projectors for stage use, the fuel of pyranoscopes has to be atomized before ignition.
In contrast to flamethrowers a shoot of a pyranoscope only is possible vertically up (± 15°).
To meet the security policies of pyranoscopes the fuel and the oxidant (compressed air) should be separated as long as possible.
Pyranoscopes basically are technical implementations of fire-breathing.
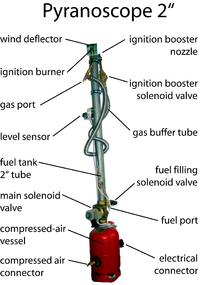
The main components of pyranoscopes are: (from bottom to top)
Compressed air vessel
The air vesselPressure vessel
A pressure vessel is a closed container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure.The pressure differential is dangerous and many fatal accidents have occurred in the history of their development and operation. Consequently, their design,...
should be amply dimensioned for one shoot. Its capacity is about ten times the volume of the fuel tank to allocate a complete combustion of the fuel.
The vessel should at least stand the double of the working pressure which is about 6 bar (90 psi).
The air connection should be secured by a non-return valve
Check valve
A check valve, clack valve, non-return valve or one-way valve is a mechanical device, a valve, which normally allows fluid to flow through it in only one direction....
.
The top of the vessel is closed by a solenoid valve
Solenoid valve
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical valve for use with liquid or gas. The valve is controlled by an electric current through a solenoid: in the case of a two-port valve the flow is switched on or off; in the case of a three-port valve, the outflow is switched between the two outlet ports...
of the same dimension
Nominal Pipe Size
Nominal Pipe Size is a North American set of standard sizes for pipes used for high or low pressures and temperatures. Pipe size is specified with two non-dimensional numbers: a nominal pipe size for diameter based on inches, and a schedule for wall thickness...
like the fuel tank.
Main solenoid valve
This valveSolenoid valve
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical valve for use with liquid or gas. The valve is controlled by an electric current through a solenoid: in the case of a two-port valve the flow is switched on or off; in the case of a three-port valve, the outflow is switched between the two outlet ports...
separates the oxidant from the fuel. Its function is to open the pressure vessel
Pressure vessel
A pressure vessel is a closed container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure.The pressure differential is dangerous and many fatal accidents have occurred in the history of their development and operation. Consequently, their design,...
abruptly to blow out and atomize the fuel.
It should have the same dimension like the fuel tank to enable an unrestricted air flow.
To trigger the pyranoscope this valve is opened for 0.5 seconds.
Fuel tank
Normally the fuel tank of pyranoscopes is made of standard steel pipes in different lengths and diameters. Its diameter determines the size of the pyranoscope (½" to 2"). The length determines the volume and the amount of fuel for one shot.The pipe has two extra connections on its lower side. One for filling and one for the level sensor. The filling pipe is attached to a small (⅛") solenoid valve. This keeps open until the level sensor sends its charged-signal. An external fuel pump provides the required fuel pressure of 2 bar (30 psi).
The most common fuel for pyranoscopes is ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
. But they also work with gasoline
Gasoline
Gasoline , or petrol , is a toxic, translucent, petroleum-derived liquid that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. Some gasolines also contain...
.
Ignition unit
On top of the fuel tank, near to the atomized fuel-stream pyranoscopes a propanePropane
Propane is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula , normally a gas, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used as a fuel for engines, oxy-gas torches, barbecues, portable stoves, and residential central...
Gas burner
Gas burner
A gas burner is a device to generate a flame to heat up products using a gaseous fuel such as acetylene, natural gas or propane. Some burners have an air inlet to mix the fuel gas with air to make a complete combustion...
is used as ignition unit. Its supply line should be made from flameproof
Flame retardant
Flame retardants are chemicals used in thermoplastics, thermosets, textiles and coatings that inhibit or resist the spread of fire. These can be separated into several different classes of chemicals:...
materials. To prevent the ignition flame from being blown off by the fuel stream it must be well justified.
Larger pyranoscopes (≥ 1½") need an ignition booster for fail-safe operation. This is put into practice by a propane-buffer-pipe of 0.5 liters terminated with another ½" solenoid valve.
A propane hit is blown in the ignition flame 0.1 seconds before opening the main valve.
Usage
Pyranoscopes are frequently used in scienceScience
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
and art
Art
Art is the product or process of deliberately arranging items in a way that influences and affects one or more of the senses, emotions, and intellect....
.
To meet the safety guidelines of pyranoscopes it is very important to connect the compressed-air-plug first and give pressure to the vessel. This avoids fuel entering the vessel at any malfunctions or operation errors.

