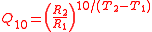Q10 (temperature coefficient)
Encyclopedia
The Q10 temperature coefficient is a measure of the rate of change of a biological or chemical system as a consequence of increasing the temperature
by 10 °C. There are many examples where the Q10 is used, one being the calculation of the nerve conduction velocity
and another being calculating the contraction velocity of muscle fibres. It can also be applied to chemical reaction
s and many other systems.
The Q10 is calculated as:
where
Q10 is a unitless quantity, as it is the factor by which a rate changes, and is a useful way to express the temperature dependence of a process.
For biological systems, the Q10 value is generally between 1 and 3.
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
by 10 °C. There are many examples where the Q10 is used, one being the calculation of the nerve conduction velocity
Nerve conduction velocity
Nerve conduction velocity is the speed at which an electrochemical signal propagates down a neural pathway. Many things can affect this, including axon diameter, myelination, the internal resistance of the axon, and temperature. Nerve conduction velocity differs from species to species, and to a...
and another being calculating the contraction velocity of muscle fibres. It can also be applied to chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
s and many other systems.
The Q10 is calculated as:
where
- R is the rate
- T is the temperature in CelsiusCelsiusCelsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
degrees or kelvinKelvinThe kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s.
Q10 is a unitless quantity, as it is the factor by which a rate changes, and is a useful way to express the temperature dependence of a process.
For biological systems, the Q10 value is generally between 1 and 3.