
Quality control and genetic algorithms
Encyclopedia
The combination of quality control and genetic algorithms led to novel solutions of complex quality control
design and optimization
problems. Quality control
is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. Quality is the degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfils a need or expectation that is stated, general implied or obligatory. Genetic algorithms are search algorithms, based on the mechanics of natural selection and natural genetics.
(QC) procedures can be applied on a process to test
statistically the null hypothesis
, that the process conforms to the quality requirements, therefore that the process is in control, against the alternative, that the process is out of control. When a true null hypothesis
is rejected, a statistical type I error is committed. We have then a false rejection of a run of the process. The probability of a type I error is called probability of false rejection. When a false null hypothesis is accepted, a statistical type II error is committed. We fail then to detect a significant change in the process. The probability of rejection of a false null hypothesis
equals the probability of detection of the nonconformity of the process to the quality requirements.
The QC procedure to be designed or optimized can be formulated as:
Q1(n1,X1)# Q2(n2,X2) #...# Qq(nq,Xq) (1)
where Qi(ni,Xi) denotes a statistical decision rule, ni denotes the size of the sample Si, that is the number of the samples the rule is applied upon, and Xi denotes the vector of the rule specific parameters, including the decision limits. Each symbol # denotes either the Boolean
operator AND or the operator OR. Obviously, for # denoting AND, and for n1 < n2 <...< nq, that is for S1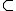 S2
S2 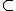 ....
....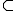 Sq, the (1) denotes a q-sampling QC procedure.
Sq, the (1) denotes a q-sampling QC procedure.
Each statistical decision rule is evaluated by calculating the respective statistic of a monitored variable of samples taken from the process. Then, if the statistic is out of the interval between the decision limits, the decision rule is considered to be true. Many statistics can be used, including the following: a single value of the variable of a sample, the range
, the mean
, and the standard deviation
of the values of the variable of the samples, the cumulative sum, the smoothed mean, and the smoothed standard deviation. Finally, the QC procedure is evaluated as a Boolean proposition. If it is true, then the null hypothesis
is considered to be false, the process is considered to be out of control, and the run is rejected.
A quality control
procedure is considered to be optimum when it minimizes (or maximizes) a context specific objective function. The objective function depends on the probabilities of detection of the nonconformity of the process and of false rejection. These probabilities depend on the parameters of the quality control
procedure (1) and on the probability density functions (see probability density function
) of the monitored variables of the process.
of the objective function to be optimized and search through large spaces quickly. Genetic algorithms have been derived from the processes of the molecular biology
of the gene
and the evolution
of life. Their operators, cross-over, mutation
, and reproduction, are isomorphic with the synonymous biological processes. Genetic algorithms have been used to solve a variety of complex optimization
problems. Additionally the classifier systems and the genetic programming
paradigm
have shown us that genetic algorithms can be used for tasks as complex as the program induction.
procedures. Usage of enumerative methods would be very tedious, especially with multi-rule procedures, as the number of the points of the parameter space to be searched grows exponentially with the number of the parameters to be optimized. Optimization
methods based on the genetic algorithms offer an appealing alternative.
Furthermore, the complexity of the design process of novel quality control
procedures is obviously greater than the complexity of the optimization
of predefined ones.
In fact, since 1993, genetic algorithms have been used successfully to optimize and to design novel quality control
procedures.
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
design and optimization
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
problems. Quality control
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. Quality is the degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfils a need or expectation that is stated, general implied or obligatory. Genetic algorithms are search algorithms, based on the mechanics of natural selection and natural genetics.
Quality control
Alternative quality controlQuality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
(QC) procedures can be applied on a process to test
Statistical hypothesis testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of making decisions using data, whether from a controlled experiment or an observational study . In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance alone, according to a pre-determined threshold...
statistically the null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
, that the process conforms to the quality requirements, therefore that the process is in control, against the alternative, that the process is out of control. When a true null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
is rejected, a statistical type I error is committed. We have then a false rejection of a run of the process. The probability of a type I error is called probability of false rejection. When a false null hypothesis is accepted, a statistical type II error is committed. We fail then to detect a significant change in the process. The probability of rejection of a false null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
equals the probability of detection of the nonconformity of the process to the quality requirements.
The QC procedure to be designed or optimized can be formulated as:
Q1(n1,X1)# Q2(n2,X2) #...# Qq(nq,Xq) (1)
where Qi(ni,Xi) denotes a statistical decision rule, ni denotes the size of the sample Si, that is the number of the samples the rule is applied upon, and Xi denotes the vector of the rule specific parameters, including the decision limits. Each symbol # denotes either the Boolean
Boolean logic
Boolean algebra is a logical calculus of truth values, developed by George Boole in the 1840s. It resembles the algebra of real numbers, but with the numeric operations of multiplication xy, addition x + y, and negation −x replaced by the respective logical operations of...
operator AND or the operator OR. Obviously, for # denoting AND, and for n1 < n2 <...< nq, that is for S1
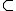 S2
S2 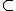 ....
....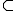 Sq, the (1) denotes a q-sampling QC procedure.
Sq, the (1) denotes a q-sampling QC procedure.Each statistical decision rule is evaluated by calculating the respective statistic of a monitored variable of samples taken from the process. Then, if the statistic is out of the interval between the decision limits, the decision rule is considered to be true. Many statistics can be used, including the following: a single value of the variable of a sample, the range
Range
-In mathematics:* Range , the set of all output values produced by a function* Interval , also called a range, a set of real numbers that includes all numbers between any two numbers in the set...
, the mean
Mean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
, and the standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
of the values of the variable of the samples, the cumulative sum, the smoothed mean, and the smoothed standard deviation. Finally, the QC procedure is evaluated as a Boolean proposition. If it is true, then the null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
is considered to be false, the process is considered to be out of control, and the run is rejected.
A quality control
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
procedure is considered to be optimum when it minimizes (or maximizes) a context specific objective function. The objective function depends on the probabilities of detection of the nonconformity of the process and of false rejection. These probabilities depend on the parameters of the quality control
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
procedure (1) and on the probability density functions (see probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
) of the monitored variables of the process.
Genetic algorithms
Genetic algorithms are robust search algorithms, that do not require knowledgeKnowledge
Knowledge is a familiarity with someone or something unknown, which can include information, facts, descriptions, or skills acquired through experience or education. It can refer to the theoretical or practical understanding of a subject...
of the objective function to be optimized and search through large spaces quickly. Genetic algorithms have been derived from the processes of the molecular biology
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
of the gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
and the evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
of life. Their operators, cross-over, mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
, and reproduction, are isomorphic with the synonymous biological processes. Genetic algorithms have been used to solve a variety of complex optimization
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
problems. Additionally the classifier systems and the genetic programming
Genetic programming
In artificial intelligence, genetic programming is an evolutionary algorithm-based methodology inspired by biological evolution to find computer programs that perform a user-defined task. It is a specialization of genetic algorithms where each individual is a computer program...
paradigm
Paradigm
The word paradigm has been used in science to describe distinct concepts. It comes from Greek "παράδειγμα" , "pattern, example, sample" from the verb "παραδείκνυμι" , "exhibit, represent, expose" and that from "παρά" , "beside, beyond" + "δείκνυμι" , "to show, to point out".The original Greek...
have shown us that genetic algorithms can be used for tasks as complex as the program induction.
Quality control and genetic algorithms
In general, we can not use algebraic methods to optimize the quality controlQuality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
procedures. Usage of enumerative methods would be very tedious, especially with multi-rule procedures, as the number of the points of the parameter space to be searched grows exponentially with the number of the parameters to be optimized. Optimization
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
methods based on the genetic algorithms offer an appealing alternative.
Furthermore, the complexity of the design process of novel quality control
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
procedures is obviously greater than the complexity of the optimization
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
of predefined ones.
In fact, since 1993, genetic algorithms have been used successfully to optimize and to design novel quality control
Quality control
Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. This approach places an emphasis on three aspects:...
procedures.

