
R Coronae Borealis
Encyclopedia
R Coronae Borealis is a yellow supergiant
star, and is the prototype of the RCB class
of variable star
s, which fade by several magnitude
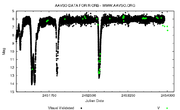
s at irregular intervals. R Coronae Borealis itself normally shines at approximately magnitude 6, just about visible to the naked eye
, in the constellation of Corona Borealis
, but at intervals of several months to many years fades to as faint as magnitude 14. Over successive months it gradually returns to its normal brightness, giving it the nickname "Fade-Out star," or "Reverse Nova
".
 The cause of this behaviour is believed to be a regular build-up of carbon
The cause of this behaviour is believed to be a regular build-up of carbon
dust in the star's atmosphere
. The sudden drop in brightness may be caused by a rapid condensation
of dust, resulting in much of the star's light being blocked. The gradual restoration to normal brightness results from the dust being dispersed by radiation pressure
.
in 1795. It was known as Variabilis Coronae, "Variable
of Corona
".
Supergiant
Supergiants are among the most massive stars. They occupy the top region of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. In the Yerkes spectral classification, supergiants are class Ia or Ib . They typically have bolometric absolute magnitudes between -5 and -12...
star, and is the prototype of the RCB class
R Coronae Borealis variable
A R Coronae Borealis variable is an eruptive variable star that varies in luminosity in two modes, one low amplitude pulsation , and one irregular unpredictably sudden fading by 1 to 9 magnitudes...
of variable star
Variable star
A star is classified as variable if its apparent magnitude as seen from Earth changes over time, whether the changes are due to variations in the star's actual luminosity, or to variations in the amount of the star's light that is blocked from reaching Earth...
s, which fade by several magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
s at irregular intervals. R Coronae Borealis itself normally shines at approximately magnitude 6, just about visible to the naked eye
Naked eye
The naked eye is a figure of speech referring to human visual perception unaided by a magnifying or light-collecting optical device, such as a telescope or microscope. Vision corrected to normal acuity using corrective lenses is considered "naked"...
, in the constellation of Corona Borealis
Corona Borealis
Corona Borealis is a small constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for "northern crown", a name inspired by its shape; its main stars form a semicircular arc. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern...
, but at intervals of several months to many years fades to as faint as magnitude 14. Over successive months it gradually returns to its normal brightness, giving it the nickname "Fade-Out star," or "Reverse Nova
Nova
A nova is a cataclysmic nuclear explosion in a star caused by the accretion of hydrogen on to the surface of a white dwarf star, which ignites and starts nuclear fusion in a runaway manner...
".

Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
dust in the star's atmosphere
Stellar atmosphere
The stellar atmosphere is the outer region of the volume of a star, lying above the stellar core, radiation zone and convection zone. It is divided into several regions of distinct character:...
. The sudden drop in brightness may be caused by a rapid condensation
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
of dust, resulting in much of the star's light being blocked. The gradual restoration to normal brightness results from the dust being dispersed by radiation pressure
Radiation pressure
Radiation pressure is the pressure exerted upon any surface exposed to electromagnetic radiation. If absorbed, the pressure is the power flux density divided by the speed of light...
.
History
Variability of R CrB has been discovered by the English astronomer, Edward PigottEdward Pigott
Edward Pigott was an English astronomer, and the son of astronomer Nathaniel Pigott and Anna Mathurine de Bériot . Probably born in Whitton, Middlesex, his elder brother, Charles Gregory, died in young age. He also had a younger sister, Mathurina...
in 1795. It was known as Variabilis Coronae, "Variable
Variable star
A star is classified as variable if its apparent magnitude as seen from Earth changes over time, whether the changes are due to variations in the star's actual luminosity, or to variations in the amount of the star's light that is blocked from reaching Earth...
of Corona
Corona Borealis
Corona Borealis is a small constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for "northern crown", a name inspired by its shape; its main stars form a semicircular arc. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern...
".
External links
- Entry in the Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy, and Spaceflight
- http://jumk.de/astronomie/special-stars/r-cor-bor.shtml
- ESO 34/07 - Science Release: "Star Caught Smoking"

