
Radiative process
Encyclopedia
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
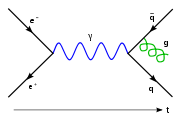
, a radiative process refers to one elementary particle
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle not known to have substructure; that is, it is not known to be made up of smaller particles. If an elementary particle truly has no substructure, then it is one of the basic building blocks of the universe from which...
emitting another and continuing to exist. This typically happens when a fermion
Fermion
In particle physics, a fermion is any particle which obeys the Fermi–Dirac statistics . Fermions contrast with bosons which obey Bose–Einstein statistics....
emits a boson
Boson
In particle physics, bosons are subatomic particles that obey Bose–Einstein statistics. Several bosons can occupy the same quantum state. The word boson derives from the name of Satyendra Nath Bose....
such as a gluon
Gluon
Gluons are elementary particles which act as the exchange particles for the color force between quarks, analogous to the exchange of photons in the electromagnetic force between two charged particles....
or photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
.

