Radio latino
Encyclopedia
A radio latino is a measuring instrument used in surveying and military engineering starting in the 16th century. It gets its name from the inventor, Latino Orsini. The radio latino can be considered a kind of geometric square.
It was a general purpose instrument that could be used for a variety of angular measurements as well as depth and inside dimension measures.
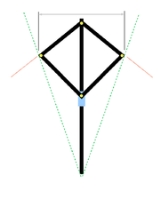
 The slider (blue in the diagram to the right) could move along the central rod, causing the deltoid
The slider (blue in the diagram to the right) could move along the central rod, causing the deltoid
formed by four other rods to change shape symmetrically. The end points of the rods had sights on them, allowing various sight lines to be defined. The central rod was graduated
with various scales. These scales allowed the angles between the end rods (represented by the red lines in the diagram) to be determined as well as the angle with its vertex
at one end of the main rod and sides (represented by the green lines in the diagram) through the outer joints of the rods.
With different graduations, one could determine or lay out:
When folded, the radio latino would resemble a sword and was stored in a sheath or scabbard
.
. The central, main rod was graduated with multiple scales. The free end of the main rod had a handle attached. Within the handle, a small compass was mounted.
The two end-most side rods were shorter than the two attached to the slider. This permitted the end rods to be set to any angle up to 180°. The slider could move along the main rod and was used as an index for reading the engraved scales.
Each hinged vertex had a sighting vane. This permitted the instrument to be used to measure or lay out angles or other dimensions visually.
It was a general purpose instrument that could be used for a variety of angular measurements as well as depth and inside dimension measures.
Usage

Kite (geometry)
In Euclidean geometry a kite is a quadrilateral whose four sides can be grouped into two pairs of equal-length sides that are next to each other. In contrast, a parallelogram also has two pairs of equal-length sides, but they are opposite each other rather than next to each other...
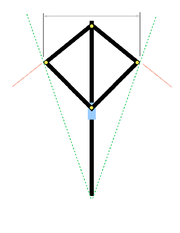
formed by four other rods to change shape symmetrically. The end points of the rods had sights on them, allowing various sight lines to be defined. The central rod was graduated
Graduation (instrument)
-Linear graduation:Linear graduation of a scale occurs on a straight instrument. The graduation can identify linear measures, such as inches or millimetres on a rule. They can also be non-linear such as logarithmic or other transcendental scales....
with various scales. These scales allowed the angles between the end rods (represented by the red lines in the diagram) to be determined as well as the angle with its vertex
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex is a special kind of point that describes the corners or intersections of geometric shapes.-Of an angle:...
at one end of the main rod and sides (represented by the green lines in the diagram) through the outer joints of the rods.
With different graduations, one could determine or lay out:
- angles between sight lines with a degree scale.
- internal angles of regular polygonRegular polygonA regular polygon is a polygon that is equiangular and equilateral . Regular polygons may be convex or star.-General properties:...
s with polygon scales. - internal diameters and dimensions (such as the inside bore of a cannon) using the distance between the outer joints (represented by the grey dimension lines in the diagram) using a length scale.
- gun elevations for cannon.
- heights of objects by measuring angles.
- shadow squareShadow squareThe shadow square, also known as an altitude scale, was an instrument used to determine the linear height of an object, in conjunction with the alidade, for angular observations. It is an early example of an analog computer. It was invented by Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī in 9th-century Baghdad....
calculations. - depths from the free end of the main rod to the slider.
When folded, the radio latino would resemble a sword and was stored in a sheath or scabbard
Scabbard
A scabbard is a sheath for holding a sword, knife, or other large blade. Scabbards have been made of many materials over the millennia, including leather, wood, and metals such as brass or steel.-Types of scabbards:...
.
Construction
The radio latino was usually constructed of brassBrass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc; the proportions of zinc and copper can be varied to create a range of brasses with varying properties.In comparison, bronze is principally an alloy of copper and tin...
. The central, main rod was graduated with multiple scales. The free end of the main rod had a handle attached. Within the handle, a small compass was mounted.
The two end-most side rods were shorter than the two attached to the slider. This permitted the end rods to be set to any angle up to 180°. The slider could move along the main rod and was used as an index for reading the engraved scales.
Each hinged vertex had a sighting vane. This permitted the instrument to be used to measure or lay out angles or other dimensions visually.
External links
- Institute and Museum of the History of Science web page on the radio latino.

