
Rail transport in Estonia
Encyclopedia

All public railways in Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
are (Russian gauge
Russian gauge
In railway terminology, Russian gauge refers to railway track with a gauge between 1,520 mm and . In a narrow sense as defined by Russian Railways it refers to gauge....
), the same as in Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
, Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
, and Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
. The gauge
Rail gauge
Track gauge or rail gauge is the distance between the inner sides of the heads of the two load bearing rails that make up a single railway line. Sixty percent of the world's railways use a standard gauge of . Wider gauges are called broad gauge; smaller gauges, narrow gauge. Break-of-gauge refers...
used in Estonia is also compatible with Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
's gauge. Sometimes it is defined to be 1,524 mm (see Rail gauge in Estonia
Rail gauge in Estonia
Estonia mainly uses a track gauge of , inherited from the Russian Empire times. Since Soviet Union converted relatively late from , there are still some sections of left...
), for example when buying track maintenance or vehicles from Finland.
Railways in Estonia today are used mostly for freight transport, but also for passenger traffic. Passenger transport is most frequent near Tallinn, centred on the main Balti jaam.
Network
- Total length: circa 1,200 km, of which 900 km in public use
- Gauge: Russian gaugeRussian gaugeIn railway terminology, Russian gauge refers to railway track with a gauge between 1,520 mm and . In a narrow sense as defined by Russian Railways it refers to gauge....
- Electrified: 133 km (82.6 mi).
The Estonian railway network is owned by the state-owned company AS Eesti Raudtee
Eesti Raudtee
Eesti Raudtee or EVR is the national railway company of Estonia. It owns a network of 691 km of broad gauge railway throughout the country, including the 132 km used by the Elektriraudtee commuter trains around Tallinn...
and the private company Edelaraudtee Infrastruktuuri AS. These railway network infrastructure operators provide all railway network services for railway operators running freight and passenger services. AS Eesti Raudtee provides approximately 800 kilometres (497.1 mi) of track, of which 107 kilometres (66.5 mi) is double track
Double track
A double track railway usually involves running one track in each direction, compared to a single track railway where trains in both directions share the same track.- Overview :...
and 133 kilometres (82.6 mi) is electrified. Edelaraudtee Infrastruktuuri AS maintains 298 kilometres (185.2 mi) of track which consists of 219 kilometres (136.1 mi) of main line and 79 kilometres (49.1 mi) of station line.
Main lines
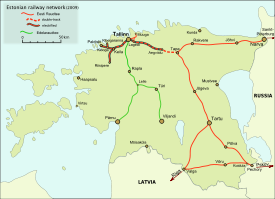
Eesti Raudtee
Eesti Raudtee or EVR is the national railway company of Estonia. It owns a network of 691 km of broad gauge railway throughout the country, including the 132 km used by the Elektriraudtee commuter trains around Tallinn...
:
- TallinnTallinnTallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
–TapaTapa, EstoniaTapa is a town in Lääne-Viru County, Estonia. Located at the junction of the country's Tallinn-Narva and Tallinn-Tartu-Valga railway lines, it is an important centre of transit for freight as well as rail passengers...
–NarvaNarvaNarva is the third largest city in Estonia. It is located at the eastern extreme point of Estonia, by the Russian border, on the Narva River which drains Lake Peipus.-Early history:...
, 209.6 km (130.2 mi). This line was completed in 1870. It was originally a part of the railway network of the Russian EmpireRussian EmpireThe Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
, connecting PaldiskiPaldiskiPaldiski is a town and Baltic Sea port situated on the Pakri peninsula of north-western Estonia. Originally a Swedish settlement known as Rågervik, it became a Russian naval base in the 18th century. The Russians renamed it Балтийский Порт Paldiski is a town and Baltic Sea port situated on the...
to St. Petersburg via Tallinn and Narva.
Passenger trains are operated by Elektriraudtee (Tallinn–AegviiduAegviiduAegviidu is a borough in northern Estonia. Administratively it constitutes Aegviidu Parish — a rural municipality within Harju County. The municipality has a population of 873 and covers an area of...
route), Edelaraudtee (Tallinn–Tartu, Tallinn–RakvereRakvereRakvere is a town in northern Estonia and the county seat of Lääne-Viru County, 20 km south of the Gulf of Finland.-History:The earliest signs of human settlement dating back to the 3rd-5th centuries AD have been found on the present theatre hill. Probably to protect that settlement, a wooden...
and Tallinn–Narva routes) and GO Rail (international trains to MoscowMoscowMoscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
, Russia). - Tallinn–KeilaKeilaKeila is a town and an urban municipality in Harju County in north-western Estonia. It is also the administrative centre of the surrounding rural municipality – Keila Parish.-History:...
–PaldiskiPaldiskiPaldiski is a town and Baltic Sea port situated on the Pakri peninsula of north-western Estonia. Originally a Swedish settlement known as Rågervik, it became a Russian naval base in the 18th century. The Russians renamed it Балтийский Порт Paldiski is a town and Baltic Sea port situated on the...
, 47.7 km (29.6 mi). Passenger trains are operated by Elektriraudtee (Tallinn–PääskülaPääskülaPääsküla is a subdistrict in the district of Nõmme, Tallinn, the capital of Estonia. It covers an area of and has a population of 9,477 , population density is .Pääsküla has a station on the Elektriraudtee western route.-References:...
, Tallinn–Keila, Tallinn–Paldiski and Tallinn–Klooga-rand routes). - Keila–RiisipereRiisipereRiisipere is a small borough in the county of Harju, Estonia, and is the Nissi Parish administrative center. Located on the Ääsmäe-Haapsalu road, its distance from Tallinn is 45 km, from Haapsalu 50 km, Märjamaa 30 km, Rapla 40 km....
, 24.4 km (15.2 mi). This line is part of the former Keila–HaapsaluHaapsaluHaapsalu is a seaside resort town located on the west coast of Estonia. It's the administrative centre of Lääne County and has a population of 11,618 ....
line, that was completed in 1905. Riisipere–Haapsalu section was abandoned in 2004.
Passenger trains are operated by Elektriraudtee (Tallinn–Riisipere route). - TapaTapa, EstoniaTapa is a town in Lääne-Viru County, Estonia. Located at the junction of the country's Tallinn-Narva and Tallinn-Tartu-Valga railway lines, it is an important centre of transit for freight as well as rail passengers...
–TartuTartuTartu is the second largest city of Estonia. In contrast to Estonia's political and financial capital Tallinn, Tartu is often considered the intellectual and cultural hub, especially since it is home to Estonia's oldest and most renowned university. Situated 186 km southeast of Tallinn, the...
, 112.5 km (69.9 mi). Completed in 1877.
Passenger trains are operated by Edelaraudtee (Tallinn–Tartu and Tartu–JõgevaJõgevaJõgeva is a small town in Estonia with a population of around 6000 people. It is the administrative centre of Jõgeva County.It is known as the coldest place in Estonia with the lowest temperature of...
routes). - Tartu–Valga, 82.5 km. Completed in 1887. International connection from Valga in Estonia to ValkaValkaValka is a town in northern Latvia, on the border with Estonia.Valka and the Estonian town Valga are twins, separated by the Estonian/Latvian border but using the slogan "One Town, Two States". The border dividing the Livonian town of Walk was marked out in 1920 by an international jury headed by...
in LatviaLatviaLatvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
.
Passenger trains are operated by Edelaraudtee. - Tartu–PechoryPechoryPechory : Petseri; ) is a town and the administrative center of Pechorsky District of Pskov Oblast, Russia. Population: The population includes a few hundred ethnic Estonians.The town is famous for the Russian Orthodox Pskovo-Pechersky Monastery....
, 83.5 km (51.9 mi). Built between 1929 and 1931. International connection from KoidulaKoidula, Põlva CountyKoidula is a village in Värska Parish, Põlva County, in southeastern Estonia, on the border with Russia. It's located few kilometeres northwest of Russian town Pechory. Koidula is the border crossing point of Karisilla–Pechory road , Tartu–Pechory and Valga–Pechory railways. Currently only...
in Estonia to Pechory in Russia.
Passenger trains are operated by Edelaraudtee (Tartu–OravaOrava, EstoniaOrava is a village in Põlva County, South East Estonia. It is the administrative centre of Orava Parish.Orava railway station on Tartu-Pechory railway line is located around 3 km north of the village. It is the last station on the Edelaraudtee Tartu-Orava route....
route). - Valga–Pechory, 91.5 km (56.9 mi). Part of RigaRigaRiga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
–PskovPskovPskov is an ancient city and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, Russia, located in the northwest of Russia about east from the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population: -Early history:...
railway, which was opened to regular traffic in 1889. International connection from Koidula in Estonia to Pechory in Russia.
The line is used only by freight trains.
Owned by Edelaraudtee Infrastruktuuri AS:
- Tallinn–LelleLelleLelle is a small borough in Kehtna Parish, Rapla County, in central Estonia. It's located on the branching point of Edelaraudtee's Tallinn–Pärnu and Tallinn–Viljandi railway lines. Lelle has a population of 522 ....
–PärnuPärnuPärnu is a city in southwestern Estonia on the coast of Pärnu Bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea. It is a popular summer vacation resort with many hotels, restaurants, and large beaches. The Pärnu River flows through the city and drains into the Gulf of Riga...
–(MõisakülaMõisakülaMõisaküla is a town and a municipality in south-western Estonia, in Viljandi County.-History:Mõisaküla arose on the fens of Abja manor. It became a town in 1 May 1938....
), 141.4 km (87.9 mi) (formerly 190.0 km). International connection has existed from Mõisaküla to Latvia, but the stretch Pärnu–Mõisaküla was abandoned in 2008. - Lelle–ViljandiViljandiViljandi is a town and municipality in southern Estonia with a population of 19,150 . It is the capital of Viljandi County. The town was first mentioned in 1283, upon being granted its town charter by Wilhelm von Endorpe....
, 78.7 km (48.9 mi). This line connects Viljandi to the Tallinn–Pärnu line via Lelle.
Major industrial railways
- Põlevkivi RaudteeEesti PõlevkiviEesti Energia Kaevandused is a subsidiary of Eesti Energia, an Estonian state-owned energy company. The core activity of Eesti Energia Kaevandused is oil-shale mining in the north-east of Estonia. The company has 3,150 employees...
(oil shale railway) maintains over 200 km (124.3 mi) of track in Ida-Virumaa. Main use of the network is transporting oil shaleOil shaleOil shale, an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock, contains significant amounts of kerogen from which liquid hydrocarbons called shale oil can be produced...
from underground and open-cast mines to the Narva Power PlantsNarva Power PlantsThe Narva Power Plants are a power generation complex in Narva in Estonia, near the border with Leningrad Oblast, Russia. The complex consists of the world's two largest oil shale-fired thermal power plants, Eesti Power Plant and Balti Power Plant . In 2007, Narva Power Plants generated about...
. The company is a subsidiary of Eesti Põlevkivi, which itself is a subsidiary of Eesti EnergiaEesti EnergiaEesti Energia AS is a state-owned energy company in Estonia with its headquarters in Tallinn. The company operates in Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Finland and Jordan. In Estonia the company operates under the name Eesti Energia, while using the brand name Enefit for international operations...
, owned by the state. - RakvereRakvereRakvere is a town in northern Estonia and the county seat of Lääne-Viru County, 20 km south of the Gulf of Finland.-History:The earliest signs of human settlement dating back to the 3rd-5th centuries AD have been found on the present theatre hill. Probably to protect that settlement, a wooden...
–Kunda, 19 km (11.8 mi). Built in 1896, this line connects the industrial town of Kunda to the Tallinn–Tapa–Narva line. The line is owned by private company Kunda Trans.
Connections to adjacent countries
A daily passenger service connects TallinnTallinn
Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list...
with Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
, operated by the Estonian company GoRail as a night train. The travel time is 15 hours. There also used to be a connection to Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
, but it was closed when the Russian railway authorities raised the track usage costs for the connection in 2008, rendering the service too expensive in comparison to bus traffic.
As of summer 2008 three daily trains operated by LDz connect Riga
Riga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
(Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
) to Valga (Estonia). The other railway lines to neighbouring countries are not used for direct passenger traffic at the moment. It is possible to travel between Tallinn and Riga over Tartu–Valga with train changes, but this takes a long time, and bus (travel time about 5 hours) or air is better.
Historic lines are Tallinn–Moscow via Tartu–Pechory, and Riga–St. Petersburg, which passed through Estonia from Valka, Latvia to Valga, Estonia–Võru
Võru
Võru is a town and a municipality in south-eastern Estonia. It is the capital of Võru County and the centre of Võru Parish.-History:Võru was founded on 21 August 1784, according to the wish of the Empress Catherine II of Russia, by the order of Riga Governor general count George Browne, on the...
–Piusa
Piusa
Piusa is a village in Orava Parish, Põlva County, in southeastern Estonia. It's located on the left bank of Piusa River, near the border of Russia.Piusa is famous for its sand caves along the river....
–Pechory, Russia. Both were closed in the 1990s.
There are plans for a new high-speed line Tallinn–Riga (continuing to Poland), Rail Baltica
Rail Baltica
thumb|300px|Map of Rail Baltica...
, planned to be in operation around 2020.
Railway links with adjacent countries
- Same gauge:
-
 LatviaRail transport in LatviaRail transport in Latvia is done on Russian gauge. The main railway company is Latvijas dzelzceļš.Historically Latvia had lot of different rail gauges, most notably standard gauge and narrow gauge.- Rail links with adjacent countries :...
LatviaRail transport in LatviaRail transport in Latvia is done on Russian gauge. The main railway company is Latvijas dzelzceļš.Historically Latvia had lot of different rail gauges, most notably standard gauge and narrow gauge.- Rail links with adjacent countries :...
– yes -
 RussiaRail transport in RussiaThe Russian railways are one of the economic wonders of the 19th, 20th, and 21st century world. In length of track they are second globally to the railways of the United States. In volume of freight hauled, they are third behind the United States and China, using the standard measure of...
RussiaRail transport in RussiaThe Russian railways are one of the economic wonders of the 19th, 20th, and 21st century world. In length of track they are second globally to the railways of the United States. In volume of freight hauled, they are third behind the United States and China, using the standard measure of...
– yes
-
Operators
Freight trains are operated by Eesti RaudteeEesti Raudtee
Eesti Raudtee or EVR is the national railway company of Estonia. It owns a network of 691 km of broad gauge railway throughout the country, including the 132 km used by the Elektriraudtee commuter trains around Tallinn...
and private companies including Estonian Railway Services (E.R.S. AS), and Spacecom.
Passenger services are offered by three operators:
External links
- Division of railways at Estonian Technical Surveillance Authority — Web pages containing various statistical information about the railway network and operations in Estonia.
- Map of public railways and railway stations
- National railway company Eesti Raudtee
- Estonian Railway Museum in Haapsalu (history page)
- Estonian private Railway Company "GoRail" official website /
- http://www.terradaily.com/2004/040822030207.mfpx57sq.html – Estonia: End of the line for Europe's passenger rail network

