
Ramapo Fault
Encyclopedia
The Ramapo Fault zone, spanning more than 185 miles (300 kilometers) in New York
, New Jersey
, and Pennsylvania
, is a system of faults between the northern Appalachian Mountains
and Piedmont areas to the east. This fault is perhaps the best known fault zone in the Mid-Atlantic region, and some small earthquakes have been known to occur in its vicinity. Recently, public knowledge about the fault has increased, especially after the 1970s, when the fault's proximity to the Indian Point nuclear plant
in New York was noticed.
Some seismologists have argued that this fault system has the potential to produce a major earthquake, but earthquakes are scattered throughout this region
, with no particular concentration of activity along the Ramapo fault (see Earthquake activity in the New York City area
). Thus, others have argued that neither the Ramapo Fault (nor any other known fault in this region) has been demonstrated to be any more active than any other fault zones in the greater New York City area.
area is part of the geologically complex structure of the Northern Appalachian Mountains
. This complex structure was formed during the past half billion years when the Earth's crust underlying the Northern Appalachians was the site of two major geological episodes, each of which has left its imprint on the NYC area bedrock. Between about 450 million years ago and about 250 million years ago, the Northern Appalachian region was affected by a continental collision
, in which the ancient African continent collided with the ancient North American continent to form the supercontinent
Pangaea
. Beginning about 200 million years ago, the present-day Atlantic ocean began to form as plate tectonic forces began to rift
apart the continent of Pangaea. The last major episode of geological activity to affect the bedrock
in the NYC area occurred about 100 million years ago, during the Mesozoic era, when continental rifting that led to the opening of the present-day Atlantic ocean formed the Hartford and Newark
Mesozoic rift basins.
Earthquake rates in the northeastern U.S. are 100 times lower than in California, but the earthquakes that do occur in the northeastern U.S. are typically felt over a much broader region than earthquakes of the same magnitude in the western U.S. This means the area of damage from an earthquake in the northeastern U.S. could be larger than the area of damage caused by an earthquake of the same magnitude in the western U.S. The cooler rocks in the northeastern U.S. contribute to the seismic energy propagating as much as ten times further than in the warmer rocks of California. A magnitude 4.0 eastern U.S. earthquake typically can be felt as far as 100 km (60 mi) from its epicenter
, but it infrequently causes damage near its source. A magnitude 5.5 eastern U.S. earthquake, although uncommon, can be felt as far as 500 km (300 mi) from its epicenter, and can cause damage as far away as 40 km (25 mi) from its epicenter. Earthquakes stronger than about magnitude 5.0 generate ground motions that are strong enough to be damaging in the epicentral area.
At well-studied plate boundaries like the San Andreas fault
system in California, scientists can often make observations that allow them to identify the specific fault on which an earthquake took place. In contrast, east of the Rocky Mountains this is rarely the case. The NYC area is far from the boundaries of the North American plate, which are in the center of the Atlantic Ocean, in the Caribbean Sea, and along the west coast of North America. The seismicity of the northeastern U.S. is generally considered to be due to ancient zones of weakness that are being reactivated in the present-day stress field. In this model, pre-existing faults that were formed during ancient geological episodes, persist in the intraplate crust, and the earthquakes occur when the present-day stress is released along these zones of weakness. The stress that causes the earthquakes is generally considered to be derived from present-day rifting at the Mid-Atlantic ridge
.
The northeastern U.S. has many known faults, but numerous smaller or deeply buried faults probably remain undetected. Virtually all of the known faults have not been active for perhaps 90 million years or more. Also, the locations of the known faults are not well determined at earthquake depths. Accordingly, few earthquakes in the region can be unambiguously linked to known faults. Given the current geological and seismological data, it is difficult to determine if a known fault is still active today and could produce a modern earthquake. As in most other areas east of the Rocky Mountains, the best guide to earthquake hazard in the northeastern U.S. is probably the locations of past earthquakes themselves.
The Ramapo Fault has been blamed for several past earthquakes, but the specific association of any significant earthquake with this fault has yet to be demonstrated. A damaging earthquake affecting New York City in 1884 was incorrectly argued to be caused by the Ramapo fault, likely because it is the most prominent mapped fault in the greater New York City area. At the present, the relationship between faults and earthquakes in the New York City area is understood to be more complex than any simple association of a specific earthquake with a specific fault.
 New Jersey, eastern Pennsylvania, and southeastern New York
New Jersey, eastern Pennsylvania, and southeastern New York
are divided geologically into four physiographic provinces
, each distinctive in their structure. Westernmost is the Valley and Ridge Province, made up of layers of Cambrian
-Devonian
sedimentary limestone
, sandstone
, and shale
remaining from ancient sea sediment, sand, and mud. East of this province is the Highlands
. This province is composed of the oldest rocks in the region - gneiss
, granite
, and Precambrian
marble
- formed by melting sedimentary rock which recrystallized in a deformed state. Paleozoic
rock belts are also present in the area.
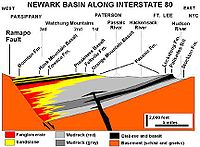
East of the Highlands is the Piedmont, specifically the Newark Basin
. The Ramapo Fault forms the boundary between the Newark Basin and the Highlands, running from Haverstraw, New York
to near Schaefferstown, Pennsylvania
. The Newark Basin, an aborted rift valley created during the breakup of Pangaea
, consists of sedimentary and volcanic rocks from the Triassic
and early Jurassic
. Smaller extensions of the Ramapo Fault, including the Hopewell, Fleminton-Furlong, and Chalfont faults, are present within the basin.
To the east of the Newark Basin are varying geologic provinces. In southeastern New York, from Westchester County
south to Staten Island, is the Manhattan Prong
Highlands and the Staten Island Serpentine belt (part of the New England province
). From the southern tip of Staten Island to Trenton, New Jersey
is the Atlantic Coastal Plain
. South of Trenton, a low relief extension of the Reading Prong
Highlands in the eastern part of the Pennsylvania Piedmont borders the Newark Basin to its southern terminus southwest of Reading.
, southeast-dipping faults, is probably inactive for the most part. Numerous 5 to 10 mile-long faults branch off the main fault.
With initial activity in the Late Precambrian - Early Paleozoic age, specifically the Cambrian
-Ordovician
period, the fault has seen six to seven major periods of seismic activity. The last period of heightened earthquake activity probably took place during the Triassic
, 200 million years ago. During this time, the Ramapo fault, originally a thrust fault active during the creation of the Appalachian Mountains
, was reactivated as the Atlantic Ocean was opening and the supercontinent
of Pangaea
was being torn apart. The fault became integrally involved in a period of intense rifting, slowly lowering the land to its east by more than nine kilometers to create the Newark Basin
. Magma was able to seep through linear fractures along the fault during the late Triassic and early Jurassic, producing episodic flood basalt
s responsible for the creation of the Watchung Mountains
.
Earthquakes in the greater New York City area affect most of New Jersey, the most densely populated state in the United States, as well New York City. It is difficult to discern the extent to which the Ramapo fault itself (or any other specific mapped fault in the area) might be any more of a source of future earthquakes than any other parts of the region. A 2008 study argued that a magnitude 6 or 7 earthquake was destined to originate from the Ramapo fault zone, which would almost definitely spawn hundreds or even thousands of fatalities and billions of dollars in damage. Studying around 400 earthquakes over the past 300 years, the study also argued that there was an additional fault zone extending from the Ramapo Fault Zone into southwestern Connecticut. On the other hand, other seismologists have argued that neither the Ramapo Fault, nor any hypothesized fault zone extending into southwestern Connecticut, has been demonstrated to be any more active than any other parts of the greater New York City area.
Just off the northern terminus of the Ramapo fault is the Indian Point Nuclear Power Plant
. Built between 1956 and 1960 by Consolidated Edison Company
, the plant began operating in 1963. At the cost of 90,000,000 1978 USD, it has been subjected to concerns that an earthquake from the Ramapo Fault will affect the plant. Whether or not the Ramapo fault actually does pose a threat to this nuclear power plant remains a question.
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
, New Jersey
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
, and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
, is a system of faults between the northern Appalachian Mountains
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains #Whether the stressed vowel is or ,#Whether the "ch" is pronounced as a fricative or an affricate , and#Whether the final vowel is the monophthong or the diphthong .), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians...
and Piedmont areas to the east. This fault is perhaps the best known fault zone in the Mid-Atlantic region, and some small earthquakes have been known to occur in its vicinity. Recently, public knowledge about the fault has increased, especially after the 1970s, when the fault's proximity to the Indian Point nuclear plant
Indian Point Energy Center
Indian Point Energy Center is a three-unit nuclear power plant station located in Buchanan, New York just south of Peekskill. It sits on the east bank of the Hudson River, 38 miles north of New York City...
in New York was noticed.
Some seismologists have argued that this fault system has the potential to produce a major earthquake, but earthquakes are scattered throughout this region
Earthquake activity in the New York City area
Although the eastern United States is, of course, not as seismically active as regions near plate boundaries, large and damaging earthquakes do occur here. Furthermore, when these rare eastern U.S. earthquakes occur, the areas affected by them are much larger than for western U.S. earthquakes of...
, with no particular concentration of activity along the Ramapo fault (see Earthquake activity in the New York City area
Earthquake activity in the New York City area
Although the eastern United States is, of course, not as seismically active as regions near plate boundaries, large and damaging earthquakes do occur here. Furthermore, when these rare eastern U.S. earthquakes occur, the areas affected by them are much larger than for western U.S. earthquakes of...
). Thus, others have argued that neither the Ramapo Fault (nor any other known fault in this region) has been demonstrated to be any more active than any other fault zones in the greater New York City area.
Background
The New York CityNew York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
area is part of the geologically complex structure of the Northern Appalachian Mountains
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains #Whether the stressed vowel is or ,#Whether the "ch" is pronounced as a fricative or an affricate , and#Whether the final vowel is the monophthong or the diphthong .), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians...
. This complex structure was formed during the past half billion years when the Earth's crust underlying the Northern Appalachians was the site of two major geological episodes, each of which has left its imprint on the NYC area bedrock. Between about 450 million years ago and about 250 million years ago, the Northern Appalachian region was affected by a continental collision
Continental collision
Continental collision is a phenomenon of the plate tectonics of Earth that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of subduction, whereby the subduction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together...
, in which the ancient African continent collided with the ancient North American continent to form the supercontinent
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is a landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton. The assembly of cratons and accreted terranes that form Eurasia qualifies as a supercontinent today.-History:...
Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
. Beginning about 200 million years ago, the present-day Atlantic ocean began to form as plate tectonic forces began to rift
Rift
In geology, a rift or chasm is a place where the Earth's crust and lithosphere are being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics....
apart the continent of Pangaea. The last major episode of geological activity to affect the bedrock
Bedrock
In stratigraphy, bedrock is the native consolidated rock underlying the surface of a terrestrial planet, usually the Earth. Above the bedrock is usually an area of broken and weathered unconsolidated rock in the basal subsoil...
in the NYC area occurred about 100 million years ago, during the Mesozoic era, when continental rifting that led to the opening of the present-day Atlantic ocean formed the Hartford and Newark
Newark Basin
The Newark Basin is a sediment-filled rift basin located mainly in northern New Jersey but also stretching into south-eastern Pennsylvania and southern New York. It is part of the system of Eastern North America Rift Basins.-Geology:...
Mesozoic rift basins.
Earthquake rates in the northeastern U.S. are 100 times lower than in California, but the earthquakes that do occur in the northeastern U.S. are typically felt over a much broader region than earthquakes of the same magnitude in the western U.S. This means the area of damage from an earthquake in the northeastern U.S. could be larger than the area of damage caused by an earthquake of the same magnitude in the western U.S. The cooler rocks in the northeastern U.S. contribute to the seismic energy propagating as much as ten times further than in the warmer rocks of California. A magnitude 4.0 eastern U.S. earthquake typically can be felt as far as 100 km (60 mi) from its epicenter
Epicenter
The epicenter or epicentre is the point on the Earth's surface that is directly above the hypocenter or focus, the point where an earthquake or underground explosion originates...
, but it infrequently causes damage near its source. A magnitude 5.5 eastern U.S. earthquake, although uncommon, can be felt as far as 500 km (300 mi) from its epicenter, and can cause damage as far away as 40 km (25 mi) from its epicenter. Earthquakes stronger than about magnitude 5.0 generate ground motions that are strong enough to be damaging in the epicentral area.
At well-studied plate boundaries like the San Andreas fault
San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental strike-slip fault that runs a length of roughly through California in the United States. The fault's motion is right-lateral strike-slip...
system in California, scientists can often make observations that allow them to identify the specific fault on which an earthquake took place. In contrast, east of the Rocky Mountains this is rarely the case. The NYC area is far from the boundaries of the North American plate, which are in the center of the Atlantic Ocean, in the Caribbean Sea, and along the west coast of North America. The seismicity of the northeastern U.S. is generally considered to be due to ancient zones of weakness that are being reactivated in the present-day stress field. In this model, pre-existing faults that were formed during ancient geological episodes, persist in the intraplate crust, and the earthquakes occur when the present-day stress is released along these zones of weakness. The stress that causes the earthquakes is generally considered to be derived from present-day rifting at the Mid-Atlantic ridge
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. It separates the Eurasian Plate and North American Plate in the North Atlantic, and the African Plate from the South...
.
The northeastern U.S. has many known faults, but numerous smaller or deeply buried faults probably remain undetected. Virtually all of the known faults have not been active for perhaps 90 million years or more. Also, the locations of the known faults are not well determined at earthquake depths. Accordingly, few earthquakes in the region can be unambiguously linked to known faults. Given the current geological and seismological data, it is difficult to determine if a known fault is still active today and could produce a modern earthquake. As in most other areas east of the Rocky Mountains, the best guide to earthquake hazard in the northeastern U.S. is probably the locations of past earthquakes themselves.
The Ramapo Fault has been blamed for several past earthquakes, but the specific association of any significant earthquake with this fault has yet to be demonstrated. A damaging earthquake affecting New York City in 1884 was incorrectly argued to be caused by the Ramapo fault, likely because it is the most prominent mapped fault in the greater New York City area. At the present, the relationship between faults and earthquakes in the New York City area is understood to be more complex than any simple association of a specific earthquake with a specific fault.
Regional setting

Downstate New York
Downstate New York is a term denoting the southeastern portion of New York State, United States, in contrast to Upstate New York. The term "Downstate New York" has significantly less currency than its counterpart term "Upstate New York", and the Downstate region is often not regarded as one...
are divided geologically into four physiographic provinces
Physiographic province
A physiographic province is a geographic region with a specific geomorphology and often specific subsurface rock type or structural elements.A continent may be subdivided into various physiographic provinces, each having a specific character, relief, and environment which contributes to its...
, each distinctive in their structure. Westernmost is the Valley and Ridge Province, made up of layers of Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
-Devonian
Devonian
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic Era spanning from the end of the Silurian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya , to the beginning of the Carboniferous Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya...
sedimentary limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
, sandstone
Sandstone
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized minerals or rock grains.Most sandstone is composed of quartz and/or feldspar because these are the most common minerals in the Earth's crust. Like sand, sandstone may be any colour, but the most common colours are tan, brown, yellow,...
, and shale
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock composed of mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals and tiny fragments of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite. The ratio of clay to other minerals is variable. Shale is characterized by breaks along thin laminae or parallel layering...
remaining from ancient sea sediment, sand, and mud. East of this province is the Highlands
Reading Prong
The Reading Prong is a physiographic subprovince of the New England Uplands section of the New England province of the Appalachian Highlands. The prong consists of mountains made up of crystalline metamorphic rock.-Location:...
. This province is composed of the oldest rocks in the region - gneiss
Gneiss
Gneiss is a common and widely distributed type of rock formed by high-grade regional metamorphic processes from pre-existing formations that were originally either igneous or sedimentary rocks.-Etymology:...
, granite
Granite
Granite is a common and widely occurring type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock. Granite usually has a medium- to coarse-grained texture. Occasionally some individual crystals are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic...
, and Precambrian
Precambrian
The Precambrian is the name which describes the large span of time in Earth's history before the current Phanerozoic Eon, and is a Supereon divided into several eons of the geologic time scale...
marble
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite.Geologists use the term "marble" to refer to metamorphosed limestone; however stonemasons use the term more broadly to encompass unmetamorphosed limestone.Marble is commonly used for...
- formed by melting sedimentary rock which recrystallized in a deformed state. Paleozoic
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic eon, spanning from roughly...
rock belts are also present in the area.
East of the Highlands is the Piedmont, specifically the Newark Basin
Newark Basin
The Newark Basin is a sediment-filled rift basin located mainly in northern New Jersey but also stretching into south-eastern Pennsylvania and southern New York. It is part of the system of Eastern North America Rift Basins.-Geology:...
. The Ramapo Fault forms the boundary between the Newark Basin and the Highlands, running from Haverstraw, New York
Haverstraw, New York
Haverstraw is the name of two locations in Rockland County, New York:*Haverstraw, New York, a town*Haverstraw , New York, a village located entirely within the townIt may also refer to:*West Haverstraw, New York*Haverstraw Bay*Haverstraw Indians...
to near Schaefferstown, Pennsylvania
Schaefferstown, Pennsylvania
Schaefferstown is a census-designated place in Lebanon County, Pennsylvania, United States and is completely surrounded by Heidelberg Township. The population was 984 at the 2000 census. Bomberger's Distillery is located near Schaefferstown.-Geography:...
. The Newark Basin, an aborted rift valley created during the breakup of Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
, consists of sedimentary and volcanic rocks from the Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
and early Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
. Smaller extensions of the Ramapo Fault, including the Hopewell, Fleminton-Furlong, and Chalfont faults, are present within the basin.
To the east of the Newark Basin are varying geologic provinces. In southeastern New York, from Westchester County
Westchester County, New York
Westchester County is a county located in the U.S. state of New York. Westchester covers an area of and has a population of 949,113 according to the 2010 Census, residing in 45 municipalities...
south to Staten Island, is the Manhattan Prong
Reading Prong
The Reading Prong is a physiographic subprovince of the New England Uplands section of the New England province of the Appalachian Highlands. The prong consists of mountains made up of crystalline metamorphic rock.-Location:...
Highlands and the Staten Island Serpentine belt (part of the New England province
New England province
The New England province is a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division of eastern North America. The province consists of the Seaboard Lowland, New England Upland, White Mountain, Green Mountain, and Taconic sections.-Geology:...
). From the southern tip of Staten Island to Trenton, New Jersey
Trenton, New Jersey
Trenton is the capital of the U.S. state of New Jersey and the county seat of Mercer County. As of the 2010 United States Census, Trenton had a population of 84,913...
is the Atlantic Coastal Plain
Atlantic Coastal Plain
The Atlantic coastal plain has both low elevation and low relief, but it is also a relatively flat landform extending from the New York Bight southward to a Georgia/Florida section of the Eastern Continental Divide, which demarcates the plain from the ACF River Basin in the Gulf Coastal Plain to...
. South of Trenton, a low relief extension of the Reading Prong
Reading Prong
The Reading Prong is a physiographic subprovince of the New England Uplands section of the New England province of the Appalachian Highlands. The prong consists of mountains made up of crystalline metamorphic rock.-Location:...
Highlands in the eastern part of the Pennsylvania Piedmont borders the Newark Basin to its southern terminus southwest of Reading.
Fault zone
The fault system, part of a series of north-east strikingStrike and dip
Strike and dip refer to the orientation or attitude of a geologic feature. The strike line of a bed, fault, or other planar feature is a line representing the intersection of that feature with a horizontal plane. On a geologic map, this is represented with a short straight line segment oriented...
, southeast-dipping faults, is probably inactive for the most part. Numerous 5 to 10 mile-long faults branch off the main fault.
With initial activity in the Late Precambrian - Early Paleozoic age, specifically the Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
-Ordovician
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
period, the fault has seen six to seven major periods of seismic activity. The last period of heightened earthquake activity probably took place during the Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
, 200 million years ago. During this time, the Ramapo fault, originally a thrust fault active during the creation of the Appalachian Mountains
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains #Whether the stressed vowel is or ,#Whether the "ch" is pronounced as a fricative or an affricate , and#Whether the final vowel is the monophthong or the diphthong .), often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians...
, was reactivated as the Atlantic Ocean was opening and the supercontinent
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is a landmass comprising more than one continental core, or craton. The assembly of cratons and accreted terranes that form Eurasia qualifies as a supercontinent today.-History:...
of Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
was being torn apart. The fault became integrally involved in a period of intense rifting, slowly lowering the land to its east by more than nine kilometers to create the Newark Basin
Newark Basin
The Newark Basin is a sediment-filled rift basin located mainly in northern New Jersey but also stretching into south-eastern Pennsylvania and southern New York. It is part of the system of Eastern North America Rift Basins.-Geology:...
. Magma was able to seep through linear fractures along the fault during the late Triassic and early Jurassic, producing episodic flood basalt
Flood basalt
A flood basalt or trap basalt is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that coats large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Flood basalts have occurred on continental scales in prehistory, creating great plateaus and mountain ranges...
s responsible for the creation of the Watchung Mountains
Watchung Mountains
The Watchung Mountains are a group of three long low ridges of volcanic origin, between 400 ft. and 500 ft. high, lying parallel to each other in northern New Jersey in the United States...
.
Earthquake hazards in the New York City area
Despite the rarity of strong East Coast earthquakes in the United States, there are some that do occur. Furthermore, when these rare eastern U.S. events do occur, the areas affected by them are on average ten times as large as western ones for events of the same magnitude. Thus, earthquakes represent at least a moderate hazard to East Coast cities.Earthquakes in the greater New York City area affect most of New Jersey, the most densely populated state in the United States, as well New York City. It is difficult to discern the extent to which the Ramapo fault itself (or any other specific mapped fault in the area) might be any more of a source of future earthquakes than any other parts of the region. A 2008 study argued that a magnitude 6 or 7 earthquake was destined to originate from the Ramapo fault zone, which would almost definitely spawn hundreds or even thousands of fatalities and billions of dollars in damage. Studying around 400 earthquakes over the past 300 years, the study also argued that there was an additional fault zone extending from the Ramapo Fault Zone into southwestern Connecticut. On the other hand, other seismologists have argued that neither the Ramapo Fault, nor any hypothesized fault zone extending into southwestern Connecticut, has been demonstrated to be any more active than any other parts of the greater New York City area.
Just off the northern terminus of the Ramapo fault is the Indian Point Nuclear Power Plant
Indian Point Energy Center
Indian Point Energy Center is a three-unit nuclear power plant station located in Buchanan, New York just south of Peekskill. It sits on the east bank of the Hudson River, 38 miles north of New York City...
. Built between 1956 and 1960 by Consolidated Edison Company
Consolidated Edison
Consolidated Edison, Inc. is one of the largest investor-owned energy companies in the United States, with approximately $14 billion in annual revenues and $36 billion in assets...
, the plant began operating in 1963. At the cost of 90,000,000 1978 USD, it has been subjected to concerns that an earthquake from the Ramapo Fault will affect the plant. Whether or not the Ramapo fault actually does pose a threat to this nuclear power plant remains a question.

