
Rankit
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, rankits of a set of data are the expected values of the order statistic
s of a sample from the standard normal distribution the same size as the data. They are primarily used in the normal probability plot
, a graphical technique for normality test
ing.
0 and variance
1 (the standard normal distribution) and then sorted into increasing order, the expected values of the resulting order statistic
s are:
Suppose the numbers in a data set are
Then one may sort these and line them up with the corresponding rankits; in order they are
which yields the points:
These points are then plotted as the vertical and horizontal coordinates of a scatter plot.
For:
the corresponding ranks are:
i.e., the number appearing first is the 5th-smallest, the number appearing second is 6th-smallest, the number appearing third is smallest, the number appearing fourth is 2nd-smallest, etc. One rearranges the expected normal order statistics accordingly, getting the rankits of this data set:
. Such a plot is necessarily nondecreasing. In large samples from a normally distributed population, such a plot will approximate a straight line. Substantial deviations from straightness are considered evidence against normality of the distribution.
Rankit plots are usually used to visually demonstrate whether data are from a specified probability distribution
.
A rankit plot is a kind of Q-Q plot
– it plots the order statistics (quantiles) of the sample against certain quantiles (the rankits) of the assumed normal distribution. Q-Q plots may use other quantiles for the normal distribution, however.
(1899–1979).
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, rankits of a set of data are the expected values of the order statistic
Order statistic
In statistics, the kth order statistic of a statistical sample is equal to its kth-smallest value. Together with rank statistics, order statistics are among the most fundamental tools in non-parametric statistics and inference....
s of a sample from the standard normal distribution the same size as the data. They are primarily used in the normal probability plot
Normal probability plot
The normal probability plot is a graphical technique for normality testing: assessing whether or not a data set is approximately normally distributed....
, a graphical technique for normality test
Normality test
In statistics, normality tests are used to determine whether a data set is well-modeled by a normal distribution or not, or to compute how likely an underlying random variable is to be normally distributed....
ing.

Example
This is perhaps most readily understood by means of an example. If an i.i.d. sample of six items is taken from a normally distributed population with expected valueExpected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
0 and variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
1 (the standard normal distribution) and then sorted into increasing order, the expected values of the resulting order statistic
Order statistic
In statistics, the kth order statistic of a statistical sample is equal to its kth-smallest value. Together with rank statistics, order statistics are among the most fundamental tools in non-parametric statistics and inference....
s are:
- −1.2672, −0.6418, −0.2016, 0.2016, 0.6418, 1.2672.
Suppose the numbers in a data set are
- 65, 75, 16, 22, 43, 40.
Then one may sort these and line them up with the corresponding rankits; in order they are
- 16, 22, 40, 43, 65, 75,
which yields the points:
| data point | rankit |
|---|---|
| 16 | −1.2672 |
| 22 | −0.6418 |
| 40 | −0.2016 |
| 43 | 0.2016 |
| 65 | 0.6418 |
| 75 | 1.2672 |
These points are then plotted as the vertical and horizontal coordinates of a scatter plot.
Alternative method
Alternatively, rather than sort the data points, one may rank them, and rearrange the rankits accordingly. This yields the same pairs of numbers, but in a different order.For:
- 65, 75, 16, 22, 43, 40,
the corresponding ranks are:
- 5, 6, 1, 2, 4, 3,
i.e., the number appearing first is the 5th-smallest, the number appearing second is 6th-smallest, the number appearing third is smallest, the number appearing fourth is 2nd-smallest, etc. One rearranges the expected normal order statistics accordingly, getting the rankits of this data set:
| data point | rank | rankit |
|---|---|---|
| 65 | 5 | 0.6418 |
| 75 | 6 | 1.2672 |
| 16 | 1 | −1.2672 |
| 22 | 2 | −0.6418 |
| 43 | 4 | 0.2016 |
| 40 | 3 | −0.2016 |
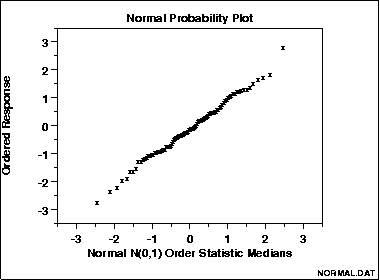
Rankit plot
A graph plotting the rankits on the horizontal axis and the data points on the vertical axis is called a rankit plot or a normal probability plotNormal probability plot
The normal probability plot is a graphical technique for normality testing: assessing whether or not a data set is approximately normally distributed....
. Such a plot is necessarily nondecreasing. In large samples from a normally distributed population, such a plot will approximate a straight line. Substantial deviations from straightness are considered evidence against normality of the distribution.
Rankit plots are usually used to visually demonstrate whether data are from a specified probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
.
A rankit plot is a kind of Q-Q plot
Q-Q plot
In statistics, a Q-Q plot is a probability plot, which is a graphical method for comparing two probability distributions by plotting their quantiles against each other. First, the set of intervals for the quantiles are chosen...
– it plots the order statistics (quantiles) of the sample against certain quantiles (the rankits) of the assumed normal distribution. Q-Q plots may use other quantiles for the normal distribution, however.
History
The rankit plot and the word rankit was introduced by the biologist and statistician Chester Ittner BlissChester Ittner Bliss
Chester Ittner Bliss was primarily a biologist, who is best known for his contributions to statistics. He was born in Springfield, Ohio in 1899 and died in 1979.-Academic qualifications:*Bachelor of Arts in Entomology from Ohio State University, 1921...
(1899–1979).

