
Recovery Consistency Objective
Encyclopedia
The term recovery consistency objective (RCO) is used in business continuity planning
in addition to recovery point objective
(RPO) and recovery time objective
(RTO). It applies data consistency
objectives to continuous data protection
services. Following the definitions for RPO and RTO, RCO defines a measurement for the consistency of distributed business data within interlinked systems after a disaster incident. Similar terms used in this context are "Recovery Consistency Characteristics" (RCC) and "recovery object granularity" (ROG).
The term RCO focuses on business data consistency across multiple systems in SOA
-driven business applications such as SAP ERP
. It can be defined per business processes and reflects the individual requirements of corresponding business data and cross-system consistency. While RTO and RPO are absolute per-system values, RCO is expressed as percentage measuring the deviation between actual and targeted state of business data across systems for individual business processes or process groups.
The following formula calculates RCO with "n" representing the number of business processes and "entities" representing an abstract value for business data:
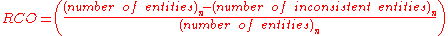
Targeting 100% RCO for a business process (distributed across several systems) would mean that no business data deviation is allowed after a disaster incident whereas any target below 100% allows deviation. Target values for RCO increase with the criticality of the underlying business data: logistics and banking-related business processes are often characterized by higher RCO requirements than those of CRM or HR systems.
Including RCO considerations in addition to RTO and RPO in the business impact analysis helps to focus on the integrity of business data and processes in complex application environments. RCO considerations should be included in the Disaster Recovery
Architecture by manually defining multiple consistency points across the landscape or by special Disaster Recovery mirroring tools.
Business continuity planning
Business continuity planning “identifies [an] organization's exposure to internal and external threats and synthesizes hard and soft assets to provide effective prevention and recovery for the organization, whilst maintaining competitive advantage and value system integrity”. It is also called...
in addition to recovery point objective
Recovery point objective
-Recovery point objective :When computers used for normal "production" business services are affected by a "Major Incident" that cannot be fixed quickly, then the Information Technology Service Continuity Plan is performed, by the ITSC recovery team...
(RPO) and recovery time objective
Recovery Time Objective
The recovery time objective is the duration of time and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster in order to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity....
(RTO). It applies data consistency
Data consistency
Data consistency summarizes the validity, accuracy, usability and integrity of related data between applications and across an IT enterprise. This ensures that each user observes a consistent view of the data, including visible changes made by the user's own transactions and transactions of other...
objectives to continuous data protection
Continuous data protection
Continuous data protection , also called continuous backup or real-time backup, refers to backup of computer data by automatically saving a copy of every change made to that data, essentially capturing every version of the data that the user saves...
services. Following the definitions for RPO and RTO, RCO defines a measurement for the consistency of distributed business data within interlinked systems after a disaster incident. Similar terms used in this context are "Recovery Consistency Characteristics" (RCC) and "recovery object granularity" (ROG).
The term RCO focuses on business data consistency across multiple systems in SOA
Service-oriented architecture
In software engineering, a Service-Oriented Architecture is a set of principles and methodologies for designing and developing software in the form of interoperable services. These services are well-defined business functionalities that are built as software components that can be reused for...
-driven business applications such as SAP ERP
SAP ERP
The SAP ERP application is an integrated enterprise resource planning software manufactured by SAP AG that targets business software requirements of midsize and large organizations in all industries and sectors...
. It can be defined per business processes and reflects the individual requirements of corresponding business data and cross-system consistency. While RTO and RPO are absolute per-system values, RCO is expressed as percentage measuring the deviation between actual and targeted state of business data across systems for individual business processes or process groups.
The following formula calculates RCO with "n" representing the number of business processes and "entities" representing an abstract value for business data:
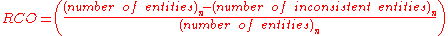
Targeting 100% RCO for a business process (distributed across several systems) would mean that no business data deviation is allowed after a disaster incident whereas any target below 100% allows deviation. Target values for RCO increase with the criticality of the underlying business data: logistics and banking-related business processes are often characterized by higher RCO requirements than those of CRM or HR systems.
Including RCO considerations in addition to RTO and RPO in the business impact analysis helps to focus on the integrity of business data and processes in complex application environments. RCO considerations should be included in the Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery
Disaster recovery is the process, policies and procedures related to preparing for recovery or continuation of technology infrastructure critical to an organization after a natural or human-induced disaster. Disaster recovery is a subset of business continuity...
Architecture by manually defining multiple consistency points across the landscape or by special Disaster Recovery mirroring tools.

