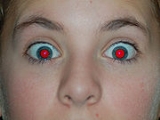
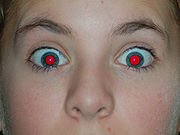
Red-eye effect
Encyclopedia
Photography
Photography is the art, science and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film...
is the common appearance of red
Red
Red is any of a number of similar colors evoked by light consisting predominantly of the longest wavelengths of light discernible by the human eye, in the wavelength range of roughly 630–740 nm. Longer wavelengths than this are called infrared , and cannot be seen by the naked eye...
pupil
Pupil
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to enter the retina. It appears black because most of the light entering the pupil is absorbed by the tissues inside the eye. In humans the pupil is round, but other species, such as some cats, have slit pupils. In...
s in color photograph
Photograph
A photograph is an image created by light falling on a light-sensitive surface, usually photographic film or an electronic imager such as a CCD or a CMOS chip. Most photographs are created using a camera, which uses a lens to focus the scene's visible wavelengths of light into a reproduction of...
s of eye
Eye
Eyes are organs that detect light and convert it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons. The simplest photoreceptors in conscious vision connect light to movement...
s. It occurs when using a photographic flash
Flash (photography)
A flash is a device used in photography producing a flash of artificial light at a color temperature of about 5500 K to help illuminate a scene. A major purpose of a flash is to illuminate a dark scene. Other uses are capturing quickly moving objects or changing the quality of light...
very close to the camera lens (as with most compact cameras
Point and shoot camera
A point-and-shoot camera, also called a compact camera, is a still camera designed primarily for simple operation. Most use focus free lenses or autofocus for focusing, automatic systems for setting the exposure options, and have flash units built in....
), in ambient low light. The effect appears in the eyes of humans and animals that have no tapetum lucidum
Tapetum lucidum
The tapetum lucidum is a layer of tissue in the eye of many vertebrate animals....
, hence no eyeshine
Tapetum lucidum
The tapetum lucidum is a layer of tissue in the eye of many vertebrate animals....
, and rarely in animals that have a tapetum lucidum. The red-eye effect can also be seen when one human observes another when there is a bright lightsource nearby.
Theatrical followspot operators, positioned nearly coincidentally with a very bright light and somewhat distant from the actors, occasionally witness red-eye in actors on stage. The effect is not visible to the rest of the audience because it is reliant on the very small angle between the followspot operator and the light.
The feature film Blade Runner
Blade Runner
Blade Runner is a 1982 American science fiction film directed by Ridley Scott and starring Harrison Ford, Rutger Hauer, and Sean Young. The screenplay, written by Hampton Fancher and David Peoples, is loosely based on the novel Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep? by Philip K...
intentionally induced a red-eye effect to indicate that certain characters were "replicants" (according to the story, an artificial life-form). The effect relied on a semi-silvered mirror directing light at the actors on the same incidence as the camera.
Causes



Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
of the flash occurs too fast for the pupil
Pupil
The pupil is a hole located in the center of the iris of the eye that allows light to enter the retina. It appears black because most of the light entering the pupil is absorbed by the tissues inside the eye. In humans the pupil is round, but other species, such as some cats, have slit pupils. In...
to close, much of the very bright light from the flash passes into the eye through the pupil, reflects
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two differentmedia so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves...
off the fundus
Fundus (eye)
The fundus of the eye is the interior surface of the eye, opposite the lens, and includes the retina, optic disc, macula and fovea, and posterior pole. The fundus can be viewed with an ophthalmoscope. The term may also be inclusive of Bruch's membrane and the choroid.The color of the fundus varies...
at the back of the eyeball and out through the pupil. The camera records this reflected light. The main cause of the red color is the ample amount of blood in the choroid
Choroid
The choroid, also known as the choroidea or choroid coat, is the vascular layer of the eye, containing connective tissue, and lying between the retina and the sclera. The human choroid is thickest at the far extreme rear of the eye , while in the outlying areas it narrows to 0.1 mm...
which nourishes the back of the eye and is located behind the retina. The blood in the retinal circulation is far less than in the choroid, and plays virtually no role. The eye contains several photostable pigments that all absorb in the short wavelength region, and hence contribute somewhat to the red eye effect. The lens
Lens (anatomy)
The crystalline lens is a transparent, biconvex structure in the eye that, along with the cornea, helps to refract light to be focused on the retina. The lens, by changing shape, functions to change the focal distance of the eye so that it can focus on objects at various distances, thus allowing a...
cuts off deep blue and violet light, below 430 nm (depending on age), and macular pigment absorbs between 400 and 500 nm, but this pigment is located exclusively in the tiny fovea
Fovea
The fovea centralis, also generally known as the fovea , is a part of the eye, located in the center of the macula region of the retina....
. Melanin
Melanin
Melanin is a pigment that is ubiquitous in nature, being found in most organisms . In animals melanin pigments are derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine. The most common form of biological melanin is eumelanin, a brown-black polymer of dihydroxyindole carboxylic acids, and their reduced forms...
, located in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and the choroid, shows a gradually increasing absorption towards the short wavelengths. But blood is the main determinant of the red color, because it is completely transparent at long wavelengths and abruptly starts absorbing at 600 nm. The amount of red light emerging from the pupil depends on the amount of melanin in the layers behind the retina. This amount varies strongly between individuals. Light skinned people with blue eyes have relatively low melanin in the fundus
Fundus (eye)
The fundus of the eye is the interior surface of the eye, opposite the lens, and includes the retina, optic disc, macula and fovea, and posterior pole. The fundus can be viewed with an ophthalmoscope. The term may also be inclusive of Bruch's membrane and the choroid.The color of the fundus varies...
and thus show a much stronger red-eye effect than dark skinned people with brown eyes. The same holds for animals. The color of the iris
Iris (anatomy)
The iris is a thin, circular structure in the eye, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupils and thus the amount of light reaching the retina. "Eye color" is the color of the iris, which can be green, blue, or brown. In some cases it can be hazel , grey, violet, or even pink...
itself is of virtually no importance for the red-eye effect. This is obvious because the red-eye effect works best when photographing dark adapted subjects, hence with fully dilated pupils. Photographs taken with infra-red light through night vision devices always show very bright pupils because, in the dark, the pupils are fully dilated and the infra-red light is not absorbed by any ocular pigment.
The role of melanin in red-eye effect is nicely demonstrated in animals with heterochromia
Heterochromia
In anatomy, heterochromia refers to a difference in coloration, usually of the iris but also of hair or skin. Heterochromia is a result of the relative excess or lack of melanin...
: only the blue eye displays the effect. The effect is still more pronounced in humans and animals with albinism
Albinism
Albinism is a congenital disorder characterized by the complete or partial absence of pigment in the skin, hair and eyes due to absence or defect of an enzyme involved in the production of melanin...
. All forms of albinism involve abnormal production and/or deposition of melanin.
Red-eye effect is seen in photographs of children also because children's eyes have more rapid dark adaption
Adaptation (eye)
In ocular physiology, adaptation is the ability of the eye to adjust to various levels of darkness and light.-Efficacy:The human eye can function from very dark to very bright levels of light; its sensing capabilities reach across nine orders of magnitude. This means that the brightest and the...
: in low light a child's pupils enlarge sooner, and an enlarged pupil accentuates the red-eye effect.
In a photograph of a child's face, red-eye in one eye but not the other may be a sign of the cancer retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rapidly developing cancer that develops in the cells of retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. In the developed world, Rb has one of the best cure rates of all childhood cancers , with more than nine out of every ten sufferers surviving into...
.
Similar effects
Similar effects, some related to red-eye effect, are of several kinds:- In many flash photographs, even those without perceptible red-eye effect, many animals' pupils display eyeshineTapetum lucidumThe tapetum lucidum is a layer of tissue in the eye of many vertebrate animals....
. Although eyeshine is an unrelated effect, animals with blue eyes may display the red-eye effect in addition to eyeshine.
- Numerous diseases of the eye cause a "white-eye effect" instead of the expected red-eye effect (see LeukocoriaLeukocoriaLeukocoria is an abnormal white reflection from the retina of the eye. Leukocoria resembles eyeshine, but leukocoria can occur in humans and other animals that lack eyeshine because their retina lacks a tapetum lucidum....
).
- A related effect, red reflexRed reflexThe red reflex refers to the reddish-orange reflection from the eye's retina that is observed when using an ophthalmoscope or retinoscope from approximately 30 cm / 1 foot...
, is seen in fundoscopy; unlike the red-eye effect, it is not a photographic effect.
- In photographs recorded with infraredInfraredInfrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
-sensitive passive (non-IR emitting) equipment, the eyes (not only the pupils) usually appear very bright. This is due not to reflection, but to radiationRadiationIn physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
of core body heat in the form of infrared light (see Night visionNight visionNight vision is the ability to see in low light conditions. Whether by biological or technological means, night vision is made possible by a combination of two approaches: sufficient spectral range, and sufficient intensity range...
).
Photography techniques for prevention and removal

- Using bounce flash in which the flash head is aimed at a nearby pale colored surface such as a ceiling or wall or at a specialist photographic reflector. This both changes the direction of the flash and ensures that only diffused flash light enters the eye.
- Placing the flash away from the camera's optical axis ensures that the light from the flash hits the eye at an oblique angle. The light enters the eye in a direction away from the optical axis of the camera and is refocused by the eye lens back along the same axis. Because of this the retina will not be visible to the camera and the eyes will appear natural.
- Taking pictures without flash by increasing the ambient lighting, opening the lens aperture, using a faster film or detector, or reducing the shutter speed.
- Using the red-eye reduction capabilities built into many modern cameras. These precede the main flash with a series of short, low-power flashes, or a continuous piercing bright light triggering the pupil to contract. (This should not be confused with the autofocus assist beam, which uses a series of flashes for focus instead.)
- Having the subject look away from the camera lens.
- The red-eye effect is not seen in subjects wearing contact lenses with UV filtering
- Increase the lighting in the room so that the subject's pupils are more constricted.
- Some computer digital image editors have the ability to lessen the red eye by desaturating the red color.
If direct flash must be used, a good rule of thumb is to separate the flash from the lens by 1/20 of the distance of the camera to the subject. For example, if the subject is 2 metres (6 feet) away, the flash head should be at least 10 cm (4 inches) away from the lens.
Professional photographers prefer to use ambient light or indirect flash as the red-eye reduction system does not always prevent red eyes, for example if people look away during the pre-flash. In addition, people do not look natural with small pupils, and direct lighting from close to the camera lens is considered to produce unflattering photographs.
Various graphics editing software packages have functions to remove red eyes from digital photographs. Some have automated this process, and can apply it to many photos at once. Red-eye removal is also built into many popular consumer programs, such as Adobe Photoshop, Apple iPhoto
IPhoto
iPhoto is a digital photograph manipulation software application developed by Apple Inc. and released with every Macintosh personal computer as part of the iLife suite of digital life management applications...
, Corel Photo-Paint
Corel PHOTO-PAINT
Corel PHOTO-PAINT is a raster graphics editor developed and marketed by Corel since 1992. Corel currently markets the software for Windows operating systems, previously having marketed versions for Linux and Mac OS...
, GIMP
GIMP
GIMP is a free software raster graphics editor. It is primarily employed as an image retouching and editing tool and is freely available in versions tailored for most popular operating systems including Microsoft Windows, Apple Mac OS X, and Linux.In addition to detailed image retouching and...
, Google Picasa
Picasa
Picasa is an image organizer and image viewer for organizing and editing digital photos, plus an integrated photo-sharing website, originally created by Idealab in 2002 and owned by Google since 2004. "Picasa" is a blend of the name of Spanish painter Pablo Picasso, the phrase mi casa for "my...
, and Microsoft Windows Live Photo Gallery
Windows Live Photo Gallery
Windows Live Photo Gallery is a photo management and photo sharing application released as a part of Microsoft's Windows Live initiative. It is an upgraded version of Windows Photo Gallery, which is a part of Windows Vista....
.

