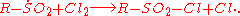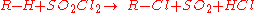
Reed reaction
Encyclopedia
The Reed reaction is a chemical reaction
that utilizes light
to oxidize
hydrocarbon
s to sulfonyl chlorides. The reaction performs via the free radicals. First, the light makes a molecule of chlorine
dissociate homolytically
, then an chlorine atom produced attacks the hydrocarbon chain to form hydrogen chloride
what results in the formation of alkyl free radical. Then SO2
as an electron donor
bonds to the reaction center, forming an sulfonyl
radical. Finally, the least one attacks another chlorine molecule to produce an sulfonyl chloride and a new chlorine atom which continues the reaction chain.
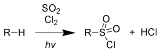
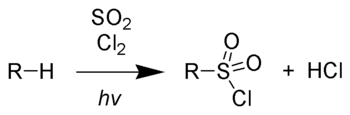 Chain initiation:
Chain initiation:
Chain propagation steps:
The resulting sulfonyl chlorides are widely used in the detergent
industry as a raw material
.
Under particular circumstances (40–80 °C) only chlorination
of alkane may take place.
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
that utilizes light
Photochemistry
Photochemistry, a sub-discipline of chemistry, is the study of chemical reactions that proceed with the absorption of light by atoms or molecules.. Everyday examples include photosynthesis, the degradation of plastics and the formation of vitamin D with sunlight.-Principles:Light is a type of...
to oxidize
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
s to sulfonyl chlorides. The reaction performs via the free radicals. First, the light makes a molecule of chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
dissociate homolytically
Homolysis
In general it means breakdown to equal pieces There are separate meanings for the word in chemistry and biology.-Homolysis in chemistry:...
, then an chlorine atom produced attacks the hydrocarbon chain to form hydrogen chloride
Hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the formula HCl. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric humidity. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry...
what results in the formation of alkyl free radical. Then SO2
Sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is released by volcanoes and in various industrial processes. Since coal and petroleum often contain sulfur compounds, their combustion generates sulfur dioxide unless the sulfur compounds are removed before burning the fuel...
as an electron donor
Electron donor
An electron donor is a chemical entity that donates electrons to another compound. It is a reducing agent that, by virtue of its donating electrons, is itself oxidized in the process....
bonds to the reaction center, forming an sulfonyl
Sulfonyl
A sulfonyl group can refer either to a functional group found primarily in sulfones or to a substituent obtained from a sulfonic acid by the removal of the hydroxyl group similarly to acyl groups...
radical. Finally, the least one attacks another chlorine molecule to produce an sulfonyl chloride and a new chlorine atom which continues the reaction chain.

Chain propagation steps:
The resulting sulfonyl chlorides are widely used in the detergent
Detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with "cleaning properties in dilute solutions." In common usage, "detergent" refers to alkylbenzenesulfonates, a family of compounds that are similar to soap but are less affected by hard water...
industry as a raw material
Raw material
A raw material or feedstock is the basic material from which a product is manufactured or made, frequently used with an extended meaning. For example, the term is used to denote material that came from nature and is in an unprocessed or minimally processed state. Latex, iron ore, logs, and crude...
.
Under particular circumstances (40–80 °C) only chlorination
Chlorination
Chlorination is the process of adding the element chlorine to water as a method of water purification to make it fit for human consumption as drinking water...
of alkane may take place.