Refractive error
Encyclopedia
A refractive error, or refraction error, is an error in the focus
ing of light
by the eye
and a frequent reason for reduced visual acuity
.
An eye that has refractive error when viewing distant objects is said to have ametropia or be ametropic. This eye, when not using accommodation, cannot focus parallel rays of light (light from distant objects) on the retina.
The word "ametropia" can be used interchangeably with "refractive error" as they refer to the same thing. Types of ametropia include myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism. They are frequently categorized as spherical errors and cylindrical errors:
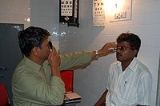
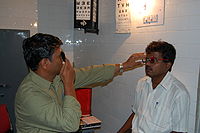 Blurry vision may result from any number of conditions not necessarily related to refractive errors. The diagnosis of a refractive error is usually confirmed by an eye care professional
Blurry vision may result from any number of conditions not necessarily related to refractive errors. The diagnosis of a refractive error is usually confirmed by an eye care professional
during an eye examination
using an instrument called a phoropter
which contains a large number of lenses of varying optical power. In combination with a retinoscope (a procedure entitled retinoscopy
), the doctor instructs the patient to view an eye chart
while he or she changes the lenses within the phoropter to objectively estimate the amount of refractive error the patient may possess. Once the doctor arrives at an estimate, he or she typically shows the patient lenses of progressively higher or weaker powers in a process known as refraction
or refractometry
.
Cycloplegic agents are frequently used to more accurately determine the amount of refractive error, particularly in children
An automated refractor
is an instrument that is sometimes used in place of retinoscopy
to objectively estimate a person's refractive error.
Vision defects caused by refractive error can be distinguished from other problems using a pinhole occluder
, which will improve vision only in the case of refractive error.
, contact lenses, refractive surgery
, or a combination of the three are typically used.
In the case of myopia, however, some believe that such treatments may also have the long-term effect of exacerbating that refractive error — i.e., making the patient even more nearsighted. This would be due to the very same prescription that is tailored for use at a 12-to-20-foot distance also commonly being used for close-up work as well, thus artificially amplifying the focusing stress that would normally be presented to the accommodation mechanisms of the eye at that distance.
However, this exacerbating effect is not generally believed to exist in the general case, although in cases where the myopia is due to accommodative spasm, removing the corrective lenses for a time may lead to improvement.
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by...
ing of light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
by the eye
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
and a frequent reason for reduced visual acuity
Visual acuity
Visual acuity is acuteness or clearness of vision, which is dependent on the sharpness of the retinal focus within the eye and the sensitivity of the interpretative faculty of the brain....
.
Classification
An eye that has no refractive error when viewing distant objects is said to have emmetropia or be emmetropic. The eye can focus parallel rays of light (light from distant objects) on the retina, without using any accommodation. A distant object in this case is defined as an object 6 meters or further away from the eye.An eye that has refractive error when viewing distant objects is said to have ametropia or be ametropic. This eye, when not using accommodation, cannot focus parallel rays of light (light from distant objects) on the retina.
The word "ametropia" can be used interchangeably with "refractive error" as they refer to the same thing. Types of ametropia include myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism. They are frequently categorized as spherical errors and cylindrical errors:
- Spherical errors occur when the optical powerOptical powerOptical power is the degree to which a lens, mirror, or other optical system converges or diverges light. It is equal to the reciprocal of the focal length of the device. The dioptre is the most common unit of measurement of optical power...
of the eye is either too large or too small to focus light on the retinaRetinaThe vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
. People with refraction error frequently have blurry vision.- MyopiaMyopiaMyopia , "shortsightedness" ) is a refractive defect of the eye in which collimated light produces image focus in front of the retina under conditions of accommodation. In simpler terms, myopia is a condition of the eye where the light that comes in does not directly focus on the retina but in...
: When the optics are too powerful for the length of the eyeball one has myopiaMyopiaMyopia , "shortsightedness" ) is a refractive defect of the eye in which collimated light produces image focus in front of the retina under conditions of accommodation. In simpler terms, myopia is a condition of the eye where the light that comes in does not directly focus on the retina but in...
or nearsightedness. This can arise from a corneaCorneaThe cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Together with the lens, the cornea refracts light, with the cornea accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is...
with too much curvature (refractive myopia) or an eyeball that is too long (axial myopia). - HyperopiaHyperopiaHyperopia, also known as farsightedness, longsightedness or hypermetropia, is a defect of vision caused by an imperfection in the eye , causing difficulty focusing on near objects, and in extreme cases causing a sufferer to be unable to focus on objects at any distance...
: When the optics are too weak for the length of the eyeball, one has hyperopiaHyperopiaHyperopia, also known as farsightedness, longsightedness or hypermetropia, is a defect of vision caused by an imperfection in the eye , causing difficulty focusing on near objects, and in extreme cases causing a sufferer to be unable to focus on objects at any distance...
or farsightedness. This can arise from a cornea with not enough curvature (refractive hyperopia) or an eyeball that is too short (axial hyperopia).
- Myopia
- Cylindrical errors occur when the optical power of the eye is too powerful or too weak across one meridian. It is as if the overall lens tends towards a cylindrical shape along that meridian. The angle along which the cylinder is placed is known as the axis of the cylinder, while 90 degrees away from the axis is known as the meridian of the cylinder.
- AstigmatismAstigmatism (eye)Astigmatism is an optical defect in which vision is blurred due to the inability of the optics of the eye to focus a point object into a sharp focused image on the retina. This may be due to an irregular or toric curvature of the cornea or lens. There are two types of astigmatism: regular and...
: People with a simple astigmatic refractive error see contours of a particular orientation as blurred, but see contours with orientations at right angles as clear. When one has a cylindrical error, one has astigmatismAstigmatism (eye)Astigmatism is an optical defect in which vision is blurred due to the inability of the optics of the eye to focus a point object into a sharp focused image on the retina. This may be due to an irregular or toric curvature of the cornea or lens. There are two types of astigmatism: regular and...
.
- Astigmatism
Diagnosis

Eye care professional
An eye care professional is an individual who provides a service related to the eyes or vision. It is a general term that can refer to any healthcare worker involved in eye care, from one with a small amount of post-secondary training to practitioners with a doctoral level of education.-Current...
during an eye examination
Eye examination
An eye examination is a battery of tests performed by an ophthalmologist, optometrist, or orthoptist assessing vision and ability to focus on and discern objects, as well as other tests and examinations pertaining to the eyes....
using an instrument called a phoropter
Phoropter
A phoropter is an instrument commonly used by eye care professionals during an eye examination, containing different lenses used for refraction of the eye during sight testing, to measure an individual's refractive error and determine his or her eyeglass prescription.Typically, the patient sits...
which contains a large number of lenses of varying optical power. In combination with a retinoscope (a procedure entitled retinoscopy
Retinoscopy
Retinoscopy is a technique to obtain an objective measurement of the refractive error of a patient's eyes. The examiner uses a retinoscope to shine light into the patient's eye and observes the reflection off the patient's retina...
), the doctor instructs the patient to view an eye chart
Eye chart
An eye chart is a chart used to measure visual acuity. Types of eye charts include the logMAR chart, Snellen chart, Landolt C, and the Lea test.-Procedure:Charts usually display several rows of optotypes , each row in a different size...
while he or she changes the lenses within the phoropter to objectively estimate the amount of refractive error the patient may possess. Once the doctor arrives at an estimate, he or she typically shows the patient lenses of progressively higher or weaker powers in a process known as refraction
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
or refractometry
Refractometry
Refractometry is the method of measuring substances' refractive index in order to, for example, assess their composition or purity. A refractometer is the instrument used to measure refractive index...
.
Cycloplegic agents are frequently used to more accurately determine the amount of refractive error, particularly in children
An automated refractor
Automated refractor
An autorefractor or automated refractor is a computer-controlled machine used during an eye examination to provide an objective measurement of a person's refractive error and prescription for glasses or contact lenses. This is achieved by measuring how light is changed as it enters a person's...
is an instrument that is sometimes used in place of retinoscopy
Retinoscopy
Retinoscopy is a technique to obtain an objective measurement of the refractive error of a patient's eyes. The examiner uses a retinoscope to shine light into the patient's eye and observes the reflection off the patient's retina...
to objectively estimate a person's refractive error.
Vision defects caused by refractive error can be distinguished from other problems using a pinhole occluder
Pinhole occluder
A pinhole occluder is an opaque disk with one or more small holes through it, used by ophthalmologists and optometrists to test visual acuity. The occluder is a simple way to focus light, as in a pinhole camera, temporarily removing the effects of refractive errors such as myopia...
, which will improve vision only in the case of refractive error.
Management
How refractive errors are treated or managed depends upon the amount and severity of the condition. Those who possess mild amounts of refractive error may elect to leave the condition uncorrected, particular if the patient is asymptomatic. For those who are symptomatic, glassesGlasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses , spectacles or simply specs , are frames bearing lenses worn in front of the eyes. They are normally used for vision correction or eye protection. Safety glasses are a kind of eye protection against flying debris or against visible and near visible light or...
, contact lenses, refractive surgery
Refractive surgery
Refractive eye surgery is any eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This can include various methods of surgical remodeling of the cornea or cataract surgery. The most common methods today use excimer lasers to...
, or a combination of the three are typically used.
In the case of myopia, however, some believe that such treatments may also have the long-term effect of exacerbating that refractive error — i.e., making the patient even more nearsighted. This would be due to the very same prescription that is tailored for use at a 12-to-20-foot distance also commonly being used for close-up work as well, thus artificially amplifying the focusing stress that would normally be presented to the accommodation mechanisms of the eye at that distance.
However, this exacerbating effect is not generally believed to exist in the general case, although in cases where the myopia is due to accommodative spasm, removing the corrective lenses for a time may lead to improvement.

