Region Connection Calculus
Encyclopedia
The region connection calculus (RCC) serves for qualitative spatial representation and reasoning
. RCC abstractly describes regions (in Euclidean space
, or in a topological space
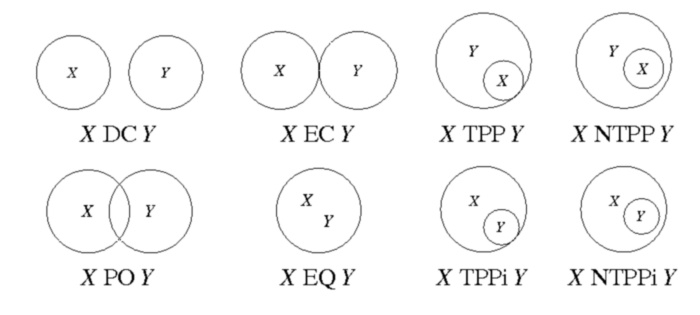
) by their possible relations to each other. RCC8 consists of 8 basic relations that are possible between two regions:
From these basic relations, combinations can be built. For example, proper part (PP) is the union of TPP and NTPP.
The spatial configuration can be formalized in RCC8 as the following constraint network:
house1 DC house2
house1 {TPP, NTPP} property1
house1 {DC, EC} property2
house1 EC road
house2 { DC, EC } property1
house2 NTPP property2
house2 EC road
property1 { DC, EC } property2
road { DC, EC, TPP, TPPi, PO, EQ, NTPP, NTPPi } property1
road { DC, EC, TPP, TPPi, PO, EQ, NTPP, NTPPi } property2
Using the RCC8 composition table and the path-consistency algorithm, we can refine the network in the following way:
road { PO, EC } property1
road { PO, TPP } property2
That is, the road either overlaps with the second property, or is even (tangential) part of it.
Other versions of the region connection calculus include RCC5 (with only five basic relations - the distinction whether two regions touch each other are ignored) and RCC23 (which allows reasoning about convexity)..
Spatial-temporal reasoning
Spatial–temporal reasoning is used in both the fields of psychology and computer science.-Spatial–temporal reasoning in psychology:Spatial-temporal reasoning is the ability to visualize spatial patterns and mentally manipulate them over a time-ordered sequence of spatial transformations.This...
. RCC abstractly describes regions (in Euclidean space
Euclidean space
In mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
, or in a topological space
Topological space
Topological spaces are mathematical structures that allow the formal definition of concepts such as convergence, connectedness, and continuity. They appear in virtually every branch of modern mathematics and are a central unifying notion...
) by their possible relations to each other. RCC8 consists of 8 basic relations that are possible between two regions:
- disconnected (DC)
- externally connected (EC)
- equal (EQ)
- partially overlapping (PO)
- tangential proper part (TPP)
- tangential proper part inverse (TPPi)
- non-tangential proper part (NTPP)
- non-tangential proper part inverse (NTPPi)
From these basic relations, combinations can be built. For example, proper part (PP) is the union of TPP and NTPP.

Composition table
The composition table of RCC8 are as follows:| o | DC | EC | PO | TPP | NTPP | TPPi | NTPPi | EQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC | * | DC,EC,PO,TPP,NTPP | DC,EC,PO,TPP,NTPP | DC,EC,PO,TPP,NTPP | DC,EC,PO,TPP,NTPP | DC | DC | DC |
| EC | DC,EC,PO,TPPi,NTPPi | DC,EC,PO,TPP,TPPi,EQ | DC,EC,PO,TPP,NTPP | EC,PO,TPP,NTPP | PO,TPP,NTPP | DC,EC | DC | EC |
| PO | DC,EC,PO,TPPi,NTPPi | DC,EC,PO,TPPi,NTPPi | * | PO,TPP,NTPP | PO,TPP,NTPP | DC,EC,PO,TPPi,NTPPi | DC,EC,PO,TPPi,NTPPi | PO |
| TPP | DC | DC,EC | DC,EC,PO,TPP,NTPP | TPP,NTPP | NTPP | DC,EC,PO,TPP,TPPi,EQ | DC,EC,PO,TPPi,NTPPi | TPP |
| NTPP | DC | DC | DC,EC,PO,TPP,NTPP | NTPP | NTPP | DC,EC,PO,TPP,NTPP | * | NTPP |
| TPPi | DC,EC,PO,TPPi,NTPPi | EC,PO,TPPi,NTPPi | PO,TPPi,NTPPi | PO,TPP,TPPi,EQ | PO,TPP,NTPP | TPPi,NTPPi | NTPPi | TPPi |
| NTPPi | DC,EC,PO,TPPi,NTPPi | PO,TPPi,NTPPi | PO,TPPi,NTPPi | PO,TPPi,NTPPi | PO,TPP,NTPP,TPPi,NTPPi,EQ | NTPPi | NTPPi | NTPPi |
| EQ | DC | EC | PO | TPP | NTPP | TPPi | NTPPi | EQ |
- "*" denotes the universal relation.
Examples
The RCC8 calculus can be used for reasoning about spatial configurations. Consider the following example: two houses are connected via a road. Each house is located on an own property. The first house possibly touches the boundary of the property; the second one surely does not. What can we infer about the relation of the second property to the road?The spatial configuration can be formalized in RCC8 as the following constraint network:
house1 DC house2
house1 {TPP, NTPP} property1
house1 {DC, EC} property2
house1 EC road
house2 { DC, EC } property1
house2 NTPP property2
house2 EC road
property1 { DC, EC } property2
road { DC, EC, TPP, TPPi, PO, EQ, NTPP, NTPPi } property1
road { DC, EC, TPP, TPPi, PO, EQ, NTPP, NTPPi } property2
Using the RCC8 composition table and the path-consistency algorithm, we can refine the network in the following way:
road { PO, EC } property1
road { PO, TPP } property2
That is, the road either overlaps with the second property, or is even (tangential) part of it.
Other versions of the region connection calculus include RCC5 (with only five basic relations - the distinction whether two regions touch each other are ignored) and RCC23 (which allows reasoning about convexity)..

