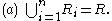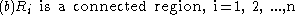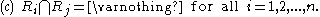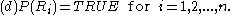Region growing
Encyclopedia
Region growing is a simple region-based image segmentation method. It is also classified as a pixel-based image segmentation method since it involves the selection of initial seed points.
This approach to segmentation examines neighboring pixels of initial “seed points” and determines whether the pixel neighbors should be added to the region. The process is iterated on, in the same manner as general data clustering
algorithms. A general discussion of the region growing algorithm is described below.
" achieve this goal by looking for the boundaries between regions based on discontinuities in gray levels or color
properties. Region-based segmentation is a technique for determining the region directly. The basic formulation for Region-Based Segmentation is:
(a) means that the segmentation must be complete; that is, every pixel must be in a region.
(b) requires that points in a region must be connected in some predefined sense.
(c) indicates that the regions must be disjoint.
(d) deals with the properties that must be satisfied by the pixels in a segmented region. For example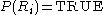 if all pixels in
if all pixels in  have the same gray level.
have the same gray level.
(e) indicates that region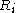 and
and  are different in the sense of predicate
are different in the sense of predicate 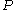 .
.
The regions are then grown from these seed points to adjacent points depending on a region membership criterion. The criterion could be, for example, pixel intensity, gray level texture, or color.
Since the regions are grown on the basis of the criterion, the image information itself is important. For example, if the criterion were a pixel intensity threshold value, knowledge of the histogram
of the image would be of use, as one could use it to determine a suitable threshold value for the region membership criterion.
There is a very simple example followed below.
Here we use 4-connected neighborhood to grow from the seed points. We can also choose 8-connected neighborhood for our pixels adjacent relationship. And the criteria we make here is the same pixel value. That is, we keep examining the adjacent pixels of seed points. If they have the same intensity value with the seed points, we classify them into the seed points. It is an iterated process until there are no change in two successive iterative stages. Of course, we can make other criteria, but the main goal is to classify the similarity of the image into regions.



 Then we can conclude several important issues about region growing:
Then we can conclude several important issues about region growing:
1.The suitable selection of seed points is important.
The selection of seed points is depending on the users. For example, in a gray-level lightning image, we may want to segment the lightning from the background. Then probably, we can examine the histogram
and choose the seed points from the highest range of it.
2.More information of the image is better.
Obviously, the connectivity or pixel adjacent information is helpful for us to determine the threshold and seed points.
3.The value, “minimum area threshold”.
No region in region growing method result will be smaller than this threshold in the segmented image.
4.The value, “Similarity threshold value“.
If the difference of pixel-value or the difference value of average gray level of a set of pixels less than “Similarity threshold value”, the regions will be considered as a same region.
The criteria of similarities or so called homogeneity we choose are also important. It usually depends on the original image and the segmentation result we want.
Here are some criteria we often use:Gray level(average intensity or variance), color
, and texture or shape.
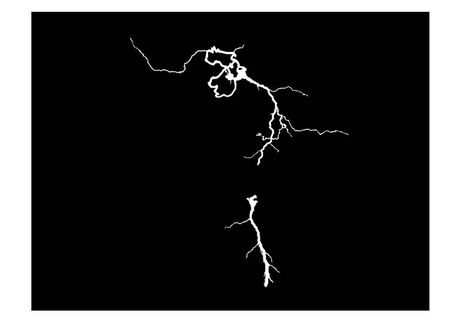
Figure. 1 is the original image which is a gray-scale lightning image. The gray-scale value of this image is from 0 to 255.
The purpose we apply region growing on this image is that we want to mark the strongest lightning part of the image and we also want the result is connected without being split apart. Therefore, we choose the points having the highest gray-scale value which is 255 as the seed points showed in the Figure. 2.
After determining the seed points, we have to determine the range of threshold. Always keeps in mind that the purpose we want to do is to mark the strongest light in the image. The third figure is the region growing result from choosing the threshold between 225 and the value of seed points (which is 255). It means we only want to mark out the points whose gray-scale values are above 225.
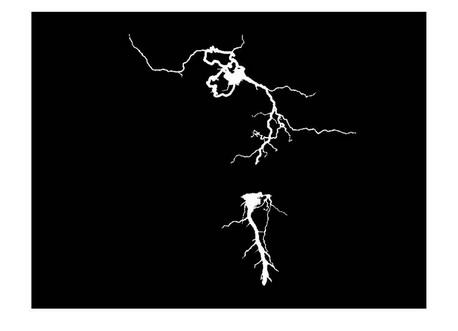
If we make the range of threshold wider, we will get a result having a bigger area of the lightning region show as the Figure. 3 and the Figure. 4.
We can observe the difference between the last two figures which have different threshold value showed above. Region growing provides the ability for us to separate the part we want connected.
As we can see in Figure. 3 to Figure. 5, the segmented result in this example are seed-oriented connected.
That means the result grew from the same seed points are the same regions. And the points will not be grown without connected with the seed points in the beginning.
Therefore, we can mention that there are still lots of points in the original image having the gray-scale value above 155 which are not marked in Figure. 5.
This characteristic ensures the reliability of the segmentation and provides the ability to resist noise. For this example, this characteristic prevents us marking out the non-lightning part in the image because the lightning is always connected as one part.
Advantages:
1. Region growing methods can correctly separate the regions that have the same properties we define.
2. Region growing methods can provide the original images which have clear edges the good segmentation results.
3. The concept is simple. We only need a small numbers of seed point to represent the property we want, then grow the region.
4. We can determine the seed points and the criteria we want to make.
5. We can choose the multiple criteria at the same time.
6. It performs well with respect to noise.
Disadvantage:
1. The computation is consuming, no matter the time or power.
2. Noise or variation of intensity may result in holes or oversegmentation.
3. This method may not distinguish the shading of the real images.
We can conquer the noise problem easily by using some mask to filter the holes or outlier. Therefore, the problem of noise actually does not exist. In conclusion, it is obvious that the most serious problem of region growing is the power and time consuming.
This approach to segmentation examines neighboring pixels of initial “seed points” and determines whether the pixel neighbors should be added to the region. The process is iterated on, in the same manner as general data clustering
Data clustering
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of assigning a set of objects into groups so that the objects in the same cluster are more similar to each other than to those in other clusters....
algorithms. A general discussion of the region growing algorithm is described below.
Region-based segmentation
The main goal of segmentation is to partition an image into regions. Some segmentation methods such as "ThresholdingThresholding (image processing)
Thresholding is the simplest method of image segmentation. From a grayscale image, thresholding can be used to create binary images Thresholding is the simplest method of image segmentation. From a grayscale image, thresholding can be used to create binary images Thresholding is the simplest method...
" achieve this goal by looking for the boundaries between regions based on discontinuities in gray levels or color
Color
Color or colour is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue and others. Color derives from the spectrum of light interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors...
properties. Region-based segmentation is a technique for determining the region directly. The basic formulation for Region-Based Segmentation is:
-
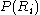 is a logical predicate defined over the points in set
is a logical predicate defined over the points in set 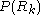 and
and 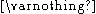 is the null set.
is the null set.
(a) means that the segmentation must be complete; that is, every pixel must be in a region.
(b) requires that points in a region must be connected in some predefined sense.
(c) indicates that the regions must be disjoint.
(d) deals with the properties that must be satisfied by the pixels in a segmented region. For example
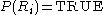 if all pixels in
if all pixels in  have the same gray level.
have the same gray level.(e) indicates that region
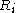 and
and  are different in the sense of predicate
are different in the sense of predicate 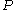 .
.Basic concept of seedpoints
The first step in region growing is to select a set of seed points. Seed point selection is based on some user criterion (for example, pixels in a certain gray-level range, pixels evenly spaced on a grid, etc.). The initial region begins as the exact location of these seeds.The regions are then grown from these seed points to adjacent points depending on a region membership criterion. The criterion could be, for example, pixel intensity, gray level texture, or color.
Since the regions are grown on the basis of the criterion, the image information itself is important. For example, if the criterion were a pixel intensity threshold value, knowledge of the histogram
Histogram
In statistics, a histogram is a graphical representation showing a visual impression of the distribution of data. It is an estimate of the probability distribution of a continuous variable and was first introduced by Karl Pearson...
of the image would be of use, as one could use it to determine a suitable threshold value for the region membership criterion.
There is a very simple example followed below.
Here we use 4-connected neighborhood to grow from the seed points. We can also choose 8-connected neighborhood for our pixels adjacent relationship. And the criteria we make here is the same pixel value. That is, we keep examining the adjacent pixels of seed points. If they have the same intensity value with the seed points, we classify them into the seed points. It is an iterated process until there are no change in two successive iterative stages. Of course, we can make other criteria, but the main goal is to classify the similarity of the image into regions.
Some important issues






1.The suitable selection of seed points is important.
The selection of seed points is depending on the users. For example, in a gray-level lightning image, we may want to segment the lightning from the background. Then probably, we can examine the histogram
Histogram
In statistics, a histogram is a graphical representation showing a visual impression of the distribution of data. It is an estimate of the probability distribution of a continuous variable and was first introduced by Karl Pearson...
and choose the seed points from the highest range of it.
2.More information of the image is better.
Obviously, the connectivity or pixel adjacent information is helpful for us to determine the threshold and seed points.
3.The value, “minimum area threshold”.
No region in region growing method result will be smaller than this threshold in the segmented image.
4.The value, “Similarity threshold value“.
If the difference of pixel-value or the difference value of average gray level of a set of pixels less than “Similarity threshold value”, the regions will be considered as a same region.
The criteria of similarities or so called homogeneity we choose are also important. It usually depends on the original image and the segmentation result we want.
Here are some criteria we often use:Gray level(average intensity or variance), color
Color
Color or colour is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue and others. Color derives from the spectrum of light interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors...
, and texture or shape.
Simulation examples
Here we show a simple example for region growing.Figure. 1 is the original image which is a gray-scale lightning image. The gray-scale value of this image is from 0 to 255.
The purpose we apply region growing on this image is that we want to mark the strongest lightning part of the image and we also want the result is connected without being split apart. Therefore, we choose the points having the highest gray-scale value which is 255 as the seed points showed in the Figure. 2.
After determining the seed points, we have to determine the range of threshold. Always keeps in mind that the purpose we want to do is to mark the strongest light in the image. The third figure is the region growing result from choosing the threshold between 225 and the value of seed points (which is 255). It means we only want to mark out the points whose gray-scale values are above 225.
If we make the range of threshold wider, we will get a result having a bigger area of the lightning region show as the Figure. 3 and the Figure. 4.
We can observe the difference between the last two figures which have different threshold value showed above. Region growing provides the ability for us to separate the part we want connected.
As we can see in Figure. 3 to Figure. 5, the segmented result in this example are seed-oriented connected.
That means the result grew from the same seed points are the same regions. And the points will not be grown without connected with the seed points in the beginning.
Therefore, we can mention that there are still lots of points in the original image having the gray-scale value above 155 which are not marked in Figure. 5.
This characteristic ensures the reliability of the segmentation and provides the ability to resist noise. For this example, this characteristic prevents us marking out the non-lightning part in the image because the lightning is always connected as one part.
The advantages and disadvantages of region growing
We briefly conclude the advantages and disadvantages of region growing.Advantages:
1. Region growing methods can correctly separate the regions that have the same properties we define.
2. Region growing methods can provide the original images which have clear edges the good segmentation results.
3. The concept is simple. We only need a small numbers of seed point to represent the property we want, then grow the region.
4. We can determine the seed points and the criteria we want to make.
5. We can choose the multiple criteria at the same time.
6. It performs well with respect to noise.
Disadvantage:
1. The computation is consuming, no matter the time or power.
2. Noise or variation of intensity may result in holes or oversegmentation.
3. This method may not distinguish the shading of the real images.
We can conquer the noise problem easily by using some mask to filter the holes or outlier. Therefore, the problem of noise actually does not exist. In conclusion, it is obvious that the most serious problem of region growing is the power and time consuming.
See also
- image segmentation
- data clusteringData clusteringCluster analysis or clustering is the task of assigning a set of objects into groups so that the objects in the same cluster are more similar to each other than to those in other clusters....
- k-means algorithm
- watershed (algorithm)Watershed (algorithm)A grey-level image may be seen as a topographic relief, where the grey level of a pixel is interpreted as its altitude in the relief.A drop of water falling on a topographic relief flows along a path to finally reach a local minimum...