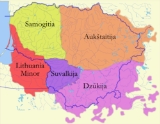
Regions of Lithuania
Encyclopedia
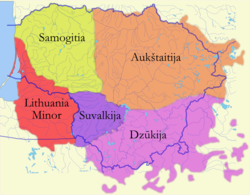
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
can be divided into historical and cultural regions (called ethnographic regions). The exact borders are not fully clear, as the regions are not official political or administrative units. They are delimited by culture, such as country traditions, traditional lifestyle, songs, tales, etc. To some extent regions correspond to the zones of Lithuanian language dialects
Lithuanian language
Lithuanian is the official state language of Lithuania and is recognized as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.96 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 170,000 abroad. Lithuanian is a Baltic language, closely related to Latvian, although they...
. This correspondence however is by no means strict. For example, although the Dzūkian dialect is called South Aukštaitian, it does not mean that Dzūkija
Dzukija
Dzūkija or Dainava is one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. Dzūkija is a cultural region defined by traditional lifestyles and dialects of the local Lithuanian population and has never been defined as a political or administrative unit...
is part of Aukštaitija
Aukštaitija
Aukštaitija is the name of one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. The name comes from the relatively high elevation of the region, particularly the eastern parts.-Geography:...
. In certain parts of some regions, dialects of other regions are spoken, while for example in Samogitia, there are three indigenous dialects (southern, northern and western Samogitian
Samogitian language
Samogitian is a dialect of the Lithuanian language spoken mostly in Samogitia . Attempts have been made to standardize it...
), some of which are subdivided into subdialects.
Regions in politics
No region, except for SamogitiaSamogitia
Samogitia is one of the five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. It is located in northwestern Lithuania. Its largest city is Šiauliai/Šiaulē. The region has a long and distinct cultural history, reflected in the existence of the Samogitian dialect...
, has ever been a political or an administrative entity. However some work was done recently to delimit their boundaries more clearly, as there is a project to change the system of counties
Counties of Lithuania
The territory of Lithuania is divided into 10 counties , all named after their capitals. The counties are divided into 60 municipalities : 9 city municipalities, 43 district municipalities and 8 municipalities...
in Lithuania into ethnographic regions, which would be called lands (singular - žemė, plural - žemės). This project is also supported by the fact that with the limited functions of counties, 10 of them are not needed for Lithuania. Another supporting argument is that in other countries historical territories are being revived, while in Lithuania artificially made counties exist. The project was supported by the former president Rolandas Paksas
Rolandas Paksas
Rolandas Paksas is a Lithuanian politician who was President of Lithuania from 2003 to 2004. He was previously Prime Minister of Lithuania in 1999 and again from 2000 to 2001, and he also served as Mayor of Vilnius from 1997 to 1999 and again from 2000 to 2001...
, yet now it is not clear when or if the project will be completed at all. However, Dzūkija
Dzukija
Dzūkija or Dainava is one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. Dzūkija is a cultural region defined by traditional lifestyles and dialects of the local Lithuanian population and has never been defined as a political or administrative unit...
quite recently adopted the coat of arms and emblem which would be used in case the reform were to be implemented. Alytus County
Alytus County
Alytus County is one of ten counties in Lithuania. It is the southernmost county, and its capital is the city of Alytus. Its territory lies within the ethnographic region of Dzūkija...
, which lies almost entirely within Dzūkija, adopted soon thereafter a coat of arms that is based on the Dzūkija coat of arms. Samogitia
Samogitia
Samogitia is one of the five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. It is located in northwestern Lithuania. Its largest city is Šiauliai/Šiaulē. The region has a long and distinct cultural history, reflected in the existence of the Samogitian dialect...
has a flag and a coat of arms dating from the time of the Duchy of Samogitia; these symbols are considerably older than the flag of Lithuania
Flag of Lithuania
The flag of Lithuania consists of a horizontal tricolor of yellow, green and red. It was adopted on March 20, 1989, almost two years before the reestablishment of Lithuania's independence following the end of the Soviet Union. Before its readoption, the flag had been used from 1918 until 1940 when...
. Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor
Lithuania Minor or Prussian Lithuania is a historical ethnographic region of Prussia, later East Prussia in Germany, where Prussian Lithuanians or Lietuvininkai lived. Lithuania Minor enclosed the northern part of this province and got its name due to the territory's substantial...
has a flag used since the 17th century, and an anthem originating from the 19th century. However, if the reform were to be implemented, most likely there would be just 4 lands, not 5, because most of Lithuania minor is occupied by Russia and many Lithuanians were expelled from there. The relatively small remaining part is also populated mostly by relative newcomers, as much of the local population died in the Second World War or was expelled. Therefore Lithuania minor would probably be attached to Samogitia
Samogitia
Samogitia is one of the five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. It is located in northwestern Lithuania. Its largest city is Šiauliai/Šiaulē. The region has a long and distinct cultural history, reflected in the existence of the Samogitian dialect...
.
Despite the fact that the regions are not political/administrative entities, most regions have their "capitals" (cities which are commonly considered to be capitals). These cities are not necessarily the largest in the region.
List of regions
- AukštaitijaAukštaitijaAukštaitija is the name of one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. The name comes from the relatively high elevation of the region, particularly the eastern parts.-Geography:...
(Literally Highlands). Region in northeastern Lithuania, also includes some historical Lithuanian territories of southwestern LatviaLatviaLatvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
and northwestern BelarusBelarusBelarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
. Capital PanevėžysPanevežysPanevėžys see also other names, is the fifth largest city in Lithuania. As of 2008, it occupied 50 square kilometers with 113,653 inhabitants. The largest multifunctional arena in Panevėžys is the Cido Arena...
, it is also largest city of region. - SamogitiaSamogitiaSamogitia is one of the five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. It is located in northwestern Lithuania. Its largest city is Šiauliai/Šiaulē. The region has a long and distinct cultural history, reflected in the existence of the Samogitian dialect...
, (Žemaitija, literally Lowlands). Region in western Lithuania. Capital is TelšiaiTelšiaiTelšiai , is a city in Lithuania with about 35,000 inhabitants. It is the capital of Telšiai County and Samogitia region, and it is located on Lake Mastis.-Names:...
, largest city is ŠiauliaiŠiauliaiŠiauliai , is the fourth largest city in Lithuania, with a population of 133,900. It is the capital of Šiauliai County. Unofficially, the city is the capital of Northern Lithuania.-Names:...
. - DzūkijaDzukijaDzūkija or Dainava is one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. Dzūkija is a cultural region defined by traditional lifestyles and dialects of the local Lithuanian population and has never been defined as a political or administrative unit...
(Dzūkija or Dainava (the latter name literally means "Land of songs")). Region in the southeast of Lithuania, also includes vast historically Lithuanian territories of BelarusBelarusBelarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
, and some territories of PolandPolandPoland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
. Capital is AlytusAlytusAlytus is a city with municipal rights in southern Lithuania. It is the capital of Alytus County. Its population in 2007 was 68,835. Alytus is the historical centre of the Dzūkija region. The city lies on the banks of the Nemunas River. The major highways linking Vilnius, Kaunas, Lazdijai, and...
, largest city is VilniusVilniusVilnius is the capital of Lithuania, and its largest city, with a population of 560,190 as of 2010. It is the seat of the Vilnius city municipality and of the Vilnius district municipality. It is also the capital of Vilnius County...
. - SuvalkijaSuvalkijaSuvalkija or Sudovia is the smallest of the five cultural regions of Lithuania. Its unofficial capital is Marijampolė. People from Suvalkija are called suvalkiečiai or suvalkietis . It is located south of the Neman River, in the former territory of Vilkaviškis bishopric...
(Sūduva or Suvalkija). Region in the southwest of Lithuania, the smallest ethnographic region. Capital is MarijampolėMarijampoleMarijampolė is an industrial city and the capital of the Marijampolė County in the south of Lithuania, bordering Poland and Russian Kaliningrad oblast, and Lake Vištytis. The population of Marijampolė is 48,700...
, largest city - KaunasKaunasKaunas is the second-largest city in Lithuania and has historically been a leading centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the biggest city and the center of a powiat in Trakai Voivodeship of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania since 1413. During Russian Empire occupation...
. - Lithuania MinorLithuania MinorLithuania Minor or Prussian Lithuania is a historical ethnographic region of Prussia, later East Prussia in Germany, where Prussian Lithuanians or Lietuvininkai lived. Lithuania Minor enclosed the northern part of this province and got its name due to the territory's substantial...
(Mažoji Lietuva). Region at the Baltic sea coast, also includes territories with large historical Lithuanian population of what is now Kaliningrad OblastKaliningrad OblastKaliningrad Oblast is a federal subject of Russia situated on the Baltic coast. It has a population of The oblast forms the westernmost part of the Russian Federation, but it has no land connection to the rest of Russia. Since its creation it has been an exclave of the Russian SFSR and then the...
and a bit of northern PolandPolandPoland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
. Largest city is KlaipėdaKlaipedaKlaipėda is a city in Lithuania situated at the mouth of the Nemunas River where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It is the third largest city in Lithuania and the capital of Klaipėda County....
.
See also
- Counties of LithuaniaCounties of LithuaniaThe territory of Lithuania is divided into 10 counties , all named after their capitals. The counties are divided into 60 municipalities : 9 city municipalities, 43 district municipalities and 8 municipalities...
- Ethnographic LithuaniaEthnographic LithuaniaEthnographic Lithuania was an early 20th century concept that defined Lithuanian territories as significant part of the territories that belonged to Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Lithuanians as all people living on them, regardless of whether those people spoke Lithuanian language and considered...
- Geography of LithuaniaGeography of LithuaniaThe largest and most populous of the Baltic states, Lithuania has of sandy coastline which faces the open Baltic Sea, between Latvia and Russia. Lithuania's major warm-water port of Klaipėda lies at the narrow mouth of Curonian Lagoon, a shallow lagoon extending south to Kaliningrad and separated...
- Historical regions of Central EuropeHistorical regions of Central EuropeThere are many historical regions of Central Europe. For the purpose of this list, Central Europe is defined as the area contained roughly within the south coast of the Baltic Sea, the Elbe River, the Alps, the Danube River, the Black Sea and the Dnepr River. Note that these regions come from...

