
Relay channel
Encyclopedia
In information theory
, a relay channel
is a probability
model of the communication
between a sender
and a receiver aided by one or more intermediate relay nodes. It is a combination of the broadcast channel (from sender to relays and receiver) and multiple access channel (from sender and relays to receiver).
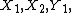 and
and 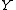 , and a conditional probability distribution
, and a conditional probability distribution 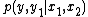 on these sets. The probability distribution of the choice of symbols selected by the encoder and the relay encoder is represented by
on these sets. The probability distribution of the choice of symbols selected by the encoder and the relay encoder is represented by 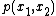 .
.
There exist three main relaying schemes: Decode-and-Forward, Compress-and-Forward and Amplify-and-Forward. The first two schemes were first proposed in the pioneer article by Cover and El-Gamal.
of the relay channel is derived in the pioneer article by Cover and El-Gamal and is known as the Cut-set upper bound. This bound says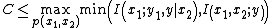 where C is the capacity of the relay channel. The first term and second term in the minimization above are called broadcast bound and multi-access bound, respectively.
where C is the capacity of the relay channel. The first term and second term in the minimization above are called broadcast bound and multi-access bound, respectively.
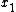 only through
only through 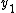 and
and 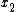 , i.e.,
, i.e., 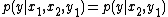 . In the article by Cover and El-Gamal it is shown that the capacity of the degraded relay channel can be achieved using Decode-and-Forward scheme. It turns out that the capacity in this case is equal to the Cut-set upper bound.
. In the article by Cover and El-Gamal it is shown that the capacity of the degraded relay channel can be achieved using Decode-and-Forward scheme. It turns out that the capacity in this case is equal to the Cut-set upper bound.
 . Cover and El-Gamal proved that the Direct Transmission Lower Bound (wherein relay is not used) is tight when the relay channel is reversely degraded.
. Cover and El-Gamal proved that the Direct Transmission Lower Bound (wherein relay is not used) is tight when the relay channel is reversely degraded.
Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
, a relay channel
Channel (communications)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
is a probability
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
model of the communication
Communication
Communication is the activity of conveying meaningful information. Communication requires a sender, a message, and an intended recipient, although the receiver need not be present or aware of the sender's intent to communicate at the time of communication; thus communication can occur across vast...
between a sender
Communication source
A source or sender is one of the basic concepts of communication and information processing. Sources are objects which encode message data and transmit the information, via a channel, to one or more observers ....
and a receiver aided by one or more intermediate relay nodes. It is a combination of the broadcast channel (from sender to relays and receiver) and multiple access channel (from sender and relays to receiver).
General discrete-time memoryless relay channel
A discrete memoryless single-relay channel can be modelled as four finite sets,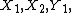 and
and 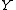 , and a conditional probability distribution
, and a conditional probability distribution 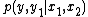 on these sets. The probability distribution of the choice of symbols selected by the encoder and the relay encoder is represented by
on these sets. The probability distribution of the choice of symbols selected by the encoder and the relay encoder is represented by 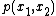 .
.
o------------------o
| Relay Encoder |
o------------------o
A |
| y1 x2 |
| V
o---------o x1 o------------------o y o---------o
| Encoder |--->| p(y,y1|x1,x2) |--->| Decoder |
o---------o o------------------o o---------o
There exist three main relaying schemes: Decode-and-Forward, Compress-and-Forward and Amplify-and-Forward. The first two schemes were first proposed in the pioneer article by Cover and El-Gamal.
- Decode-and-Forward (DF): In this relaying scheme, the relay decodes the source message in one block and transmits the re-encoded message in the following block. The achievable rate of DF is known as
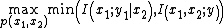 .
.
- Compress-and-Forward (CF): In this relaying scheme, the relay quantizes the received signal in one block and transmits the encoded version of the quantized received signal in the following block. The achievable rate of CF is known as
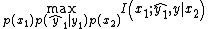 subject to
subject to 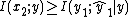 .
.
- Amplify-and-Forward (AF): In this relaying scheme, the relay sends an amplified version of the received signal in the last time-slot. Comparing with DF and CF, AF requires much less delay as the relay node operates time-slot by time-slot. Also, AF requires much less computing power as no decoding or quantizing operation is performed at the relay side.
Cut-set upper bound
The first upper bound on the capacityChannel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
of the relay channel is derived in the pioneer article by Cover and El-Gamal and is known as the Cut-set upper bound. This bound says
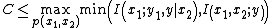 where C is the capacity of the relay channel. The first term and second term in the minimization above are called broadcast bound and multi-access bound, respectively.
where C is the capacity of the relay channel. The first term and second term in the minimization above are called broadcast bound and multi-access bound, respectively.Degraded relay channel
A relay channel is said to be degraded if y depends on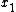 only through
only through 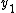 and
and 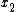 , i.e.,
, i.e., 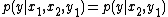 . In the article by Cover and El-Gamal it is shown that the capacity of the degraded relay channel can be achieved using Decode-and-Forward scheme. It turns out that the capacity in this case is equal to the Cut-set upper bound.
. In the article by Cover and El-Gamal it is shown that the capacity of the degraded relay channel can be achieved using Decode-and-Forward scheme. It turns out that the capacity in this case is equal to the Cut-set upper bound.Reversely degraded relay channel
A relay channel is said to be reversely degraded if . Cover and El-Gamal proved that the Direct Transmission Lower Bound (wherein relay is not used) is tight when the relay channel is reversely degraded.
. Cover and El-Gamal proved that the Direct Transmission Lower Bound (wherein relay is not used) is tight when the relay channel is reversely degraded.External links
- Many resources on the Relay Channel and Cooperative Communications are available at http://students.itsoc.org/Cooperation/

