
Resistive ballooning mode
Encyclopedia
The resistive ballooning mode (RBM) is an instability occurring in magnetized plasma
s, particularly in magnetic confinement devices such as tokamaks, when the pressure gradient is opposite to the effective gravity created by a magnetic field
.
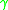 of the RBM instability is given as
of the RBM instability is given as
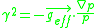
where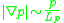 is the pressure gradient
is the pressure gradient 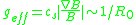 is the effective gravity produced by a non-homogeneous magnetic field, R0 is the major radius of the device, Lp is a characteristic length of the pressure gradient, and cs is the plasma sound speed.
is the effective gravity produced by a non-homogeneous magnetic field, R0 is the major radius of the device, Lp is a characteristic length of the pressure gradient, and cs is the plasma sound speed.
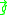 replaced by the effective gravity
replaced by the effective gravity 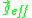 , except that for the RT instability,
, except that for the RT instability, 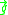 acts on the mass density
acts on the mass density 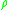 of the fluid, whereas for the RBM instability,
of the fluid, whereas for the RBM instability, 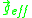 acts on the pressure
acts on the pressure 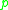 of the plasma.
of the plasma.
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
s, particularly in magnetic confinement devices such as tokamaks, when the pressure gradient is opposite to the effective gravity created by a magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
.
Linear growth rate
The linear growth rate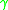 of the RBM instability is given as
of the RBM instability is given as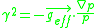
where
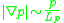 is the pressure gradient
is the pressure gradient 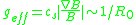 is the effective gravity produced by a non-homogeneous magnetic field, R0 is the major radius of the device, Lp is a characteristic length of the pressure gradient, and cs is the plasma sound speed.
is the effective gravity produced by a non-homogeneous magnetic field, R0 is the major radius of the device, Lp is a characteristic length of the pressure gradient, and cs is the plasma sound speed.Similarity with the Rayleigh–Taylor instability
The RBM instability is similar to the Rayleigh–Taylor instability (RT), with Earth gravity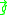 replaced by the effective gravity
replaced by the effective gravity 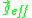 , except that for the RT instability,
, except that for the RT instability, 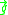 acts on the mass density
acts on the mass density 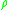 of the fluid, whereas for the RBM instability,
of the fluid, whereas for the RBM instability, 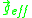 acts on the pressure
acts on the pressure 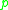 of the plasma.
of the plasma.

