
Reticulocyte index
Encyclopedia


Anemia
Anemia is a decrease in number of red blood cells or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin in the blood. However, it can include decreased oxygen-binding ability of each hemoglobin molecule due to deformity or lack in numerical development as in some other types of hemoglobin...
. This calculation is necessary because the raw reticulocyte count is misleading in anemic patients. The problem arises because the reticulocyte count is not really a count but rather a percentage: it reports the number of reticulocytes as a percentage of the number of red blood cells. In anemia, the patient's red blood cells are depleted, creating an erroneously elevated reticulocyte count.
Physiology
ReticulocyteReticulocyte
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells, typically composing about 1% of the red cells in the human body.Reticulocytes develop and mature in the red bone marrow and then circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. Like mature red blood cells,...
s are newly-produced red blood cells. They are slightly larger than totally mature red blood cells, and have some residual ribosomal RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
. The presence of RNA allows a visible blue stain to bind or, in the case of fluorescent dye, result in a different brightness. This allows them to be detected and counted as a distinct population.
The idea of the RPI is to assess whether the bone marrow
Bone marrow
Bone marrow is the flexible tissue found in the interior of bones. In humans, bone marrow in large bones produces new blood cells. On average, bone marrow constitutes 4% of the total body mass of humans; in adults weighing 65 kg , bone marrow accounts for approximately 2.6 kg...
is producing an appropriate response to an anemic state. Reticulocyte production should increase in response to any loss of red blood cells. It should increase within 2-3 days of a major acute hemorrhage, for instance, and reach its peak in 6-10 days. If reticulocyte production is not raised in response to anemia, then the anemia may be due to an acute cause with insufficient time to compensate, or there is a defect with red blood cell production in the bone marrow. Marrow defects include nutritional deficiencies (i.e. iron, folate, or B12) or insufficient erythropoietin
Erythropoietin
Erythropoietin, or its alternatives erythropoetin or erthropoyetin or EPO, is a glycoprotein hormone that controls erythropoiesis, or red blood cell production...
, the stimulus for red blood cell production. Reticulocytopenia
Reticulocytopenia
Reticulocytopenia, or "aplastic crisis", is the medical term for an abnormal decrease of reticulocytes in the body. Reticulocytopenia can originate from congenital hemolytic anemia, especially when exacerbated by Parvovirus B19 infection...
, or "aplastic crisis", is the medical term for an abnormal decrease of reticulocytes in the body
The reticulocyte percentage index may find new use as a more reliable detector of erythropoietin-doping in athletes. The use of this method is referred to as "biological passport."
Calculation
Reticulocyte Production Index is calculated as follows:1.
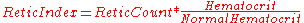
A value of 45 is usually used as a normal hematocrit.
2.The next step is to correct for the longer life span of prematurely released reticulocytes in the blood--a phenomenon of increased red blood cell production. This relies on a table:
| Hematocrit (%) | Retic survival (days) = maturation correction |
|---|---|
| 36-45 | 1.0 |
| 26-35 | 1.5 |
| 16-25 | 2.0 |
| 15 and below | 2.5 |
So, in a person whose reticulocyte count is 5%, hemoglobin 7.5 g/dL, hematocrit 25%, the RPI would be:
 → RPI
→ RPI 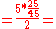 1.4
1.4Alternatively some books provide the following formula:

Interpretation
- The reticulocyte index (RI) should be between 1.0% and 2.0% for a healthy individual.
- RI < 1% with anemia indicates decreased production of reticulocytes and therefore red blood cells.
- RI > 2% with anemia indicates loss of red blood cells (destruction, bleeding, etc.) leading to increased compensatory production of reticulocytes to replace the lost red blood cells.

