
Return-to-zero
Encyclopedia
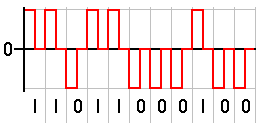
Return-to-zero (RZ) describes a line code
Line code
In telecommunication, a line code is a code chosen for use within a communications system for baseband transmission purposes...
used in telecommunication
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
s signals in which the signal drops (returns) to zero between each pulse
Pulse (signal processing)
In signal processing, the term pulse has the following meanings:#A rapid, transient change in the amplitude of a signal from a baseline value to a higher or lower value, followed by a rapid return to the baseline value....
. This takes place even if a number of consecutive 0's or 1's occur in the signal. The signal is self-clocking
Self-clocking signal
In telecommunications and electronics, a self-clocking signal is one that can be decoded without the need for a separate clock signal or other source of synchronization...
. This means that a separate clock does not need to be sent alongside the signal, but suffers from using twice the bandwidth to achieve the same data-rate as compared to non-return-to-zero
Non-return-to-zero
In telecommunication, a non-return-to-zero line code is a binary code in which 1's are represented by one significant condition and 0's are represented by some other significant condition , with no other neutral or rest condition. The pulses have more energy than a RZ code...
format.
The "zero" between each bit is a neutral or rest condition, such as a zero amplitude in pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), zero phase shift
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
in phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal ....
(PSK), or mid-frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
in frequency-shift keying
Frequency-shift keying
Frequency-shift keying is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier wave. The simplest FSK is binary FSK . BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary information. With this scheme, the "1" is called...
(FSK).
That "zero" condition is typically halfway between the significant condition representing a 1 bit and the other significant condition representing a 0 bit.
Although return-to-zero (RZ) contains a provision for synchronization, it still has a DC component resulting in “baseline wander” during long strings of 0 or 1 bits, just like the line code non-return-to-zero
Non-return-to-zero
In telecommunication, a non-return-to-zero line code is a binary code in which 1's are represented by one significant condition and 0's are represented by some other significant condition , with no other neutral or rest condition. The pulses have more energy than a RZ code...
.
Return to zero, inverted
Return-to-zero, inverted (RZI) is a method of mapping for transmission. The two-level RZI signal has a pulsePulse (signal processing)
In signal processing, the term pulse has the following meanings:#A rapid, transient change in the amplitude of a signal from a baseline value to a higher or lower value, followed by a rapid return to the baseline value....
(shorter than a clock cycle) if the binary signal is 0, and no pulse if the binary signal is 1. It is used (with a pulse 3/16 of a bit long) by the IrDA
IRDA
IRDA may refer to:* Infrared Data Association, in information and communications technology , a standard for communication between devices over short distances using infrared signals...
serial infrared (SIR) physical layer specification.
See also
Other line codes that have 3 states:- hybrid ternary codeHybrid ternary codeThe hybrid ternary line code operates on a hybrid principle that combines the binary non-return-to-zero-level and the polar return-to-zero codes and thus it is called H-ternary....
- bipolar encodingBipolar encodingIn telecommunication, bipolar encoding is a type of line code . A duobinary signal is such an encoding.- Advantages :...
- MLT-3 encodingMLT-3 encodingMLT-3 encoding is a line code that uses three voltage levels...
- 4B3T4B3T4B3T stands for 4 Binary 3 Ternary, a line encoding scheme used for ISDN BRI interface. 4B3T represents four binary bits using three pulses.It uses three states:* + ,* 0 , and* − ....

