
Rev (HIV)
Encyclopedia
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
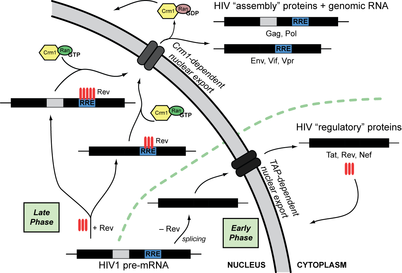
. The name rev stands for "Regulator of Virion Expression".
Function
The gene's protein product allows fragments of HIV mRNA that contain a Rev Response Element (RRE)HIV Rev response element
The HIV-1 Rev response element is a highly structured, ~350 nucleotide RNA segment present in the Env coding region of unspliced and partially spliced viral mRNAs...
to be exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.

Host (biology)
In biology, a host is an organism that harbors a parasite, or a mutual or commensal symbiont, typically providing nourishment and shelter. In botany, a host plant is one that supplies food resources and substrate for certain insects or other fauna...
RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
splicing machinery in the nucleus quickly splices the RNA so that only the smaller, regulatory proteins can be produced. In the presence of rev, RNA is exported from the nucleus before it can be spliced, so that the structural proteins and RNA genome can be produced. This mechanism allows a positive feedback loop to allow HIV to overwhelm the host's defenses, and provides time-dependent regulation of replication
Viral replication
Viral replication is the term used by virologists to describe the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. From the perspective of the virus, the purpose of viral replication is...
.

