
Rhomphaia
Encyclopedia

Thracians
The ancient Thracians were a group of Indo-European tribes inhabiting areas including Thrace in Southeastern Europe. They spoke the Thracian language – a scarcely attested branch of the Indo-European language family...
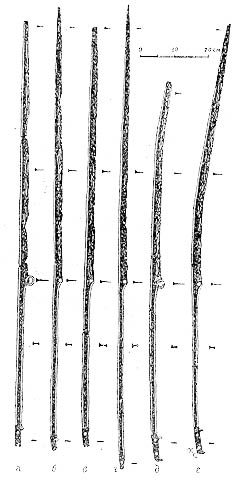
as early as 400 BC. Most rhomphaias were polearms, featuring a straight or slightly curved single-edged blade
Blade
A blade is that portion of a tool, weapon, or machine with a cutting edge and/or a pointed tip that is designed to cut and/or puncture, stab, slash, chop, slice, thrust, or scrape animate or inanimate surfaces or materials...
attached to a pole that was considerably shorter than the blade. Some rhomphaias had short handles that extended to only the length of the blade. Although the rhomphaia was similar to the Falx
Falx
Falx is a Latin word originally meaning sickle, but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge such as a scythe...
, most archaeological evidence suggests that rhomphaias were forged with straight or slightly curved blades, presumably to enable their use as both a thrusting and slashing weapon. The blade itself was constructed of iron and used a triangular cross section to accommodate the single cutting edge with a tang
Tang (weaponry)
A tang or shank is the back portion of a tool where it extends into stock material or is connected to a handle as on a knife, sword, spear, arrowhead, chisel, screwdriver, etc...
of rectangular cross section. Length varied, but a typical rhomphaia would have a blade of approximately 60–80 cm and a tang of approximately 50 cm. From the length of the tang, it can be presumed that when attached to the hilt, this portion of the weapon would be of similar length to the blade.
Usage
Used almost exclusively by the ThraciansThracians
The ancient Thracians were a group of Indo-European tribes inhabiting areas including Thrace in Southeastern Europe. They spoke the Thracian language – a scarcely attested branch of the Indo-European language family...
, examples have been found dating from 300-400 BC. As a weapon, the rhomphaia was feared (like the Falx) because of the cutting power afforded to it by the polearm like design. The Falx forced the only documented change in Roman armour brought about by an encounter with a new weapon. After encountering the Falx in Dacia, the Romans added extra reinforcing bars to their helmets to protect against the powerful blows of this weapon.
The Byzantines
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
used the Rhomphaia, an exclusive Thracian weapon, although it most likely was used by a few units of foot soldiers dating somewhere between Byzantium's golden age of 900
900
Year 900 was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar.- Asia :* April 21 – Namwaran and his children, Lady Angkatan and Bukah, are granted pardon by the Datu of Tondo, as represented Jayadewa, Lord Minister of Pila, which released them of all their debts as inscribed in the...
-1071 and maybe even earlier. It was not mentioned as a weapon like the falx however. It was indeed a falx
Falx
Falx is a Latin word originally meaning sickle, but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge such as a scythe...
-like weapon. Michael Psellus writes that all Varangians
Varangians
The Varangians or Varyags , sometimes referred to as Variagians, were people from the Baltic region, most often associated with Vikings, who from the 9th to 11th centuries ventured eastwards and southwards along the rivers of Eastern Europe, through what is now Russia, Belarus and Ukraine.According...
without exception used what he refers to as a "rhomphaia," but in doing so was referring to the Varangian daneaxe.
Differences from the falx
The rhomphaia's blade was straight or only slightly curved, while the falx's blade was significantly curved. Because its straighter blade facilitated a thrusting motion and an overhead or sidewards hacking motion, the rhomphaia could be used by tightly packed troopTroop
A troop is a military unit, originally a small force of cavalry, subordinate to a squadron and headed by the troop leader. In many armies a troop is the equivalent unit to the infantry section or platoon...
s as a defensive weapon. However, the straighter blade limited the use of the cutting edge.
Rhomphaia in historical texts
Rhomphaia was first ‘a spear’, later ‘a sword’ (PlutarchPlutarch
Plutarch then named, on his becoming a Roman citizen, Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus , c. 46 – 120 AD, was a Greek historian, biographer, essayist, and Middle Platonist known primarily for his Parallel Lives and Moralia...
: Life of Aemilius Paulus 18; Eustathius
Eustathius
Eustathius or Eustathios may refer to:* Eustathius of Antioch, Patriarch of Antioch * Eustathius of Sebaste * Eustathius of Cappadocia Neoplatonist, orator, and diplomat...
, on Iliad
Iliad
The Iliad is an epic poem in dactylic hexameters, traditionally attributed to Homer. Set during the Trojan War, the ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Greek states, it tells of the battles and events during the weeks of a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles...
verse VI 166; Hesychius
Hesychius of Alexandria
Hesychius of Alexandria , a grammarian who flourished probably in the 5th century CE, compiled the richest lexicon of unusual and obscure Greek words that has survived...
; also Luke
Gospel of Luke
The Gospel According to Luke , commonly shortened to the Gospel of Luke or simply Luke, is the third and longest of the four canonical Gospels. This synoptic gospel is an account of the life and ministry of Jesus of Nazareth. It details his story from the events of his birth to his Ascension.The...
2;35 and the Revelation
Revelation
In religion and theology, revelation is the revealing or disclosing, through active or passive communication with a supernatural or a divine entity...
of John of Patmos
John of Patmos
John of Patmos is the name given, in the Book of Revelation, as the author of the apocalyptic text that is traditionally cannonized in the New Testament...
, several times.).
In Latin, it has the forms:
- rumpia (LivyLivyTitus Livius — known as Livy in English — was a Roman historian who wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people. Ab Urbe Condita Libri, "Chapters from the Foundation of the City," covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome well before the traditional foundation in 753 BC...
, Aulus GelliusAulus GelliusAulus Gellius , was a Latin author and grammarian, who was probably born and certainly brought up in Rome. He was educated in Athens, after which he returned to Rome, where he held a judicial office...
, Ascon. ad Mil.) - romphea (Isidore of SevilleIsidore of SevilleSaint Isidore of Seville served as Archbishop of Seville for more than three decades and is considered, as the historian Montalembert put it in an oft-quoted phrase, "le dernier savant du monde ancien"...
.), - romphaea vel romfea (CGL 7, 212).
W. Tomaschek listed the Bulgarian. roféja, rufja ‘a thunderbolt’ and the Albanian rrufë as derivatives of that word.
Rhomphaia was also preserved in modern Greek as rhomphaia ‘a big broad sword’. The Thracian rhomphaia contains the IE stem *rump- in the Latin rumpo, -ere ‘to break, to tear’.
Rhomphaia was also mentioned in Michael Psellos' Chronographia where he describes it as a "one-edged sword of heavy iron which they [the palace guards at Constantinople] carry suspended from the right shoulder."
It is also mentioned in Anna Komnene
Anna Komnene
Anna Komnene, Latinized as Comnena was a Greek princess and scholar and the daughter of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos of Byzantium and Irene Doukaina...
's The Alexiad. She explains that during the battle her father, Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos, Latinized as Alexius I Comnenus , was Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118, and although he was not the founder of the Komnenian dynasty, it was during his reign that the Komnenos family came to full power. The title 'Nobilissimus' was given to senior army commanders,...
, fought against the rebel Nicephorus Bryennius. Alexius happened upon a horse saddled for an emperor which also had a number of grooms, some of whom "had in their hands the great iron swords which normally accompany the emperors". Anna does not however name these as rhomphaia, but her editor and translator E.R.A. Sewter does, and they seem to have been very distinctive for the Byzantines who, after an initial rout, saw "the general display of the royal horse with its insignia and the sight of the great swords (which all but spoke for themselves) convinced them that the news was true: Bryennius, who was guarded by these swords, had fallen into the hands of his enemies".

