
Ricart-Agrawala algorithm
Encyclopedia
The Ricart-Agrawala Algorithm is an algorithm for mutual exclusion
on a distributed system. This algorithm is an extension and optimization of Lamport's Distributed Mutual Exclusion Algorithm
, by removing the need for messages. It was developed by Glenn Ricart and Ashok Agrawala.
messages. It was developed by Glenn Ricart and Ashok Agrawala.
Receiving Site:
Critical Section:
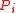 has received a
has received a  message from site
message from site 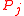 , site
, site 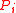 may enter the critical section without receiving permission from
may enter the critical section without receiving permission from 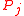 until
until 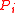 has sent a
has sent a  message to
message to  .
.
This optimization is called Roucairol & Carvalho Optimization.
This problem can be solved by detecting failure of nodes after some timeout.
Mutual exclusion
Mutual exclusion algorithms are used in concurrent programming to avoid the simultaneous use of a common resource, such as a global variable, by pieces of computer code called critical sections. A critical section is a piece of code in which a process or thread accesses a common resource...
on a distributed system. This algorithm is an extension and optimization of Lamport's Distributed Mutual Exclusion Algorithm
Lamport's Distributed Mutual Exclusion Algorithm
Lamport's Distributed Mutual Exclusion Algorithm is a contention-based algorithm for mutual exclusion on a distributed system.- Nodal properties :# Every process maintains a queue of pending requests for entering critical section order...
, by removing the need for
 messages. It was developed by Glenn Ricart and Ashok Agrawala.
messages. It was developed by Glenn Ricart and Ashok Agrawala.Terminology
- A site is any computing device which is running the Ricart-Agrawala Algorithm
- The requesting site is the site which is requesting entry into the critical section.
- The receiving site is every other site which is receiving the request from the requesting site.
Algorithm
Requesting Site:- Sends a message to all sites. This message includes the site's name, and the current timestamp of the system according to its logical clockLogical clockA logical clock is a mechanism for capturing chronological and causal relationships in a distributed system.Logical clock algorithms of note are:* Lamport timestamps, which are monotonically increasing software counters....
(which is assumed to be synchronized with the other sites)
Receiving Site:
- Upon reception of a request message, immediately send a timestamped reply message if and only if:
- the receiving process is not currently interested in the critical section OR
- the receiving process has a lower priority (usually this means having a later timestamp)
- Otherwise, the receiving process will defer the reply message. This means that a reply will be sent only after the receiving process has finished using the critical section itself.
Critical Section:
- Requesting site enters its critical section only after receiving all reply messages.
- Upon exiting the critical section, the site sends all deferred reply messages.
Performance
- Number of network messages; 2*(N-1)
- Synchronization Delays: One message propagation delay
Common Optimizations
Once site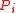 has received a
has received a  message from site
message from site 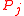 , site
, site 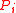 may enter the critical section without receiving permission from
may enter the critical section without receiving permission from 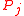 until
until 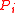 has sent a
has sent a  message to
message to  .
.This optimization is called Roucairol & Carvalho Optimization.
Problems
One of the problems in this algorithm is failure of a node. In such a situation a process may starve forever.This problem can be solved by detecting failure of nodes after some timeout.
See also
- Lamport's Bakery AlgorithmLamport's bakery algorithmLamport's bakery algorithm is a computer algorithm devised by computer scientist Leslie Lamport, which is intended to improve the safety in the usage of shared resources among multiple threads by means of mutual exclusion....
- Lamport's Distributed Mutual Exclusion AlgorithmLamport's Distributed Mutual Exclusion AlgorithmLamport's Distributed Mutual Exclusion Algorithm is a contention-based algorithm for mutual exclusion on a distributed system.- Nodal properties :# Every process maintains a queue of pending requests for entering critical section order...
- Maekawa's AlgorithmMaekawa's algorithmMaekawa's algorithm is an algorithm for mutual exclusion on a distributed system. The basis of this algorithm is a quorum like approach where any one site needs only to seek permissions from a subset of other sites.- Terminology :...
- Suzuki-Kasami's Algorithm
- Raymond's AlgorithmRaymond's algorithmRaymond's Algorithm is a token based algorithm for mutual exclusion on a distributed system. It imposes a logical structure on distributed resources...
- Naimi-Trehel's Algorithm

