
Rician fading
Encyclopedia
Ricean fading is a stochastic
model for radio
propagation
anomaly caused by partial cancellation of a radio signal by itself — the signal arrives at the receiver by several different paths (hence exhibiting multipath interference
), and at least one of the paths is changing (lengthening or shortening). Rician fading occurs when one of the paths, typically a line of sight signal
, is much stronger than the others. In Rician fading, the amplitude gain is characterized by a Rician distribution.
Rayleigh fading
is the specialised model for stochastic fading when there is no line of sight signal
, and is sometimes considered as a special case of the more generalised concept of Rician fading. In Rayleigh fading, the amplitude gain is characterized by a Rayleigh distribution.
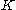 and
and 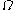 .
.  is the ratio between the power in the direct path and the power in the other, scattered, paths.
is the ratio between the power in the direct path and the power in the other, scattered, paths. 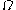 is the total power from both paths (
is the total power from both paths (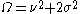 ), and acts as a scaling factor to the distribution.
), and acts as a scaling factor to the distribution.
The received signal amplitude (not the received signal power)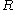 is then Rice distributed
is then Rice distributed
with parameters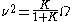 and
and 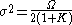 . The resulting PDF
. The resulting PDF
then is: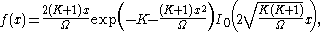
where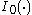 is the 0th order modified Bessel function
is the 0th order modified Bessel function
of the first kind.
Stochastic
Stochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
model for radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
propagation
Wave propagation
Wave propagation is any of the ways in which waves travel.With respect to the direction of the oscillation relative to the propagation direction, we can distinguish between longitudinal wave and transverse waves....
anomaly caused by partial cancellation of a radio signal by itself — the signal arrives at the receiver by several different paths (hence exhibiting multipath interference
Multipath interference
Multipath interference is a phenomenon in the physics of waves whereby a wave from a source travels to a detector via two or more paths and, under the right condition, the two components of the wave interfere...
), and at least one of the paths is changing (lengthening or shortening). Rician fading occurs when one of the paths, typically a line of sight signal
Line-of-sight propagation
Line-of-sight propagation refers to electro-magnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line...
, is much stronger than the others. In Rician fading, the amplitude gain is characterized by a Rician distribution.
Rayleigh fading
Rayleigh fading
Rayleigh fading is a statistical model for the effect of a propagation environment on a radio signal, such as that used by wireless devices.Rayleigh fading models assume that the magnitude of a signal that has passed through such a transmission medium will vary randomly, or fade, according to a...
is the specialised model for stochastic fading when there is no line of sight signal
Non-line-of-sight propagation
Non-line-of-sight or near-line-of-sight is a term used to describe radio transmission across a path that is partially obstructed, usually by a physical object in the innermost Fresnel zone....
, and is sometimes considered as a special case of the more generalised concept of Rician fading. In Rayleigh fading, the amplitude gain is characterized by a Rayleigh distribution.
Channel characterization
A Rician fading channel can be described by two parameters: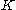 and
and 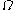 .
.  is the ratio between the power in the direct path and the power in the other, scattered, paths.
is the ratio between the power in the direct path and the power in the other, scattered, paths. 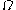 is the total power from both paths (
is the total power from both paths (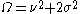 ), and acts as a scaling factor to the distribution.
), and acts as a scaling factor to the distribution.The received signal amplitude (not the received signal power)
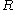 is then Rice distributed
is then Rice distributedRice distribution
In probability theory, the Rice distribution or Rician distribution is the probability distribution of the absolute value of a circular bivariate normal random variable with potentially non-zero mean. It was named after Stephen O...
with parameters
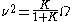 and
and 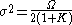 . The resulting PDF
. The resulting PDFProbability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
then is:
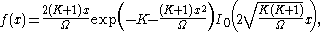
where
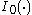 is the 0th order modified Bessel function
is the 0th order modified Bessel functionBessel function
In mathematics, Bessel functions, first defined by the mathematician Daniel Bernoulli and generalized by Friedrich Bessel, are canonical solutions y of Bessel's differential equation:...
of the first kind.
See also
- FadingFadingIn wireless communications, fading is deviation of the attenuation that a carrier-modulated telecommunication signal experiences over certain propagation media. The fading may vary with time, geographical position and/or radio frequency, and is often modelled as a random process. A fading channel...
- Multipath propagation
- Diversity schemeDiversity schemeIn telecommunications, a diversity scheme refers to a method for improving the reliability of a message signal by using two or more communication channels with different characteristics. Diversity plays an important role in combatting fading and co-channel interference and avoiding error bursts...
s - Rayleigh fadingRayleigh fadingRayleigh fading is a statistical model for the effect of a propagation environment on a radio signal, such as that used by wireless devices.Rayleigh fading models assume that the magnitude of a signal that has passed through such a transmission medium will vary randomly, or fade, according to a...
- Stochastics
- StatisticsStatisticsStatistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....

