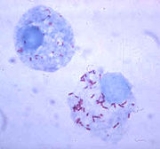
Rickettsia
Overview
Rickettsia is a genus
of non-motile
, Gram-negative
, non-sporeforming
, highly pleomorphic bacteria
that can present as cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), rods (1–4 μm long) or thread-like (10 μm long). Being obligate intracellular parasites, the Rickettsia survival depends on entry, growth, and replication within the cytoplasm
of eukaryotic
host cells (typically endothelial cells). Because of this, Rickettsia cannot live in artificial nutrient environments and are grown either in tissue
or embryo
cultures (typically, chicken embryos are used).
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
of non-motile
Motility
Motility is a biological term which refers to the ability to move spontaneously and actively, consuming energy in the process. Most animals are motile but the term applies to single-celled and simple multicellular organisms, as well as to some mechanisms of fluid flow in multicellular organs, in...
, Gram-negative
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain crystal violet dye in the Gram staining protocol. In a Gram stain test, a counterstain is added after the crystal violet, coloring all Gram-negative bacteria with a red or pink color...
, non-sporeforming
Endospore
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and temporarily non-reproductive structure produced by certain bacteria from the Firmicute phylum. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form , but it is not a true spore . It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce...
, highly pleomorphic bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
that can present as cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), rods (1–4 μm long) or thread-like (10 μm long). Being obligate intracellular parasites, the Rickettsia survival depends on entry, growth, and replication within the cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
of eukaryotic
Eukaryote
A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
host cells (typically endothelial cells). Because of this, Rickettsia cannot live in artificial nutrient environments and are grown either in tissue
Biological tissue
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
or embryo
Embryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
cultures (typically, chicken embryos are used).

