
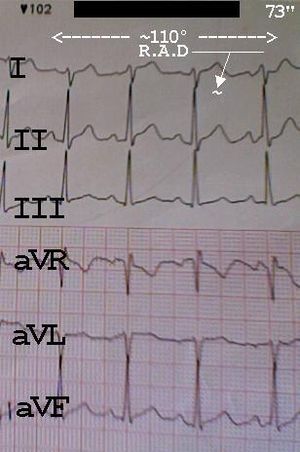
Right axis deviation
Encyclopedia
Heart disease
Heart disease, cardiac disease or cardiopathy is an umbrella term for a variety of diseases affecting the heart. , it is the leading cause of death in the United States, England, Canada and Wales, accounting for 25.4% of the total deaths in the United States.-Types:-Coronary heart disease:Coronary...
wherein the electrical conduction of the heart is greater than +105 degrees. Between +90 degrees and +180 degrees the condition may be termed Indeterminate Deviation or more often Extreme Right Axis Deviation. The degrees' deviation may be determined by a 12-lead ECG.
RAD is common in taller individuals, as the apex
Apex of the heart
The apex of the heart is the lowest superficial part of the heart.It is directed downward, forward, and to the left, and is overlapped by the left lung and pleura.-External anatomy:...
of the heart generally moves lower into the thorax
Chest
The chest is a part of the anatomy of humans and various other animals. It is sometimes referred to as the thorax or the bosom.-Chest anatomy - Humans and other hominids:...
. This can also be seen in individuals with Situs Inversus
Situs inversus
Situs inversus is a congenital condition in which the major visceral organs are reversed or mirrored from their normal positions. The normal arrangement is known as situs solitus...
, a medical condition where the visceral organs are flipped across a vertical axis. More commonly, however, a severe RAD is indicative of a posterior block.

