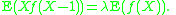Robbins lemma
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, the Robbins lemma, named after Herbert Robbins
, states that if X is a random variable
with a Poisson distribution
, and f is any function for which the expected value
E(f(X)) exists, then
Robbins introduced this proposition while developing empirical Bayes method
s.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the Robbins lemma, named after Herbert Robbins
Herbert Robbins
Herbert Ellis Robbins was an American mathematician and statistician who did research in topology, measure theory, statistics, and a variety of other fields. He was the co-author, with Richard Courant, of What is Mathematics?, a popularization that is still in print. The Robbins lemma, used in...
, states that if X is a random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
with a Poisson distribution
Poisson distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
, and f is any function for which the expected value
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
E(f(X)) exists, then
Robbins introduced this proposition while developing empirical Bayes method
Empirical Bayes method
Empirical Bayes methods are procedures for statistical inference in which the prior distribution is estimated from the data. This approach stands in contrast to standardBayesian methods, for which the prior distribution is fixed before any data are observed...
s.