
Root mean square fluctuation
Encyclopedia
The mean square fluctuation (MSF) is a measure of the deviation between the position of particle i and some reference position.
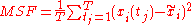 ,
,
where T is the time over which one wants to average, and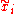 is the reference position of particle i. Typically this reference position will be the time-averaged position of the same particle i, ie.
is the reference position of particle i. Typically this reference position will be the time-averaged position of the same particle i, ie. 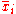
Note that the difference between RMSD and RMSF is that with the latter the average is taken over time, giving a value for each particle i. With RMSD the average is taken over the particles, giving time specific values.
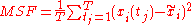 ,
,where T is the time over which one wants to average, and
 is the reference position of particle i. Typically this reference position will be the time-averaged position of the same particle i, ie.
is the reference position of particle i. Typically this reference position will be the time-averaged position of the same particle i, ie. 
Note that the difference between RMSD and RMSF is that with the latter the average is taken over time, giving a value for each particle i. With RMSD the average is taken over the particles, giving time specific values.
See also
- Quadratic meanRoot mean squareIn mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
- Root mean square deviation (bioinformatics)
- Root Mean Square Fluctuation calculated by GROMACS http://www.gromacs.org/documentation/reference/online/g_rmsf.html

