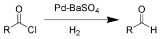
Rosenmund reduction
Encyclopedia
The Rosenmund reduction is a chemical reaction
that reduces
an acid halide to an aldehyde
using hydrogen gas
over palladium-on-carbon poisoned
with barium sulfate
. The reaction was named after Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund
.
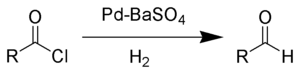 The catalyst must be poisoned because otherwise the catalyst is too active and will reduce the acid chloride to a primary alcohol
The catalyst must be poisoned because otherwise the catalyst is too active and will reduce the acid chloride to a primary alcohol
.
Diisobutylaluminium hydride
(DIBALH) can also reduce acid chlorides to aldehydes.
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
that reduces
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
an acid halide to an aldehyde
Aldehyde
An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group....
using hydrogen gas
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
over palladium-on-carbon poisoned
Catalyst poisoning
Catalyst poisoning refers to the effect that a catalyst can be 'poisoned' if it reacts with another compound that bonds chemically to its active surface sites. This effectively reduces the usefulness of the catalyst...
with barium sulfate
Barium sulfate
Barium sulfate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula BaSO4. It is a white crystalline solid that is odorless and insoluble in water. It occurs as the mineral barite, which is the main commercial source of barium and materials prepared from it...
. The reaction was named after Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund
Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund
Karl Wilhelm Rosenmund was a German chemist. He was born in Berlin and died in Kiel.Rosenmund studied chemistry and received his Ph.D. 1906 from University of Berlin for his work with Otto Paul Hermann Diels. He discovered the Rosenmund reduction, which is the reduction of acyl chlorides to...
.
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
.
Diisobutylaluminium hydride
Diisobutylaluminium hydride
Diisobutylaluminium hydride, DIBAL, DIBAL-H or DIBAH, is a reducing agent with the formula 2, where i-Bu represents isobutyl...
(DIBALH) can also reduce acid chlorides to aldehydes.

