
Rossby radius of deformation
Encyclopedia
In atmospheric dynamics and physical oceanography
, the Rossby radius of deformation is the length scale at which rotational effects become as important as buoyancy
or gravity wave
effects in the evolution of the flow
about some disturbance.
For a barotropic
ocean
:
For baroclinic flow:
The associated dimensionless parameter is the Rossby number
. Both are named in honor of Carl-Gustav Rossby.
Chelton et al. evaluated its geographic variability.
Oceanography
Oceanography , also called oceanology or marine science, is the branch of Earth science that studies the ocean...
, the Rossby radius of deformation is the length scale at which rotational effects become as important as buoyancy
Buoyancy
In physics, buoyancy is a force exerted by a fluid that opposes an object's weight. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus a column of fluid, or an object submerged in the fluid, experiences greater pressure at the bottom of the...
or gravity wave
Gravity wave
In fluid dynamics, gravity waves are waves generated in a fluid medium or at the interface between two media which has the restoring force of gravity or buoyancy....
effects in the evolution of the flow
Flow
-Relating to the movement of material:* Fluid dynamics, or fluid flow, the motion of a gas or liquid* Environmental flow, the amount of water necessary in a watercourse to maintain a healthy ecosystem* Flow chemistry, a chemical reaction run in a continuous stream...
about some disturbance.
For a barotropic
Barotropic
In meteorology, a barotropic atmosphere is one in which the pressure depends only on the density and vice versa, so that isobaric surfaces are also isopycnic surfaces . The isobaric surfaces will also be isothermal surfaces, hence the geostrophic wind is independent of height...
ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
:
-
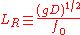 , where
, where 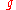 is the gravitational accelerationGravitational accelerationIn physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration on an object caused by gravity. Neglecting friction such as air resistance, all small bodies accelerate in a gravitational field at the same rate relative to the center of mass....
is the gravitational accelerationGravitational accelerationIn physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration on an object caused by gravity. Neglecting friction such as air resistance, all small bodies accelerate in a gravitational field at the same rate relative to the center of mass....
,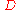 is the water depth, and
is the water depth, and 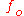 is the Coriolis parameter at the reference latitudeLatitudeIn geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
is the Coriolis parameter at the reference latitudeLatitudeIn geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
.
For baroclinic flow:
-
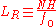 , where
, where  is the Brunt–Väisälä frequency and
is the Brunt–Väisälä frequency and 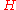 is the scale heightScale heightIn various scientific contexts, a scale height is a distance over which a quantity decreases by a factor of e...
is the scale heightScale heightIn various scientific contexts, a scale height is a distance over which a quantity decreases by a factor of e...
.
The associated dimensionless parameter is the Rossby number
Rossby number
The Rossby number, named for Carl-Gustav Arvid Rossby, is a dimensionless number used in describing fluid flow. The Rossby number is the ratio of inertial to Coriolis force, terms v\cdot\nabla v\sim U^2 / L and \Omega\times v\sim U\Omega in the Navier–Stokes equations, respectively...
. Both are named in honor of Carl-Gustav Rossby.
Chelton et al. evaluated its geographic variability.

