
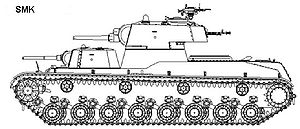
SMK tank
Encyclopedia
SMK was an armored vehicle prototype developed by the Soviet Union
prior to the Second World War. The SMK was also known to German intelligence as the T-35C.
Only one was built and after a poor showing against other designs and brief use in the war with Finland, the project was dropped.
(formerly the Putilov Works) at Leningrad designed the tank. Competition came from the former OKMO
designer Barykov at the Bolshevik Plant
In spite of the lessons that could have been learned during the Spanish Civil War, the specification drawn up for the "Anti-Tank Gun Destroyer" in 1937 required the ability to withstand 45 mm anti-tank guns at point-blank range and 75 mm artillery fire at 1200 m (1,312.3 yd).
Meetings in 1938 reduced the number of turrets in the specification and a move to torsion bar from spring suspension. Kotin and his assistant independently designed a single-turret version of the SMK which received Stalin's approval and the name KV. Production of two prototypes was ordered.
The SMK's armament was a short 76.2 mm gun in the upper centrally placed turret and a 45 mm in the forward turret.
against Finland. The vehicles formed a company of the 91st Tank Battalion of the 20th Heavy Tank Brigade. The unit was under the command of the son of the Defence Commissar. After being immobilized by a mine, the SMK had to be abandoned and not recovered until 2 month later.
The KV design proved superior in both trials and Finland and was accepted.
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
prior to the Second World War. The SMK was also known to German intelligence as the T-35C.
Only one was built and after a poor showing against other designs and brief use in the war with Finland, the project was dropped.
Design and development
The SMK was among the designs competing to replace the unreliable and expensive T-35 multi-turreted heavy tank. A design team under Kotin at the Kirovski WorksKirov Plant
The Kirov Plant Kirov Factory or Leningrad Kirov Plant is a major Russian machine-building plant in St. Petersburg, Russia....
(formerly the Putilov Works) at Leningrad designed the tank. Competition came from the former OKMO
OKMO
OKMO was the main tank design team in the Soviet Union during the early 1930s. It produced the design of the T-26 infantry tank , of which about 12,000 would be produced...
designer Barykov at the Bolshevik Plant
In spite of the lessons that could have been learned during the Spanish Civil War, the specification drawn up for the "Anti-Tank Gun Destroyer" in 1937 required the ability to withstand 45 mm anti-tank guns at point-blank range and 75 mm artillery fire at 1200 m (1,312.3 yd).
Meetings in 1938 reduced the number of turrets in the specification and a move to torsion bar from spring suspension. Kotin and his assistant independently designed a single-turret version of the SMK which received Stalin's approval and the name KV. Production of two prototypes was ordered.
The SMK's armament was a short 76.2 mm gun in the upper centrally placed turret and a 45 mm in the forward turret.
Service history
The SMK, the two KV-1 prototypes and the two T-100 prototypes were put through proving trials before being tested operationally in combat during the Winter WarWinter War
The Winter War was a military conflict between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet offensive on 30 November 1939 – three months after the start of World War II and the Soviet invasion of Poland – and ended on 13 March 1940 with the Moscow Peace Treaty...
against Finland. The vehicles formed a company of the 91st Tank Battalion of the 20th Heavy Tank Brigade. The unit was under the command of the son of the Defence Commissar. After being immobilized by a mine, the SMK had to be abandoned and not recovered until 2 month later.
The KV design proved superior in both trials and Finland and was accepted.
Armor
| Location | Front | Side | Rear | Top/bottom |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hull | 60 mm at a 45° angle(nose) 40 mm at a 15° angle(glacis) 60 mm at a 55° angle(driver) |
60 mm at a 75-90° angle | 60 mm round(lower) 60 mm at a 60° angle 20 mm at a 15° angle(engine) |
20-30 mm flat(bottom) 20 mm flat(top) |
| Upper Turret | 60 mm at a 75° angle and round | 60 mm at a 75° angle | 60 mm at a 80° angle | 20 mm at a 0-15° angle |
| Lower Turret | 60 mm at a 75° angle and round | 60 mm at a 75° angle | 60 mm at a 80° angle | 20 mm flat to a 15° angle |


