
SMS Bayern (1878)
Encyclopedia
SMS Bayern was one of four armored frigates of the German
Imperial Navy
. Her sisterships were , , and . Named for Bavaria
, Bayern was built by the Imperial Dockyard
in Kiel
from 1874 to 1881. The ship was commissioned into the Imperial Navy in August 1881. She was armed with a main battery of six 26 cm (10.2 in) guns in two open barbette
s.
After her commissioning, Bayern served with the fleet on numerous training exercises and cruises. She participated in several cruises escorting Kaiser Wilhelm II on state visits to Great Britain and to various cities in the Baltic Sea
in the late 1880s and early 1890s. During 1895–1898, the ship was modernized at the Schichau-Werke
dockyard in Danzig; she served for another decade with the fleet before being withdrawn from active service in 1910. She was used as a target ship after 1911, until she was sold in 1919 and broken up for scrap.
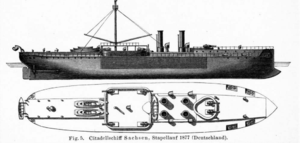 Bayern was ordered by the Imperial Navy under the contract name "A," which denoted that the vessel was a new addition to the fleet. She was built at the Imperial Dockyard
Bayern was ordered by the Imperial Navy under the contract name "A," which denoted that the vessel was a new addition to the fleet. She was built at the Imperial Dockyard
in Wilhelmshaven
; her keel was laid in 1874 under construction number 3. The ship was launched on 13 May 1878 and commissioned into the German fleet on 4 August 1881. Along with her three sisters, Bayern was the first large, armored warship built for the German navy that relied entirely on engines for propulsion.
The ship was 98.2 metres (322.2 ft) long overall and had a beam of 18.4 m (60.4 ft) and a draft of 6.32 m (20.7 ft) forward. Bayern was powered by two 3-cylinder triple expansion engines, which were supplied with steam by eight coal-fired Dürr boilers. The ship's top speed was 13 knots (7.1 m/s), at 5600 ihp Her standard complement consisted of 32 officers and 285 enlisted men, though while serving as a squadron flagship this was augmented by another 7 officers and 34 men.
She was armed with six 26 cm (10.2 in) guns, two of which were single-mounted in an open barbette
forward of the conning tower
and the remaining four mounted amidships, also on single mounts in an open barbette. As built, the ship was also equipped with six 8.7 cm (3.4 in) L/24 guns and eight 3.7 cm (1.5 in) Hotchkiss revolver cannons
. Bayern's armor was made of wrought iron, and was concentrated in an armored citadel amidships. The armor ranged from 203 to 254 mm (8 to 10 in) on the armored citadel, and between 50–75 mm (2–3 in) on the deck. The barbette armor was 254 mm of wrought iron backed by 250 mm of teak
.
.
Bayern remained with the fleet for the 1885 maneuvers, though she was joined only by the older ironclads and . The maneuvers were begun with a visit to Ålesund
, Norway, after which the fleet went to the Baltic Sea
for training exercises. Bayern was demobilized at the close of maneuvers.
In October 1885, August von Thomsen
, who had been appointed chief gunner, set up the first long range gunnery experiments on Bayern. He went on to gain fame as "the father of German naval artillery." Bayerns three sisters and the new ironclad comprised the training squadron for 1886. Bayern returned to active duty in 1888, when she participated in a tour of the Baltic by the newly crowned Kaiser Wilhelm II. The fleet stopped in St. Petersburg, Stockholm
, and Copenhagen
on the seventeen-day cruise.
Bayern participated in the ceremonial transfer of the island of Helgoland from British to German control in the summer of 1890. She was present during the fleet maneuvers in September, where the entire eight-ship armored squadron simulated a Russian fleet blockading Kiel
. She remained with the I Division in 1891; the year's maneuvers simulated a two-front war against Russia and either France of Denmark. Bayern participated in the 1892 fleet maneuvers as well. Three separate simulations were conducted, which included French blockades of the German North Sea
coast and a Russian attack on Kiel
. Vice Admiral Wilhelm Schröder commanded the fleet maneuvers of 1893, which simulated a protracted campaign against a superior French fleet. Bayern and her three sisters served as the Russian Baltic Fleet
during the 1894 maneuvers.
The four Sachsen-class ships were transferred to the II Division before the winter cruise of 1894–1895, following the completion of the four s. The German fleet now possessed two homogenous squadrons of four ships each. The two divisions steamed to Orkney and the Shetland Islands
in the spring of 1895. Bayern joined a massive fleet review on 21 July 1895 for the opening of the Kaiser Wilhelm Canal, which connected Kiel to the North Sea. The Autumn 1895 maneuvers simulated a high-seas battle between the I and II Divisions in the North Sea, followed by combined maneuvers with the rest of the fleet in the Baltic.
After the conclusion of the 1895 maneuvers, Bayern was taken into drydock at the Schichau-Werke
in Danzig for reconstruction. The ship's old wrought iron and teak armor was replaced with new Krupp
nickel-steel armor. The four funnels were trunked into a single large funnel and new engines were also installed, which increased the ship's speed to 15.4 kn (8.4 m/s). The ship's 8.7 cm guns were replaced with quick-firing 8.8 cm (3.5 in) SK L/30 guns and four 3.7 cm (1.5 in) autocannons. Work was completed in 1898. Bayerns three sisters were similarly modified between 1896 and 1899. Bayern remained with the fleet until 19 February 1910, when the ship was stricken from the naval register. She was converted into a target ship for the fleet and served in this capacity off Stollergrund after 1911. On 5 May 1919, Bayern was sold for scrapping and broken up in Kiel.
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
Imperial Navy
Kaiserliche Marine
The Imperial German Navy was the German Navy created at the time of the formation of the German Empire. It existed between 1871 and 1919, growing out of the small Prussian Navy and Norddeutsche Bundesmarine, which primarily had the mission of coastal defense. Kaiser Wilhelm II greatly expanded...
. Her sisterships were , , and . Named for Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
, Bayern was built by the Imperial Dockyard
Kaiserliche Werft Kiel
Kaiserliche Werft Kiel was a German shipbuilding company founded in 1867, first as Königliche Werft Kiel but renamed in 1871 with the proclamation of the German Empire...
in Kiel
Kiel
Kiel is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 238,049 .Kiel is approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the north of Germany, the southeast of the Jutland peninsula, and the southwestern shore of the...
from 1874 to 1881. The ship was commissioned into the Imperial Navy in August 1881. She was armed with a main battery of six 26 cm (10.2 in) guns in two open barbette
Barbette
A barbette is a protective circular armour feature around a cannon or heavy artillery gun. The name comes from the French phrase en barbette referring to the practice of firing a field gun over a parapet rather than through an opening . The former gives better angles of fire but less protection...
s.
After her commissioning, Bayern served with the fleet on numerous training exercises and cruises. She participated in several cruises escorting Kaiser Wilhelm II on state visits to Great Britain and to various cities in the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
in the late 1880s and early 1890s. During 1895–1898, the ship was modernized at the Schichau-Werke
Schichau-Werke
The Schichau-Werke was a German engineering works and shipyard based in Elbing, formerly part of the German Empire, and which is today the town of Elbląg in northern Poland. It also had a subsidiary shipyard in Danzig .-Early years:...
dockyard in Danzig; she served for another decade with the fleet before being withdrawn from active service in 1910. She was used as a target ship after 1911, until she was sold in 1919 and broken up for scrap.
Construction

Kaiserliche Werft Wilhelmshaven
Kaiserliche Werft Wilhelmshaven was a German shipbuilding company in Wilhelmshaven, Prussian Hanover. It was founded in 1853, first as Königliche Werft Wilhelmshaven but renamed in 1871 with the proclamation of the German Empire...
in Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea.-History:...
; her keel was laid in 1874 under construction number 3. The ship was launched on 13 May 1878 and commissioned into the German fleet on 4 August 1881. Along with her three sisters, Bayern was the first large, armored warship built for the German navy that relied entirely on engines for propulsion.
The ship was 98.2 metres (322.2 ft) long overall and had a beam of 18.4 m (60.4 ft) and a draft of 6.32 m (20.7 ft) forward. Bayern was powered by two 3-cylinder triple expansion engines, which were supplied with steam by eight coal-fired Dürr boilers. The ship's top speed was 13 knots (7.1 m/s), at 5600 ihp Her standard complement consisted of 32 officers and 285 enlisted men, though while serving as a squadron flagship this was augmented by another 7 officers and 34 men.
She was armed with six 26 cm (10.2 in) guns, two of which were single-mounted in an open barbette
Barbette
A barbette is a protective circular armour feature around a cannon or heavy artillery gun. The name comes from the French phrase en barbette referring to the practice of firing a field gun over a parapet rather than through an opening . The former gives better angles of fire but less protection...
forward of the conning tower
Conning tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armored, from which an officer can con the vessel; i.e., give directions to the helmsman. It is usually located as high on the ship as practical, to give the conning team good visibility....
and the remaining four mounted amidships, also on single mounts in an open barbette. As built, the ship was also equipped with six 8.7 cm (3.4 in) L/24 guns and eight 3.7 cm (1.5 in) Hotchkiss revolver cannons
Hotchkiss gun
The Hotchkiss gun can refer to different products of the Hotchkiss arms company starting in the late 19th century. It usually refers to the 1.65-inch light mountain gun; there was also a 3-inch Hotchkiss gun...
. Bayern's armor was made of wrought iron, and was concentrated in an armored citadel amidships. The armor ranged from 203 to 254 mm (8 to 10 in) on the armored citadel, and between 50–75 mm (2–3 in) on the deck. The barbette armor was 254 mm of wrought iron backed by 250 mm of teak
Teak
Teak is the common name for the tropical hardwood tree species Tectona grandis and its wood products. Tectona grandis is native to south and southeast Asia, mainly India, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Burma, but is naturalized and cultivated in many countries, including those in Africa and the...
.
Service history
After her commissioning in August 1881, Bayern was placed in reserve. She was not activated for service with the fleet until 1884; this in part had to do with the poor performance of her sister in the fleet maneuvers of 1880. Among the problems associated with the Sachsen class ships was a tendency to roll dangerously due to their flat bottoms, which greatly reduced the accuracy of their guns. The ships were also poorly armored, compared to their contemporaries. In addition, they were slow and suffered from poor maneuverability. Nevertheless, Bayern and her three sisters served as the I Division in the 1884 fleet maneuvers, under the command of Rear Admiral Alexander von MontsAlexander von Monts
Alexander Graf von Monts was an officer in the German Imperial navy, the Kaiserliche Marine....
.
Bayern remained with the fleet for the 1885 maneuvers, though she was joined only by the older ironclads and . The maneuvers were begun with a visit to Ålesund
Ålesund
is a town and municipality in Møre og Romsdal county, Norway. It is part of the traditional district of Sunnmøre, and the center of the Ålesund Region. It is a sea port, and is noted for its unique concentration of Art Nouveau architecture....
, Norway, after which the fleet went to the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
for training exercises. Bayern was demobilized at the close of maneuvers.
In October 1885, August von Thomsen
August von Thomsen
August von Thomsen was an Admiral of the German Imperial Navy...
, who had been appointed chief gunner, set up the first long range gunnery experiments on Bayern. He went on to gain fame as "the father of German naval artillery." Bayerns three sisters and the new ironclad comprised the training squadron for 1886. Bayern returned to active duty in 1888, when she participated in a tour of the Baltic by the newly crowned Kaiser Wilhelm II. The fleet stopped in St. Petersburg, Stockholm
Stockholm
Stockholm is the capital and the largest city of Sweden and constitutes the most populated urban area in Scandinavia. Stockholm is the most populous city in Sweden, with a population of 851,155 in the municipality , 1.37 million in the urban area , and around 2.1 million in the metropolitan area...
, and Copenhagen
Copenhagen
Copenhagen is the capital and largest city of Denmark, with an urban population of 1,199,224 and a metropolitan population of 1,930,260 . With the completion of the transnational Øresund Bridge in 2000, Copenhagen has become the centre of the increasingly integrating Øresund Region...
on the seventeen-day cruise.
Bayern participated in the ceremonial transfer of the island of Helgoland from British to German control in the summer of 1890. She was present during the fleet maneuvers in September, where the entire eight-ship armored squadron simulated a Russian fleet blockading Kiel
Kiel
Kiel is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 238,049 .Kiel is approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the north of Germany, the southeast of the Jutland peninsula, and the southwestern shore of the...
. She remained with the I Division in 1891; the year's maneuvers simulated a two-front war against Russia and either France of Denmark. Bayern participated in the 1892 fleet maneuvers as well. Three separate simulations were conducted, which included French blockades of the German North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
coast and a Russian attack on Kiel
Kiel
Kiel is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 238,049 .Kiel is approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the north of Germany, the southeast of the Jutland peninsula, and the southwestern shore of the...
. Vice Admiral Wilhelm Schröder commanded the fleet maneuvers of 1893, which simulated a protracted campaign against a superior French fleet. Bayern and her three sisters served as the Russian Baltic Fleet
Baltic Fleet
The Twice Red Banner Baltic Fleet - is the Russian Navy's presence in the Baltic Sea. In previous historical periods, it has been part of the navy of Imperial Russia and later the Soviet Union. The Fleet gained the 'Twice Red Banner' appellation during the Soviet period, indicating two awards of...
during the 1894 maneuvers.
The four Sachsen-class ships were transferred to the II Division before the winter cruise of 1894–1895, following the completion of the four s. The German fleet now possessed two homogenous squadrons of four ships each. The two divisions steamed to Orkney and the Shetland Islands
Shetland Islands
Shetland is a subarctic archipelago of Scotland that lies north and east of mainland Great Britain. The islands lie some to the northeast of Orkney and southeast of the Faroe Islands and form part of the division between the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the North Sea to the east. The total...
in the spring of 1895. Bayern joined a massive fleet review on 21 July 1895 for the opening of the Kaiser Wilhelm Canal, which connected Kiel to the North Sea. The Autumn 1895 maneuvers simulated a high-seas battle between the I and II Divisions in the North Sea, followed by combined maneuvers with the rest of the fleet in the Baltic.
After the conclusion of the 1895 maneuvers, Bayern was taken into drydock at the Schichau-Werke
Schichau-Werke
The Schichau-Werke was a German engineering works and shipyard based in Elbing, formerly part of the German Empire, and which is today the town of Elbląg in northern Poland. It also had a subsidiary shipyard in Danzig .-Early years:...
in Danzig for reconstruction. The ship's old wrought iron and teak armor was replaced with new Krupp
Krupp
The Krupp family , a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, have become famous for their steel production and for their manufacture of ammunition and armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th...
nickel-steel armor. The four funnels were trunked into a single large funnel and new engines were also installed, which increased the ship's speed to 15.4 kn (8.4 m/s). The ship's 8.7 cm guns were replaced with quick-firing 8.8 cm (3.5 in) SK L/30 guns and four 3.7 cm (1.5 in) autocannons. Work was completed in 1898. Bayerns three sisters were similarly modified between 1896 and 1899. Bayern remained with the fleet until 19 February 1910, when the ship was stricken from the naval register. She was converted into a target ship for the fleet and served in this capacity off Stollergrund after 1911. On 5 May 1919, Bayern was sold for scrapping and broken up in Kiel.

