
SR USA Class
Encyclopedia
The SR USA class were ex-United States Army Transportation Corps
S100 Class
steam locomotives purchased by the Southern Railway after the end of the Second World War.
in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania
in 1942 to the design specifications of the USATC by Col. Howard G. Hill. The remaining two were built by H. K. Porter, Inc
of Pittsburgh
. Overall, 382 of the class had been ordered from Davenport Locomotive Works
of Davenport, Iowa
, H. K. Porter and Vulcan Iron Works. They were shipped to Great Britain in 1943 and stored awaiting the invasion of Mainland Europe, after which many were shipped to Europe, but others, including those purchased, had hardly been used and were lying around in dumps awaiting disposal.
The key to their success, after being acquired by the Southern Railway, was their short wheelbase, which was able to negotiate the tight curves found at Southampton Docks. They were also powerful, able to haul heavy freight trains as well as full-length passenger trains in the harbour area.
After the war they replaced ageing B4
, D1
and E1
class tanks in Southampton Docks at the recommendation of Oliver Bulleid
. Steam heating, vacuum ejectors, sliding cab windows, additional lamp irons and new cylinder drain cocks had to be added for them to operate on British metals. More modifications became necessary once the locomotives started to enter traffic, including large roof-top ventilators, British-style regulators (as built they had US-style pull-out ones), three rectangular cab-front lookout windows, extended coal bunkers, separate steam and vacuum brake controls and wooden tip-up seats. This meant that it took until November 1947 for the entire class to be ready for work.
Others found industrial uses in Great Britain with the National Coal Board
, Longmoor Military Railway
and Austin Motors.
Thirteen of the locomotives were re-numbered 61-73 by the Southern; 4326 retained its War Department number instead of being renumbered 74, while the locomotive used for spares was not numbered.
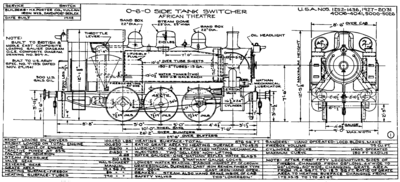
Under the BR Standard numbering system they were renumbered 30061-30074.
0-4-0
T tank locomotives, many of which required new boilers. Although they were excellent performers, their austerity construction meant that they deteriorated very quickly. Their steel fireboxes rusted and fatigued quickly, and this came to a head in 1951 when several had to have new fireboxes constructed.
Telephones were installed on the footplate to improve communication on the vast network of sidings at Southampton. They were replaced by British Rail Class 07
diesel-electric shunters, introduced in 1962. Nine remained in departmental use within the military and National Coal Board
, and five survived until the end of steam on the Southern Region
, in 1967, in departmental use at workshops and loco sheds.
plus two ex-JZ Class 62
locomotives, built to a broadly similar design, which are to be converted to British USA Class specifications.
, is a modified version of this type of locomotive.
United States Army Transportation Corps
The Transportation Corps was established 31 July 1942 by Executive Order 9082. The Transportation Corps is a combat service support branch of the U.S. Army, and was headquartered at Fort Eustis, Virginia, but has now moved to Fort Lee, Virginia. The Transportation Corps is responsible for the...
S100 Class
USATC S100 Class
The United States Army Transportation Corps S100 Class is a 0-6-0 steam locomotive that was designed for switching duties in Europe and North Africa during World War II...
steam locomotives purchased by the Southern Railway after the end of the Second World War.
Construction history
Thirteen out of the Southern's 15 locomotives (14 for traffic plus one for spares) were built at the Vulcan Iron WorksVulcan Iron Works
Since Vulcan was the Roman god of fire and smithery, the name was an obvious choice for an iron foundry or mechanical engineering works in the nineteenth century, both in England, the birthplace of the Industrial Revolution, and in the United States.-England:...
in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania
Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania
Wilkes-Barre is a city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, the county seat of Luzerne County. It is at the center of the Wyoming Valley area and is one of the principal cities in the Scranton/Wilkes-Barre metropolitan area, which had a population of 563,631 as of the 2010 Census...
in 1942 to the design specifications of the USATC by Col. Howard G. Hill. The remaining two were built by H. K. Porter, Inc
H. K. Porter, Inc
H. K. Porter, Inc. manufactured light-duty railroad locomotives in the USA, starting in 1866. The company became the largest producer of industrial locomotives, and built almost eight thousand of them...
of Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Pittsburgh is the second-largest city in the US Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Allegheny County. Regionally, it anchors the largest urban area of Appalachia and the Ohio River Valley, and nationally, it is the 22nd-largest urban area in the United States...
. Overall, 382 of the class had been ordered from Davenport Locomotive Works
Davenport Locomotive Works
The Davenport Locomotive Works, of Davenport, Iowa, USA built locomotives from 1902 until 1956. The company acquired the locomotive business of H. K...
of Davenport, Iowa
Davenport, Iowa
Davenport is a city located along the Mississippi River in Scott County, Iowa, United States. Davenport is the county seat of and largest city in Scott County. Davenport was founded on May 14, 1836 by Antoine LeClaire and was named for his friend, George Davenport, a colonel during the Black Hawk...
, H. K. Porter and Vulcan Iron Works. They were shipped to Great Britain in 1943 and stored awaiting the invasion of Mainland Europe, after which many were shipped to Europe, but others, including those purchased, had hardly been used and were lying around in dumps awaiting disposal.
The key to their success, after being acquired by the Southern Railway, was their short wheelbase, which was able to negotiate the tight curves found at Southampton Docks. They were also powerful, able to haul heavy freight trains as well as full-length passenger trains in the harbour area.
After the war they replaced ageing B4
LSWR B4 Class
The London and South Western Railway B4 class is a class of 0-4-0T dock tank.The London and South Western Railway's built twenty to a design by their Locomotive Superintendent William Adams at its Nine Elms Works during the 1891–1893 period...
, D1
LB&SCR D1 class
The LB&SCR D1 class were powerful 0-4-2 suburban passenger tank locomotives, designed by William Stroudley of the London Brighton and South Coast Railway in 1873. They were originally known as "D-tanks" but later reclassified as class D1...
and E1
LB&SCR E1 class
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway E1 Class were 0-6-0T steam locomotives designed by William Stroudley in 1874 for short-distance goods and piloting duties. They were originally classified E, and generally known as "E-tanks"; They were reclassified E1 in the time of D. E...
class tanks in Southampton Docks at the recommendation of Oliver Bulleid
Oliver Bulleid
Oliver Vaughan Snell Bulleid was a British railway and mechanical engineer best known as the Chief Mechanical Engineer of the Southern Railway between 1937 and the 1948 nationalisation, developing many well-known locomotives.- Early life and Great Northern Railway :He was born in Invercargill,...
. Steam heating, vacuum ejectors, sliding cab windows, additional lamp irons and new cylinder drain cocks had to be added for them to operate on British metals. More modifications became necessary once the locomotives started to enter traffic, including large roof-top ventilators, British-style regulators (as built they had US-style pull-out ones), three rectangular cab-front lookout windows, extended coal bunkers, separate steam and vacuum brake controls and wooden tip-up seats. This meant that it took until November 1947 for the entire class to be ready for work.
Others found industrial uses in Great Britain with the National Coal Board
National Coal Board
The National Coal Board was the statutory corporation created to run the nationalised coal mining industry in the United Kingdom. Set up under the Coal Industry Nationalisation Act 1946, it took over the mines on "vesting day", 1 January 1947...
, Longmoor Military Railway
Longmoor Military Railway
The Longmoor Military Railway was a British military railway in Hampshire, built by the Royal Engineers from 1903 in order to train soldiers on railway construction and operations.-Route:...
and Austin Motors.
War Department and Southern
Livery during the Second World War was USATC black with white numbering and lettering 'Transportation Dept.' on the watertank sides. Prior to nationalisation, the locomotives were painted in Southern black livery with 'Southern' in "Sunshine Yellow" lettering.Thirteen of the locomotives were re-numbered 61-73 by the Southern; 4326 retained its War Department number instead of being renumbered 74, while the locomotive used for spares was not numbered.

Post-1948 (nationalisation)
The class was allocated the BR power classification 3F, whilst the lettering on the tank sides was changed to 'British Railways' during 1948 as a transitional measure. Finally, the class was outshopped in BR Departmental Malachite livery, with BR crests on the watertank sides and numbers on the cab sides.Under the BR Standard numbering system they were renumbered 30061-30074.
Operational details
They were used for shunting in Southampton Docks and replaced the elderly LSWR B4 ClassLSWR B4 Class
The London and South Western Railway B4 class is a class of 0-4-0T dock tank.The London and South Western Railway's built twenty to a design by their Locomotive Superintendent William Adams at its Nine Elms Works during the 1891–1893 period...
0-4-0
0-4-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-4-0 represents one of the simplest possible types, that with two axles and four coupled wheels, all of which are driven...
T tank locomotives, many of which required new boilers. Although they were excellent performers, their austerity construction meant that they deteriorated very quickly. Their steel fireboxes rusted and fatigued quickly, and this came to a head in 1951 when several had to have new fireboxes constructed.
Telephones were installed on the footplate to improve communication on the vast network of sidings at Southampton. They were replaced by British Rail Class 07
British Rail Class 07
The British Rail Class 07 diesel locomotive is an off-centre cab dock shunter used in Southampton Docks, to replace SR USA Class steam locomotives. It is a 0-6-0 diesel-electric shunter built by Ruston & Hornsby in 1962...
diesel-electric shunters, introduced in 1962. Nine remained in departmental use within the military and National Coal Board
National Coal Board
The National Coal Board was the statutory corporation created to run the nationalised coal mining industry in the United Kingdom. Set up under the Coal Industry Nationalisation Act 1946, it took over the mines on "vesting day", 1 January 1947...
, and five survived until the end of steam on the Southern Region
Southern Region
Southern Region may be:* Southern Region, Malawi* Southern Region of British Railways* Southern Region, Eritrea* Southern Region, Brazil, an official grouping of states for economic and statistical purposes* Southern Region, Serbia...
, in 1967, in departmental use at workshops and loco sheds.
Preservation
Four examples have been preserved in England:- 30064 Bluebell RailwayBluebell RailwayThe Bluebell Railway is a heritage line running for nine miles along the border between East and West Sussex, England. Steam trains are operated between and , with an intermediate station at .The railway is managed and run largely by volunteers...
- 30065 Kent and East Sussex RailwayKent and East Sussex RailwayThe Kent & East Sussex Railway refers to both an historical private railway company in Kent and Sussex in England, as well as a heritage railway currently running on part of the route of the historical company.-Historical Company:-Background:...
- 30070 Kent and East Sussex RailwayKent and East Sussex RailwayThe Kent & East Sussex Railway refers to both an historical private railway company in Kent and Sussex in England, as well as a heritage railway currently running on part of the route of the historical company.-Historical Company:-Background:...
- 30072 Keighley and Worth Valley RailwayKeighley and Worth Valley RailwayThe Keighley and Worth Valley Railway is a long branch line that served mills and villages in the Worth Valley and is now a heritage railway line in West Yorkshire, England. It runs from Keighley to Oxenhope. It connects to the national rail network line at Keighley railway station...
plus two ex-JZ Class 62
JŽ Class 62
The Jugoslovenskih Železnica Class 62 was a class formed of 106 ex-United States Army Transportation Corps S100 Class 0-6-0 steam locomotives, surplus after the Second World War, plus about 90 similar examples built by Djuro Djakovic of Slavonski Brod, Croatia between 1952 and 1961.These...
locomotives, built to a broadly similar design, which are to be converted to British USA Class specifications.
In fiction
An engine of this prototype featured in the Thomas and Friends TV Series as Rosie, introduced in Season 10. Also, the Goods Engine from TUGSTUGS
TUGS is a British children's television series, first broadcast in 1988. It was created by the producers of Thomas the Tank Engine and Friends, Robert D. Cardona and David Mitton. The series dealt with the adventures of two anthropomorphized tugboat fleets, the Star Fleet and the Z-Stacks, who...
, is a modified version of this type of locomotive.
External links
- http://www.semgonline.com/steam/usa_01.html
- http://ukhrail.uel.ac.uk/cgi-bin/rlylocos?NO=&NA=&CL=USA&CO=ANY&BL=&WN=&LO=
- http://www.kesr-operating.org.uk/LocoTrust.htm
- http://www.bluebell-railway.co.uk/bluebell/loco_static.html#usa

