
SYN flood
Encyclopedia
Denial-of-service attack
A denial-of-service attack or distributed denial-of-service attack is an attempt to make a computer resource unavailable to its intended users...
in which an attacker sends a succession of
SYN requests to a target's system in an attempt to consume enough server resources to make the system unresponsive to legitimate traffic.Technical details
Normally when a client attempts to start a TCPTransmission Control Protocol
The Transmission Control Protocol is one of the core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite. TCP is one of the two original components of the suite, complementing the Internet Protocol , and therefore the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP...
connection to a server, the client
Client (computing)
A client is an application or system that accesses a service made available by a server. The server is often on another computer system, in which case the client accesses the service by way of a network....
and server
Server (computing)
In the context of client-server architecture, a server is a computer program running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients". Thus, the "server" performs some computational task on behalf of "clients"...
exchange a series of messages which normally runs like this:
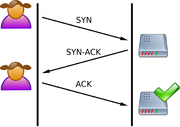
- The client requests a connection by sending a
SYN(synchronize) message to the server. - The server acknowledges this request by sending
SYN-ACKback to the client. - The client responds with an
ACK, and the connection is established.
This is called the TCP three-way handshake, and is the foundation for every connection established using the TCP protocol.
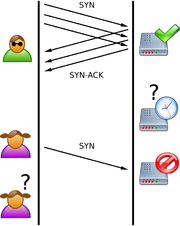
A SYN flood attack works by not responding to the server with the expected
ACK code. The malicious client can either simply not send the expected ACK, or by spoofingIP address spoofing
In computer networking, the term IP address spoofing or IP spoofing refers to the creation of Internet Protocol packets with a forged source IP address, called spoofing, with the purpose of concealing the identity of the sender or impersonating another computing system.-Background:The basic...
the source IP address
IP address
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing...
in the
SYN, causing the server to send the SYN-ACK to a falsified IP address - which will not send an ACK because it "knows" that it never sent a SYN.The server will wait for the acknowledgement for some time, as simple network congestion could also be the cause of the missing
ACK, but in an attack increasingly large numbers of half-open connectionHalf-open connection
The term half-open refers to TCP connections which state is out of synchronization between the two communicating hosts, possibly due to crash of one side...
s will bind resources on the server until no new connections can be made, resulting in a denial of service to legitimate traffic. Some systems may also malfunction badly or even crash if other operating system functions are starved of resources in this way.
Countermeasures
There are a number of well-known countermeasures,including:SYN cookies
SYN cookies
SYN Cookies are the key element of a technique used to guard against SYN flood attacks. Daniel J. Bernstein, the technique's primary inventor, defines SYN Cookies as "particular choices of initial TCP sequence numbers by TCP servers." In particular, the use of SYN Cookies allows a server to avoid...
provide protection against the SYN flood by eliminating the resources allocated on the target host.
Limiting new connections per source per timeframe is not a general solution since the attacker can spoof the packets to have multiple sources.
Some systems can mis-detect a SYN Flood when being scanned for open proxies, as commonly done by IRC servers and services. These are not SYN Floods, merely an automated system designed to check the connecting IP.
See also
- Denial-of-service attackDenial-of-service attackA denial-of-service attack or distributed denial-of-service attack is an attempt to make a computer resource unavailable to its intended users...
- IP address spoofingIP address spoofingIn computer networking, the term IP address spoofing or IP spoofing refers to the creation of Internet Protocol packets with a forged source IP address, called spoofing, with the purpose of concealing the identity of the sender or impersonating another computing system.-Background:The basic...
- Internet Control Message ProtocolInternet Control Message ProtocolThe Internet Control Message Protocol is one of the core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite. It is chiefly used by the operating systems of networked computers to send error messages indicating, for example, that a requested service is not available or that a host or router could not be...
- Ping floodPing floodA ping flood is a simple denial-of-service attack where the attacker/s overwhelms the victim with ICMP Echo Request packets. It is most successful if the attacker has more bandwidth than the victim...
- UDP flood attackUDP flood attackA UDP flood attack is a denial-of-service attack using the User Datagram Protocol , a sessionless/connectionless computer networking protocol....
- Fraggle attackFraggle attackIn computer security a fraggle attack is a type of denial-of-service attack where an attacker sends a large amount of UDP echo traffic to IP broadcast addresses, all of it having a fake source address...
- Smurf attackSmurf attackThe Smurf attack is a way of generating significant computer network traffic on a victim network. This is a type of denial-of-service attack that floods a target system via spoofed broadcast ping messages....

