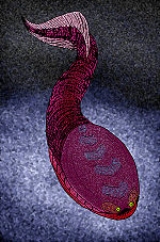
Sacabambaspis
Encyclopedia
Sacabambaspis is an extinct genus of jawless fish that lived in the Ordovician
period. It is related to Astraspis
.
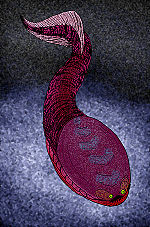 Sacabambaspis had a head shield made from a large upper (dorsal) plate that rose to a slight ridge in the midline, and a deep curved lower (ventral) plate. Also it had narrow branchial
Sacabambaspis had a head shield made from a large upper (dorsal) plate that rose to a slight ridge in the midline, and a deep curved lower (ventral) plate. Also it had narrow branchial
plates which link these two along the sides, and cover the gill area. The rest of body was covered by long, strap-like scales behind the head shield. The eyes were far forward and between them are possibly two small nostrils, and the mouth was armed with very thin plates (oral
plates).
The fossils of Sacabambaspis and Astraspis show clear evidence of a sensory structure (lateral line
system). The arrangement of these organs in regular lines allows the fish to detect the direction and distance from which a disturbance in the water is coming.
Ordovician
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six of the Paleozoic Era, and covers the time between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago . It follows the Cambrian Period and is followed by the Silurian Period...
period. It is related to Astraspis
Astraspis
Astraspis is an extinct genus of primitive jawless fish from the Ordovician of Central North America and Bolivia . It is related to other Ordovician fishes, such as the South American Sacabambaspis, and the Australian Arandaspis.-Basic Anatomy:Astraspids are hypothesized to have been about 200mm...
.
Description

Gill
A gill is a respiratory organ found in many aquatic organisms that extracts dissolved oxygen from water, afterward excreting carbon dioxide. The gills of some species such as hermit crabs have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist...
plates which link these two along the sides, and cover the gill area. The rest of body was covered by long, strap-like scales behind the head shield. The eyes were far forward and between them are possibly two small nostrils, and the mouth was armed with very thin plates (oral
Mouth
The mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food andsaliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth....
plates).
The fossils of Sacabambaspis and Astraspis show clear evidence of a sensory structure (lateral line
Lateral line
The lateral line is a sense organ in aquatic organisms , used to detect movement and vibration in the surrounding water. Lateral lines are usually visible as faint lines running lengthwise down each side, from the vicinity of the gill covers to the base of the tail...
system). The arrangement of these organs in regular lines allows the fish to detect the direction and distance from which a disturbance in the water is coming.

