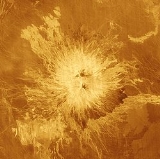
Sapas Mons
Encyclopedia
Sapas Mons is a large volcano
located in the Atla Regio region of Venus
.
Sapas Mons measures about 400 kilometres (248.5 mi) across and 1.5 kilometre (0.93205910497471 mi) high. Its flanks show numerous overlapping lava flows. The dark flows on the lower right of the radar image are thought to be smoother than the brighter ones near the central part of the volcano. Many of the flows appear to have been erupted along the flanks of the volcano rather than from the double summit. This type of flank eruption is common on large volcanoes on Earth
, such as the Hawaii
an volcanoes. The summit area has two flat-topped mesas, whose smooth tops give a relatively dark appearance in the radar image. Also seen near the summit are groups of pits, some as large as one kilometer (0.6 mile) across. These are thought to have formed when underground chambers of magma
were drained through other subsurface tubes and lead to a collapse at the surface. A 20 kilometres (12.4 mi) impact crater
northeast of the volcano is partially buried by the lava flows. Little was known about Atla Regio prior to the Magellan probe
. The new data, acquired in February 1991, show the region to be composed of at least five large volcanoes such as Sapas Mons, which are commonly linked by complex systems of fractures or rift zones. If comparable to similar features on Earth, Atla Regio probably formed when large volumes of molten rock upwelled from areas within the interior of Venus known as 'hot spot
s.'
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
located in the Atla Regio region of Venus
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows...
.
Sapas Mons measures about 400 kilometres (248.5 mi) across and 1.5 kilometre (0.93205910497471 mi) high. Its flanks show numerous overlapping lava flows. The dark flows on the lower right of the radar image are thought to be smoother than the brighter ones near the central part of the volcano. Many of the flows appear to have been erupted along the flanks of the volcano rather than from the double summit. This type of flank eruption is common on large volcanoes on Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, such as the Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
an volcanoes. The summit area has two flat-topped mesas, whose smooth tops give a relatively dark appearance in the radar image. Also seen near the summit are groups of pits, some as large as one kilometer (0.6 mile) across. These are thought to have formed when underground chambers of magma
Magma
Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and is expected to exist on other terrestrial planets. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and dissolved gas and sometimes also gas bubbles. Magma often collects in...
were drained through other subsurface tubes and lead to a collapse at the surface. A 20 kilometres (12.4 mi) impact crater
Impact crater
In the broadest sense, the term impact crater can be applied to any depression, natural or manmade, resulting from the high velocity impact of a projectile with a larger body...
northeast of the volcano is partially buried by the lava flows. Little was known about Atla Regio prior to the Magellan probe
Magellan probe
The Magellan spacecraft, also referred to as the Venus Radar Mapper, was a 1,035-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on May 4, 1989, to map the surface of Venus using Synthetic Aperture Radar and measure the planetary gravity...
. The new data, acquired in February 1991, show the region to be composed of at least five large volcanoes such as Sapas Mons, which are commonly linked by complex systems of fractures or rift zones. If comparable to similar features on Earth, Atla Regio probably formed when large volumes of molten rock upwelled from areas within the interior of Venus known as 'hot spot
Hotspot (geology)
The places known as hotspots or hot spots in geology are volcanic regions thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the mantle elsewhere. They may be on, near to, or far from tectonic plate boundaries. There are two hypotheses to explain them...
s.'

