
Saposin
Encyclopedia
Saposins are small lysosomal proteins that serve as activators of various lysosomal lipid-degrading enzymes. They probably act by isolating the lipid substrate from the membrane surroundings, thus making it more accessible to the soluble degradative enzymes. All mammalian saposins are synthesized as a single precursor molecule (prosaposin
) which contains four Saposin-B domains, yielding the active saposins after proteolytic cleavage, and two Saposin-A domains that are removed in the activation reaction. The Saposin-B domains also occur in other proteins, many of them active in the lysis of membranes.
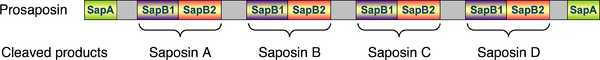
protein depicting the N- and C-terminal SapA domains and the four SapB1 and four SapB2 domains. Proteolytic
cleavage of the proprotein
occurs in the grey regions. Adjacent pairs of SapB1 and SapB2 domains remain connected after proteolytic processing of prosaposin and each pair comprises one of the mature saponin A-D proteins.
Prosaposin
Prosaposin also known as PSAP is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PSAP gene.This gene encodes a highly conserved glycoprotein which is a precursor for 4 cleavage products: saposins A, B, C, and D. Saposin is an acronym for Sphingolipid Activator PrO[S]teINs...
) which contains four Saposin-B domains, yielding the active saposins after proteolytic cleavage, and two Saposin-A domains that are removed in the activation reaction. The Saposin-B domains also occur in other proteins, many of them active in the lysis of membranes.
Domain organization
Below is a schematic diagram of the 1D structure of the prosaposinProsaposin
Prosaposin also known as PSAP is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PSAP gene.This gene encodes a highly conserved glycoprotein which is a precursor for 4 cleavage products: saposins A, B, C, and D. Saposin is an acronym for Sphingolipid Activator PrO[S]teINs...
protein depicting the N- and C-terminal SapA domains and the four SapB1 and four SapB2 domains. Proteolytic
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the directed degradation of proteins by cellular enzymes called proteases or by intramolecular digestion.-Purposes:Proteolysis is used by the cell for several purposes...
cleavage of the proprotein
Protein precursor
A protein precursor, also called a pro-protein or pro-peptide, is an inactive protein that can be turned into an active form by posttranslational modification. The name of the precursor for a protein is often prefixed by pro...
occurs in the grey regions. Adjacent pairs of SapB1 and SapB2 domains remain connected after proteolytic processing of prosaposin and each pair comprises one of the mature saponin A-D proteins.

Human proteins containing this domain
- AOAHAOAHAcyloxyacyl hydrolase , also known as AOAH, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the AOAH gene.- Function :Acyloxyacyl hydrolase is a 2-subunit lipase which selectively hydrolyzes the secondary fatty acyl chains from the lipid A region of bacterial lipopolysaccharides...
- GNLYGNLYGranulysin, also known as GNLY, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the GNLY gene.- Function :Granulysin is a protein present in cytotoxic granules of cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells. Granulysin is a member of the saposin-like protein family and is released from cytotoxic T cells...
- ProsaposinProsaposinProsaposin also known as PSAP is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PSAP gene.This gene encodes a highly conserved glycoprotein which is a precursor for 4 cleavage products: saposins A, B, C, and D. Saposin is an acronym for Sphingolipid Activator PrO[S]teINs...
- PSAPL1
- SFTPB
External links
- Saposin B-type domain in PROSITEPROSITEPROSITE is a protein database. It consists of entries describing the protein families, domains and functional sites as well as amino acid patterns, signatures, and profiles in them. These are manually curated by a team of the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and tightly integrated into Swiss-Prot...

