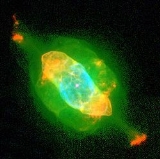
Saturn Nebula
Encyclopedia
The Saturn Nebula is a planetary nebula
in the constellation
Aquarius
. It was discovered by William Herschel
on September 7, 1782, using a telescope of his own design in the garden at his home in Datchet
, England
, and was one of his earliest discoveries in his sky survey. The nebula was originally a low-mass star that transformed into a bright white dwarf star
of apparent magnitude
11.5. The Saturn Nebula gets its name from its superficial resemblance to the planet Saturn with its rings nearly edge-on to the observer. It was so named by Lord Rosse in the 1840s, when telescopes had improved to the point that its Saturn-like shape could be discerned. William Henry Smyth
said that the Saturn Nebula is one of Struve's nine "Rare Celestial Objects."
The Saturn Nebula is a complex planetary nebula and contains many morphological and kinematic sub-systems in three dimensions. It includes a halo, jet-like streams, multiple shells, ansae ("handles"), and small-scale filaments and knots. The ansae are expanding non-radially from the central star.
The distance of the Saturn Nebula is not known precisely because no reference stars have been detected in its neighborhood that could be used to accurately gauge it. Therefore any distance given is somewhat suspect. estimates the distance to be 5,200 light-years (1.6 kpc
). In 1963 O'Dell estimated it to be 3,900 light-years (1.2 kpc), which gives an approximate diameter of 0.5 light years for the object as a whole.
The central star, a very hot bluish dwarf with a temperature of 55,000 K, from which the nebula is believed to originate, has an absolute magnitude of +1.5, which equates to a luminosity of about 20 Suns and a visual magnitude of 11.5. This strong ultraviolet irradiation from the central star is believed to create the characteristic fluorescent green tint of the nebula via the radiation of doubly ionized oxygen. The object overall has a visual magnitude of 8 and a radial velocity of 28 miles per second in approach.
The nebula can be spotted 1 degree west of the star Nu Aquarii. The central portion measures 25″ 17″, while the outer shell extends to 41″ × 35″. It is a beautiful object with a high surface brightness.
The object is on many "best of" observing lists, including: SAC 110 best NGC object list, RASC's Finest N.G.C. Objects Objects, and The Caldwell Catalog (#55).
Planetary nebula
A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life...
in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Aquarius
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for "water-bearer" or "cup-bearer", and its symbol is , a representation of water....
. It was discovered by William Herschel
William Herschel
Sir Frederick William Herschel, KH, FRS, German: Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel was a German-born British astronomer, technical expert, and composer. Born in Hanover, Wilhelm first followed his father into the Military Band of Hanover, but emigrated to Britain at age 19...
on September 7, 1782, using a telescope of his own design in the garden at his home in Datchet
Datchet
Datchet is an English Thameside village and civil parish situated in the unitary authority of Windsor and Maidenhead in the county of Berkshire. It was transferred to Berkshire from Buckinghamshire in 1974....
, England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, and was one of his earliest discoveries in his sky survey. The nebula was originally a low-mass star that transformed into a bright white dwarf star
White dwarf
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored...
of apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
11.5. The Saturn Nebula gets its name from its superficial resemblance to the planet Saturn with its rings nearly edge-on to the observer. It was so named by Lord Rosse in the 1840s, when telescopes had improved to the point that its Saturn-like shape could be discerned. William Henry Smyth
William Henry Smyth
William Henry Smyth was an English sailor, hydrographer, astronomer and numismatist.-Private Life:...
said that the Saturn Nebula is one of Struve's nine "Rare Celestial Objects."
The Saturn Nebula is a complex planetary nebula and contains many morphological and kinematic sub-systems in three dimensions. It includes a halo, jet-like streams, multiple shells, ansae ("handles"), and small-scale filaments and knots. The ansae are expanding non-radially from the central star.
The distance of the Saturn Nebula is not known precisely because no reference stars have been detected in its neighborhood that could be used to accurately gauge it. Therefore any distance given is somewhat suspect. estimates the distance to be 5,200 light-years (1.6 kpc
Parsec
The parsec is a unit of length used in astronomy. It is about 3.26 light-years, or just under 31 trillion kilometres ....
). In 1963 O'Dell estimated it to be 3,900 light-years (1.2 kpc), which gives an approximate diameter of 0.5 light years for the object as a whole.
The central star, a very hot bluish dwarf with a temperature of 55,000 K, from which the nebula is believed to originate, has an absolute magnitude of +1.5, which equates to a luminosity of about 20 Suns and a visual magnitude of 11.5. This strong ultraviolet irradiation from the central star is believed to create the characteristic fluorescent green tint of the nebula via the radiation of doubly ionized oxygen. The object overall has a visual magnitude of 8 and a radial velocity of 28 miles per second in approach.
The nebula can be spotted 1 degree west of the star Nu Aquarii. The central portion measures 25″ 17″, while the outer shell extends to 41″ × 35″. It is a beautiful object with a high surface brightness.
The object is on many "best of" observing lists, including: SAC 110 best NGC object list, RASC's Finest N.G.C. Objects Objects, and The Caldwell Catalog (#55).
External links
- NASA APOD (1997-12-30) – NGC 7009: The Saturn Nebula

