
Scaling and root planing
Encyclopedia
The objective of scaling and root planing, otherwise known as conventional periodontal therapy, non-surgical periodontal therapy or deep cleaning, is to remove or eliminate the etiologic agents which cause inflammation: dental plaque
, its products and calculus
, thus helping to establish a periodontium
that is free of disease.
The longer plaque is left on the teeth, the harder it gets. After 24 hours, some plaque hardens into calculus, otherwise known as tartar. Calculus is mineralized plaque and does not come off with the brush and floss anymore. The bacteria in plaque and calculus causes an ongoing state of inflammation called gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more serious disease called periodontitis. The most common treatment for periodontitis is Scaling and Root Planing.
procedures "include the removal of plaque, calculus and stain from the crown and root surfaces of teeth. Root planing is a specialized skill involving scaling of the root of the tooth, made up of cementum. Because cementum is softer than enamel, it is affected more by ongoing build-up and inflammatory byproducts. A smooth cementum provides less opportunity for bacteria to hang out and form calculus, so root planing is an important part of stopping periodontal disease where it is at, and preventing periodontal disease from getting worse, specially once deeper pockets have formed in the gums, which is really in the bone. So, root planing is a specific treatment that removes the roughened cementum
and surface dentin
that is impregnated with calculus, microorganisms and their toxin
s."
Because in periodontal disease pockets form that are deeper than the usual gingival depth, such scaling and root planing are often referred to as deep cleaning, and may be performed using a number of dental tools, including ultrasonic
instruments and hand instruments, such as periodontal scaler
s and curette
s.
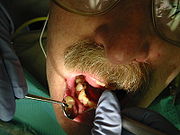 Removal of adherent plaque and calculus with hand instruments can also be performed on patients without periodontal disease. This treatment would then be referred to as a prophylaxis. A prophylaxis (a preventive cleaning, literally it means "action taken to prevent disease") or a prophy for short refers to scaling and polishing of the teeth in order to prevent oral diseases. Polishing does not remove calculus, only some plaque and stains, and should therefore only be done in conjunction with scaling.
Removal of adherent plaque and calculus with hand instruments can also be performed on patients without periodontal disease. This treatment would then be referred to as a prophylaxis. A prophylaxis (a preventive cleaning, literally it means "action taken to prevent disease") or a prophy for short refers to scaling and polishing of the teeth in order to prevent oral diseases. Polishing does not remove calculus, only some plaque and stains, and should therefore only be done in conjunction with scaling.
Sometimes a device may be electric, known as an ultrasonic
or sonic scaler. Ultrasonic scalers vibrate at a frequency that breaks down bacterial cell membranes and removes both plaque and calculus. Hand instruments are used to complete the fine hand scaling that removes anything the ultrasonic scaler left behind.
 Sonic and ultrasonic scalers are powered by a system that causes the tip to vibrate. Sonic scalers are typically powered by an air-driven turbine
Sonic and ultrasonic scalers are powered by a system that causes the tip to vibrate. Sonic scalers are typically powered by an air-driven turbine
. Ultrasonic scalers typically use either magnetostrictive
or piezoelectric systems to create vibration. Magnetostrictive scalers use a stack of metal plates bonded to the tool tip. The stack is induced to vibrate by an external coil connected to an AC source
. Ultrasonic scalers also include a liquid output or lavage
, which aids in cooling the tool during use, as well as rinsing all the unwanted materials from the teeth and gum line. The lavage can also be used to deliver antimicrobial
agents.
There is some debate over whether there is an advantage to sonic or ultrasonic scaling over hand scaling and some issues arise from powered scalers. Although the final result of ultrasonic scalers can be produced by using hand scalers, ultrasonic scalers are sometimes faster and less irritating to the client. Ultrasonic scalers do create aerosols, which can spread pathogens when a client carries an infectious disease. Relying solely on ultrasonic scalers for all scaling is inadequate; it is best to follow ultrasonic scaling with hand scaling. Of particular importance to dentists themselves is that use of an ultrasonic scaler will greatly decrease their likelihood of getting Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (Or other similar forms of RSI).
. This requires optimal home care and ongoing periodontal maintenance therapy, usually every 3 to 4 months to sustain health.
Dental plaque
Dental plaque is a biofilm, usually a pale yellow, that develops naturally on the teeth. Like any biofilm, dental plaque is formed by colonizing bacteria trying to attach themselves to a smooth surface...
, its products and calculus
Calculus (dental)
In dentistry, calculus or tartar is a form of hardened dental plaque. It is caused by the continual accumulation of minerals from saliva on plaque on the teeth...
, thus helping to establish a periodontium
Periodontium
Periodontium refers to the specialized tissues that both surround and support the teeth, maintaining them in the maxillary and mandibular bones. The word comes from the Greek terms peri-, meaning "around" and -odons, meaning "tooth." Literally taken, it means that which is "around the tooth"...
that is free of disease.
Plaque
Plaque is a soft, sticky mixture of bacteria, waste products from bacteria, and some food debris. It irritates the gums, or gingiva, and causes inflammation over time: gingivitis.The longer plaque is left on the teeth, the harder it gets. After 24 hours, some plaque hardens into calculus, otherwise known as tartar. Calculus is mineralized plaque and does not come off with the brush and floss anymore. The bacteria in plaque and calculus causes an ongoing state of inflammation called gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more serious disease called periodontitis. The most common treatment for periodontitis is Scaling and Root Planing.
Plaque build up and bone loss
Because the bone is alive, it has cells in it that build bone, and cells that break down bone. Usually these work at the same speed, and keep each other in balance: it is called bone remodeling. The chemical by-products of ongoing inflammation stimulate the cells that break down bone, which now start working faster than the cells that build bone. The net result is that bone is lost, and the loss of bone and attachment tissues is called periodontal disease.Periodontal scaling
Periodontal scalingPeriodontal scaler
Periodontal scalers are dental instruments used primarily in the prophylactic and periodontal care of human teeth. The working ends come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but they are always narrow at the tip, so as to allow for access to narrow embrasure spaces between teeth...
procedures "include the removal of plaque, calculus and stain from the crown and root surfaces of teeth. Root planing is a specialized skill involving scaling of the root of the tooth, made up of cementum. Because cementum is softer than enamel, it is affected more by ongoing build-up and inflammatory byproducts. A smooth cementum provides less opportunity for bacteria to hang out and form calculus, so root planing is an important part of stopping periodontal disease where it is at, and preventing periodontal disease from getting worse, specially once deeper pockets have formed in the gums, which is really in the bone. So, root planing is a specific treatment that removes the roughened cementum
Cementum
Cementum is a specialized calcified substance covering the root of a tooth. Cementum is excreted by cells called cementoblasts within the root of the tooth and is thickest at the root apex. These cementoblasts develop from undifferentiated mesenchymal cells in the connective tissue of the dental...
and surface dentin
Dentin
Dentine is a calcified tissue of the body, and along with enamel, cementum, and pulp is one of the four major components of teeth. Usually, it is covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp...
that is impregnated with calculus, microorganisms and their toxin
Toxin
A toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; man-made substances created by artificial processes are thus excluded...
s."
Because in periodontal disease pockets form that are deeper than the usual gingival depth, such scaling and root planing are often referred to as deep cleaning, and may be performed using a number of dental tools, including ultrasonic
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
instruments and hand instruments, such as periodontal scaler
Periodontal scaler
Periodontal scalers are dental instruments used primarily in the prophylactic and periodontal care of human teeth. The working ends come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but they are always narrow at the tip, so as to allow for access to narrow embrasure spaces between teeth...
s and curette
Periodontal curette
A periodontal curette is a dental instrument used primarily in the prophylactic and periodontal care of human teeth. The working tips are fashioned in a variety of shapes and sizes, but they are always rounded at the tip in order to make subgingival cleansing less traumatic to the gingiva...
s.

Sometimes a device may be electric, known as an ultrasonic
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
or sonic scaler. Ultrasonic scalers vibrate at a frequency that breaks down bacterial cell membranes and removes both plaque and calculus. Hand instruments are used to complete the fine hand scaling that removes anything the ultrasonic scaler left behind.

Turbine
A turbine is a rotary engine that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work.The simplest turbines have one moving part, a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades, or the blades react to the flow, so that they move and...
. Ultrasonic scalers typically use either magnetostrictive
Magnetostriction
Magnetostriction is a property of ferromagnetic materials that causes them to change their shape or dimensions during the process of magnetization. The variation of material's magnetization due to the applied magnetic field changes the magnetostrictive strain until reaching its saturation value, λ...
or piezoelectric systems to create vibration. Magnetostrictive scalers use a stack of metal plates bonded to the tool tip. The stack is induced to vibrate by an external coil connected to an AC source
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
. Ultrasonic scalers also include a liquid output or lavage
Lavage
In medicine, therapeutic irrigation or lavage is a general term referring to cleaning or rinsing.Specific types include:* Antiseptic lavage* Bronchoalveolar lavage* Gastric lavage* Peritoneal lavage* Arthroscopic lavage* Ductal lavage...
, which aids in cooling the tool during use, as well as rinsing all the unwanted materials from the teeth and gum line. The lavage can also be used to deliver antimicrobial
Antimicrobial
An anti-microbial is a substance that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or protozoans. Antimicrobial drugs either kill microbes or prevent the growth of microbes...
agents.
There is some debate over whether there is an advantage to sonic or ultrasonic scaling over hand scaling and some issues arise from powered scalers. Although the final result of ultrasonic scalers can be produced by using hand scalers, ultrasonic scalers are sometimes faster and less irritating to the client. Ultrasonic scalers do create aerosols, which can spread pathogens when a client carries an infectious disease. Relying solely on ultrasonic scalers for all scaling is inadequate; it is best to follow ultrasonic scaling with hand scaling. Of particular importance to dentists themselves is that use of an ultrasonic scaler will greatly decrease their likelihood of getting Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (Or other similar forms of RSI).
Effectiveness
Scaling and root planing is considered the basic treatment of periodontal diseases and may be the only treatment required to treat mild cases of periodontitis; however, it may also be the initial therapy prior to future surgical needs. For the procedure to be considered effective, the patient must be able to be maintained at a level of periodontal health that will prevent reinfection with periodontal pathogens periodontal diseasePeriodontal disease
Periodontitis is a set of inflammatory diseases affecting the periodontium, i.e., the tissues that surround and support the teeth. Periodontitis involves progressive loss of the alveolar bone around the teeth, and if left untreated, can lead to the loosening and subsequent loss of teeth...
. This requires optimal home care and ongoing periodontal maintenance therapy, usually every 3 to 4 months to sustain health.

