Scanning confocal electron microscopy
Encyclopedia
Scanning confocal electron microscopy (SCEM) is an electron microscopy technique analogous to scanning confocal optical microscopy
(SCOM). In this technique, the studied sample is illuminated by a focussed electron beam, as in other scanning microscopy techniques, such as scanning transmission electron microscopy
or scanning electron microscopy. However, in SCEM, the collection optics is arranged symmetrically to the illumination optics to gather only the electrons that pass the beam focus. This results in superior depth resolution of the imaging. The technique is relatively new and is being actively developed.
. His first scanning confocal electron microscope demonstrated the 3D properties of the SCEM, but have not realized the sub-nanometer lateral spatial resolution achievable with high-energy electrons (lateral resolution of only ~80 nm has been demonstrated). Several groups are currently working on construction of atomic resolution SCEM. In particular, atomically resolved SCEM images have already been obtained
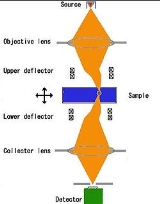
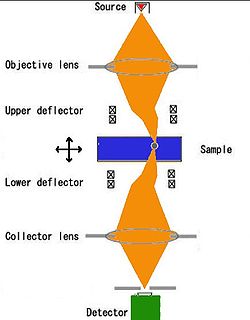 The sample is illuminated by a focussed electron beam, and the beam is re-focussed on the detector, thus collecting only electrons passing through the focus. In order to produce an image, the beam should be laterally scanned. In the original design, this was achieved by placing synchronized scanning and descanning deflectors. Such design is complex and only a few custom-built setups exist. Another approach is to use stationary illumination and collection, but perform scan by moving the sample with a high-precision piezo-controlled holder. Such holders are readily available and can fit into most commercial electron microscopes thereby realizing the SCEM mode. As a practical demonstration, atomically resolved SCEM images have been recorded.
The sample is illuminated by a focussed electron beam, and the beam is re-focussed on the detector, thus collecting only electrons passing through the focus. In order to produce an image, the beam should be laterally scanned. In the original design, this was achieved by placing synchronized scanning and descanning deflectors. Such design is complex and only a few custom-built setups exist. Another approach is to use stationary illumination and collection, but perform scan by moving the sample with a high-precision piezo-controlled holder. Such holders are readily available and can fit into most commercial electron microscopes thereby realizing the SCEM mode. As a practical demonstration, atomically resolved SCEM images have been recorded.
of SCEM as compared to SCOM (lateral resolution <1 nm vs. >400 nm).
As compared to conventional electron microscopy (TEM
, STEM
, SEM
), SCEM offers 3-dimensional imaging. 3D imaging in SCEM was expected from the confocal geometry of SCEM, and it has recently been confirmed by theoretical modeling. In particular, it is predicted that a heavy layer (gold) can be identified in light matrix (aluminum) with ~10 nm precision in depth; this depth resolution is limited by the convergence angle of the electron beam and could be improved to a few nanometers in next-generation electron microscopes equipped with two fifth-order spherical aberration
correctors.
Confocal microscopy
Confocal microscopy is an optical imaging technique used to increase optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole to eliminate out-of-focus light in specimens that are thicker than the focal plane. It enables the reconstruction of...
(SCOM). In this technique, the studied sample is illuminated by a focussed electron beam, as in other scanning microscopy techniques, such as scanning transmission electron microscopy
Scanning transmission electron microscopy
A scanning transmission electron microscope is a type of transmission electron microscope . As with any transmission illumination scheme, the electrons pass through a sufficiently thin specimen...
or scanning electron microscopy. However, in SCEM, the collection optics is arranged symmetrically to the illumination optics to gather only the electrons that pass the beam focus. This results in superior depth resolution of the imaging. The technique is relatively new and is being actively developed.
History
The idea of SCEM logically follows from SCOM and thus is rather old. However, practical design and construction of scanning confocal electron microscope is a complex problem first solved by Nestor J. ZaluzecNestor J. Zaluzec
Nestor J. Zaluzec is an American scientist and inventor who works at Argonne National Laboratory. He invented and patented the Scanning Confocal Electron Microscope...
. His first scanning confocal electron microscope demonstrated the 3D properties of the SCEM, but have not realized the sub-nanometer lateral spatial resolution achievable with high-energy electrons (lateral resolution of only ~80 nm has been demonstrated). Several groups are currently working on construction of atomic resolution SCEM. In particular, atomically resolved SCEM images have already been obtained
Operation

Advantages of SCEM
High energies of incident particles (200 keV electrons vs. 2 eV photons) result in much higher spatial resolutionAngular resolution
Angular resolution, or spatial resolution, describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object...
of SCEM as compared to SCOM (lateral resolution <1 nm vs. >400 nm).
As compared to conventional electron microscopy (TEM
Transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy is a microscopy technique whereby a beam of electrons is transmitted through an ultra thin specimen, interacting with the specimen as it passes through...
, STEM
Scanning transmission electron microscopy
A scanning transmission electron microscope is a type of transmission electron microscope . As with any transmission illumination scheme, the electrons pass through a sufficiently thin specimen...
, SEM
Scanning electron microscope
A scanning electron microscope is a type of electron microscope that images a sample by scanning it with a high-energy beam of electrons in a raster scan pattern...
), SCEM offers 3-dimensional imaging. 3D imaging in SCEM was expected from the confocal geometry of SCEM, and it has recently been confirmed by theoretical modeling. In particular, it is predicted that a heavy layer (gold) can be identified in light matrix (aluminum) with ~10 nm precision in depth; this depth resolution is limited by the convergence angle of the electron beam and could be improved to a few nanometers in next-generation electron microscopes equipped with two fifth-order spherical aberration
Spherical aberration
thumb|right|Spherical aberration. A perfect lens focuses all incoming rays to a point on the [[Optical axis|optic axis]]. A real lens with spherical surfaces suffers from spherical aberration: it focuses rays more tightly if they enter it far from the optic axis than if they enter closer to the...
correctors.
See also
- Confocal microscopyConfocal microscopyConfocal microscopy is an optical imaging technique used to increase optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole to eliminate out-of-focus light in specimens that are thicker than the focal plane. It enables the reconstruction of...
- Confocal laser scanning microscopyConfocal laser scanning microscopyConfocal laser scanning microscopy is a technique for obtaining high-resolution optical images with depth selectivity. The key feature of confocal microscopy is its ability to acquire in-focus images from selected depths, a process known as optical sectioning...
- Electron microscopy
- Scanning electron microscopeScanning electron microscopeA scanning electron microscope is a type of electron microscope that images a sample by scanning it with a high-energy beam of electrons in a raster scan pattern...
- Scanning transmission electron microscopyScanning transmission electron microscopyA scanning transmission electron microscope is a type of transmission electron microscope . As with any transmission illumination scheme, the electrons pass through a sufficiently thin specimen...
- Transmission electron microscopyTransmission electron microscopyTransmission electron microscopy is a microscopy technique whereby a beam of electrons is transmitted through an ultra thin specimen, interacting with the specimen as it passes through...

