Scorpion toxin
Encyclopedia
Scorpion toxins are proteins found in the venom of scorpion
s. Their toxic effect may be mammal or insect specific, and acts by binding to sodium channels, inhibiting the inactivation of activated channels and blocking neuronal transmission.
The family includes related short- and long-chain scorpion
toxins. It also contains a group of proteinase inhibitors
from the plants Arabidopsis thaliana
and Brassica spp
.
The Brassica napus (Oil seed rape) and Sinapis alba (White mustard) inhibitors, inhibit the catalytic activity of bovine beta-trypsin and bovine alpha-chymotrypsin
, which belong to MEROPS
peptidase family S1 .
This group of proteins is now used in the creation of insecticides, vaccines, and protein engineering scaffolds.
, an anti-epilepsy peptide isolated from the venom of the Manchurian scorpion, shows similarity to both scorpion neurotoxins and anti-insect toxins.
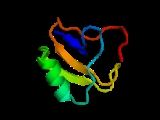
This protein's structure was determined by X-ray diffraction. The resolution of the structure is fairly high at 1.3 Angstroms with alpha, beta, and gamma angles of 90 degrees. It is a polypeptide chain 64 residues in length. The Ramachandran plot shows 66 out of 67 (98.5%) of all residues are in the favored regions with no outliers present.
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arthropod animals of the order Scorpiones within the class Arachnida. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping claws and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger...
s. Their toxic effect may be mammal or insect specific, and acts by binding to sodium channels, inhibiting the inactivation of activated channels and blocking neuronal transmission.
The family includes related short- and long-chain scorpion
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arthropod animals of the order Scorpiones within the class Arachnida. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping claws and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger...
toxins. It also contains a group of proteinase inhibitors
Protease inhibitor (biology)
In biology and biochemistry, protease inhibitors are molecules that inhibit the function of proteases. Many naturally occurring protease inhibitors are proteins....
from the plants Arabidopsis thaliana
Arabidopsis thaliana
Arabidopsis thaliana is a small flowering plant native to Europe, Asia, and northwestern Africa. A spring annual with a relatively short life cycle, arabidopsis is popular as a model organism in plant biology and genetics...
and Brassica spp
Brassica
Brassica is a genus of plants in the mustard family . The members of the genus may be collectively known either as cabbages, or as mustards...
.
The Brassica napus (Oil seed rape) and Sinapis alba (White mustard) inhibitors, inhibit the catalytic activity of bovine beta-trypsin and bovine alpha-chymotrypsin
Chymotrypsin
Chymotrypsin is a digestive enzyme that can perform proteolysis. Chymotrypsin preferentially cleaves peptide amide bonds where the carboxyl side of the amide bond is a tyrosine, tryptophan, or phenylalanine. These amino acids contain an aromatic ring in their sidechain that fits into a...
, which belong to MEROPS
Merops
Merops may refer to:* Merops , a genus of bee-eaters.* MEROPS, an on-line database for peptidases.It may also refer to several figures from Greek mythology:* King of Ethiopia, husband of Clymene, who lay with Helios and bore Phaethon...
peptidase family S1 .
This group of proteins is now used in the creation of insecticides, vaccines, and protein engineering scaffolds.
Structure
The complete covalent structure of the toxins has been deduced: it comprises around 66 amino acid residues and is cross- linked by 4 disulfide bridges. BmKAEPBmKAEP
BmKAEP is a neurotoxin from the venom of the Manchurian scorpion . It is a β-toxin, which shift the activation voltage of sodium channels towards more negative potentials.- Etymology :...
, an anti-epilepsy peptide isolated from the venom of the Manchurian scorpion, shows similarity to both scorpion neurotoxins and anti-insect toxins.
This protein's structure was determined by X-ray diffraction. The resolution of the structure is fairly high at 1.3 Angstroms with alpha, beta, and gamma angles of 90 degrees. It is a polypeptide chain 64 residues in length. The Ramachandran plot shows 66 out of 67 (98.5%) of all residues are in the favored regions with no outliers present.
Function
The toxin's molecular function is to inhibit ion channels. Scorpion toxins are used in insecticides, vaccines, and protein engineering scaffolds. The toxins are now used to treat cancer patients by injecting fluorescent scorpion toxin into cancerous tissue to show tumor boundaries. Scorpion toxin genes are also used to kill insect pests by creating hypervirulent fungus in the insect through gene insertion.External links
- Scorpion short toxins in PROSITEPROSITEPROSITE is a protein database. It consists of entries describing the protein families, domains and functional sites as well as amino acid patterns, signatures, and profiles in them. These are manually curated by a team of the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics and tightly integrated into Swiss-Prot...
- http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1PTX in PDBProtein Data BankThe Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
- http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/images/1PTX_ram_m_500.pdf Ramachandran plot
- http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1G1-10342207.html
- http://www.nwrage.org/index.php?name=News&file=article&sid=1969
- http://www.latoxan.com/VENOM/SCORPION/Androctonus-australis-hector.html

